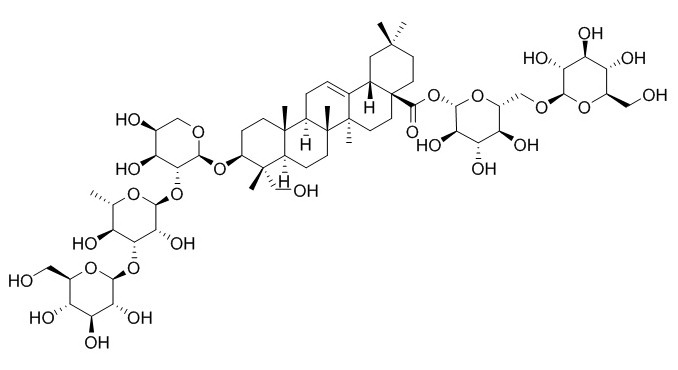
Macranthoidin A
Macranthoidin A, found in the herbs of Lonicera japonica Thunb., has anti-inflammation activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Asian J Beauty Cosmetol2024, 22(1): 103-112.
Trop J Nat Prod Res2023, 7(12):5611-5615.
Microb Biotechnol.2021, 14(5):2009-2024.
Front Pharmacol.2022, 13:906763.
Applied Biological Chemistry2020, 63:37.
Srinakharinwirot University2023, 2669.
Korean Herb. Med. Inf.2020, 8(2):205-213
Hortic Res.2023, 10(4):uhad039.
Anticancer Res.2014, 34(7):3505-9
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.2020, 84(3):621-632
Related and Featured Products
Journal of Chromatography B Volume 877, Issue 3, 15 January 2009, Pages 159–165
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of macranthoidin B, macranthoidin A, dipsacoside B, and macranthoside B in rat plasma for the pharmacokinetic investigation[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry method has been developed and validated for identification and quantification of four major bioactive saponins in rat plasma after oral administration of extraction of saponins from Flos Lonicerae, i.e., macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, dipsacoside B, and macranthoside B. Plasma samples were extracted with solid-phase extraction, separated on a Shim-pack CLC-ODS column and detected by MS in negative selective ion monitoring mode. Calibration curves offered linear ranges of two orders of magnitude with r2 > 0.999. The method showed the low limit quantification of 7.72, 6.06, 7.16, and 1.43 ng/mL for macranthoidin B, Macranthoidin A, dipsacoside B, and macranthoside B, respectively. The inter- and intra-CV precision (R.S.D.) were all within 10% and accuracy (% bias) ranged from −10 to 10%. The overall recovery was more than 70%.
CONCLUSIONS:
This developed method was subsequently successfully applied to pharmacokinetic profiles of the four saponins in rats. After oral administration of extraction of saponins in rats, the concentration–time course was found to be the double peaks of curve.
J Chromatogr A. 2005 Apr 8;1070(1-2):43-8.
Quality evaluation of Flos lonicerae through a simultaneous determination of seven saponins by HPLC with ELSD.[Pubmed:
15861786]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new HPLC coupled with evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD) method has been developed for the simultaneous quantitative determination of seven major saponins, namely macranthoidin B (1), Macranthoidin A (2), dipsacoside B (3), hederagenin-28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(6-->1)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (4), macranthoside B (5), macranthoside A (6), and hederagenin-3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl(2-->1)-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (7) in Flos Lonicerae, a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) herb. Simultaneous separation of these seven saponins was achieved on a C18 analytical column. The mobile phase consisted of (A) acetonitrile-acetic acid (95:0.5) and (B) 0.5% aqueous acetic acid using a gradient elution of 29%A at 0-10 min, 29-46%A at 10-25 min and 46%A at 25-30 min. The drift tube temperature of ELSD was set at 106 degrees C, and with the nitrogen flow-rate of 2.6 l/min. All calibration curves showed good linear regression (r2>0.9922) within test ranges. This method showed good reproducibility for the quantification of these seven saponins in Flos Lonicerae with intra- and inter-day variations of less than 3.0% and 6.0%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The validated method was successfully applied to quantify seven saponins in five sources of Flos Lonicerae, which provides a new basis of overall assessment on quality of Flos Lonicerae.