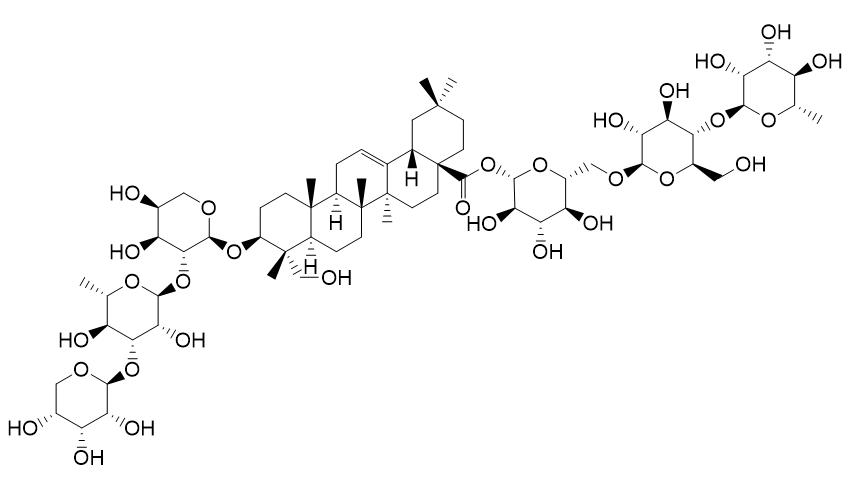
Huzhangoside D
Huzhangoside D shows insecticidal activities against termite (Coptotermis homii), the LC50 of 0.2 mg/mL.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8850744.
J Nat Prod.2018, 81(4):966-975
Chem Biol Interact.2024, 395:110999.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(11):1831.
Wageningen University & Research2018, January 2018
Eur J Pharm Sci.2016, 94:33-45
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:762829.
Applied Biological Chemistry2020, 63:37.
Chem Biol Interact.2016, 258:59-68
Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy2020, 40(7)
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Sep;10(9):1525-8.
Triterpenoid Saponins from Clematis graveolens and Evaluation of their Insecticidal Activities.[Pubmed:
26594749]
A new hederagenin based triterpenoid saponin, clematograveolenoside A (1), along with three known saponins, tomentoside A (2), Huzhangoside D (3) and clematoside S (4), were isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Clematis graveolens.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structure of new compound was elucidated on the basis of detailed analysis of chemical and spectroscopic data including 1D- and 2D NMR spectra. Compound 2 was found the most effective against aphid (Aphis craccivora) with an LC50 of 1.2 and 0.5 mg/mL after treatment for 72 and 96 h, respectively and was followed by compound 4 (LC50 = 2.3 and 1.9 mg/mL) and 1 (LC50 = 3.2 and 2.6 mg/mL). In case of termite (Coptotermis homii), compound 1 was found more toxic with an LC50 of 0.1 mg/L after 24 h of treatment followed by compound 2, 3 and 4 (LC50 = 0.1, 0.2 and 0.2 mg/mL, respectively).
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1995 Dec;43(12):2187-94.
Studies on the constituents of Clematis species. VI. The constituents of Clematis stans Sieb. et Zucc.[Pubmed:
8582022]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the roots of Clematis stans three new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins named clemastanoside A, B and C, and two new lignan glycosides named clemastanin A and B, have been isolated together with three known triterpenoid saponins, huzhangoside B, C and D, and three known lignan glycosides, (+)-lariciresinol 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, (+)-lariciresinol 4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside and (+)-pinoresinol 4,4'-O-bis-beta-D-glucopyranoside. In addition, from the leaves, four new oleanane-type triterpenoid saponins, named clemastanoside D, E, F and G, have been isolated together with five known triterpenoid saponins, hederasaponin B, kizutasaponin K12, huzhangoside B, sieboldianoside B and Huzhangoside D, and three known flavonoids, isoquercitrin, rutin and quercetin 3-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside.
Pak J Biol Sci. 2007 Jun 15;10(12):2066-72.
Chemodiversity of saponins and their taxonomic importance in Clematis genus (Ranunculaceae).[Pubmed:
19093448 ]
Distribution patterns of chemical compounds in plants have been used for biosystematic and phylogenetic studies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Saponin profile of twelve major taxa of Clematis genus, belonging to sections, Rectae, Clematis, Meclatis, Tubulosae and Viorna were analyzed by HPLC coupled with diode array detector and ESI-MS. The chemodiversity profile of saponins has unambiguously delimited the taxa of Clematis at subgenus, section and subsection level. The distribution of saponins in Clematis genus provides useful taxonomic markers and results are presented in phenograms.
CONCLUSIONS:
The compound Huzhangoside D was common and the most abundant in analyzed species of the genus. The morphological analysis was also conducted of the same taxa and presented as cluster tree. The distribution and chemotaxonomic importance of saponins profile within the genus is discussed.