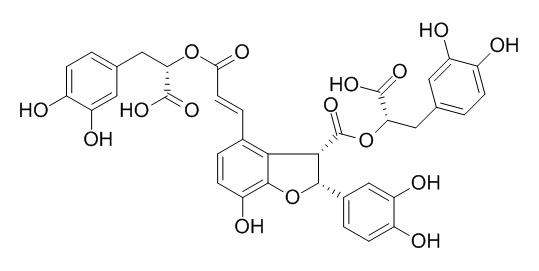
Salvianolic acid Y
Salvianolic acid Y is a new protector of PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury from Salvia officinalis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Jurnal Ilmu Pertanian Indonesia2023, 28(4):525-533.
Asian Journal of Chemistry2014, 26(22):7811-7816
Molecules.2019, 24(10):E1926
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(10):5813.
Molecules.2016, 21(6)
Phytochemistry.2024, 222:114102.
Molecules 2022, 27(3),960.
J Ethnopharmacol.2020, 260:112988.
Journal of Holistic Integrative Pharmacy2024, 5(1):45-55.
Nat Prod Communications2018, 10.1177
Related and Featured Products
Molecules. 2015 Jan 6;20(1):683-92.
Salvianolic acid Y: a new protector of PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury from Salvia officinalis.[Pubmed:
25569522 ]
Salvianolic acid Y (TSL 1), a new phenolic acid with the same planar structure as salvianolic acid B, was isolated from Salvia officinalis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structural elucidation and stereochemistry determination were achieved by spectroscopic and chemical methods, including 1D, 2D-NMR (1H-1H COSY, HMQC and HMBC) and circular dichroism (CD) experiments. The biosynthesis pathway of salvianolic acid B and Salvianolic acid Y (TSL 1) was proposed based on structural analysis. The protection of PC12 cells from injury induced by H2O2 was assessed in vitro using a cell viability assay.
CONCLUSIONS:
Salvianolic acid Y (TSL 1) protected cells from injury by 54.2%, which was significantly higher than salvianolic acid B (35.2%).
Phytomedicine. 2018 May 15;44:138-147.
A quality marker study on salvianolic acids for injection.[Pubmed:
29544864 ]
The quality of Chinese medicine (CM) has being an active and challenging research area for CM. Prof. Chang-Xiao Liu et al first proposed the concept of quality marker (Q-Marker) for the quality evaluation and control on CM. This article describe the exploratory studies of Q-Marker in salvianolic acids for injection (SAI) based on this new concept. This study was designed to screen Q-Marker of SAI and establish its quality control method based on the concept of CM Q-Marker.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Based on the concept of CM Q-Marker, the SAI was investigated for the identification of chemical components and their sources. The pharmacological effects on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion induced injury in rats were also investigated. Furthermore, the target cell extracts and pharmacokinetic studies were conducted to screen Q-Markers. Finally, the fingerprints and determination based on Q-Markers were established to assess the quality of SAI more effectively. Overall, 20 constituents in SAI were identified. It was found that salvianolic acid B (SA-B), rosmarinic acid (RA), lithospermic acid (LA), salvianolic acid D (SA-D) and Salvianolic acid Y (SA-Y) are major chemical components of SAI. Based on chemical components identifications, analysis of their sources, target cell extracts and pharmacokinetic studies, four phenolic acids, namely SA-B, RA, LA and SA-D, were screened and determined as effective Q-Markers of SAI.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study demonstrated that the described method is a powerful approach for detecting Q-Markers, which can be used as control index for the quality assessment of CM.