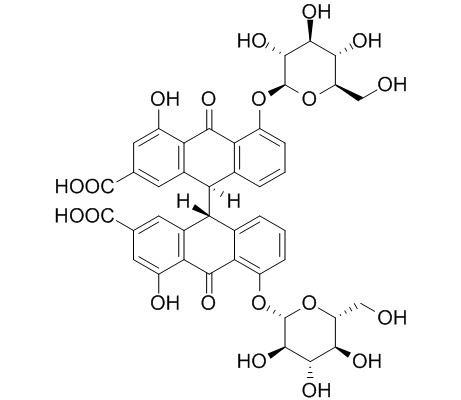
Sennoside A
Sennoside A, a kind of irritant laxative isolated from rhei rhizome, causes purgative actions in the intestine, it and Sennoside B have protective effects on gastric lesion.
Sennoside A also is a new dual HIV-1 inhibitor effective on HIV-1 replication.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
The Journal of Korean Medicine2023, 44(4):26-40.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(23):15213.
Phytomedicine.2024, 126:155442.
Food Addit Contam Part A.2021, 38(12):1985-1994.
J Cell Mol Med.2021, 25(5):2645-2654.
Translational Neuroscience2024, 15:20220339
Cell Death Differ.2021, 1-8.
Data Science for Genomics2023, 107-128.
Drug Des Devel Ther.2023, 17:2461-2479.
J Cell Mol Med.2023, 27(10):1423-1435.
Related and Featured Products
Phytomedicine. 2016 Nov 15;23(12):1383-1391.
Sennoside A, derived from the traditional chinese medicine plant Rheum L., is a new dual HIV-1 inhibitor effective on HIV-1 replication.[Pubmed:
27765358 ]
Despite the availability of effective antiretroviral therapies, drugs for HIV-1 treatment with new mode of action are still needed. An innovative approach is aimed to identify dual HIV-1 inhibitors, small molecules that can inhibit two viral functions at the same time. Rhubarb, originated from Rheum palmatum L. and Rheum officinale Baill., is one of the earliest and most commonly used medicinal plants in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practice. We wanted to explore TCM for the identification of new chemical scaffolds with dual action abilities against HIV-1.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
R. palmatum L. and R. officinale Baill. extracts along with their main single isolated constituents anthraquinone derivatives were tested on both HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase (RT)-associated DNA Polymerase (RDDP) and Ribonuclease H (RNase H) activities in biochemical assays. Active compounds were then assayed for their effects on HIV-1 mutated RTs, integrase (IN) and viral replication.
Both R. palmatum L. and R. officinale Baill. extracts inhibited the HIV-1 RT-associated RNase H activity. Among the isolated constituents, Sennoside A and B were effective on both RDDP and RNase H RT-associated functions in biochemical assays. Sennoside A was less potent when tested on K103N, Y181C, Y188L, N474A and Q475A mutated RTs, suggesting the involvement of two RT binding sites for its antiviral activity. Sennoside A affected also HIV-1 IN activity in vitro and HIV-1 replication in cell-based assays. Viral DNA production and time of addition studies showed that Sennoside A targets the HIV-1 reverse transcription process.
CONCLUSIONS:
Sennoside A is a new scaffold for the development of HIV-1 dual RT inhibitors.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(9):1438-42.
The influence of glycyrrhiza and antibiotics on the purgative action of sennoside a from Daiokanzoto in mice.[Pubmed:
21881230]
Daiokanzoto (DKT), a Kampo medicine that includes the combination of two crude drugs (rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), is clinically effective for constipation.
The aim of this study is to clarify the influence of glycyrrhiza, three glycyrrhiza constituents (glycyrrhizin, liquiritin, and liquiritin apioside), and eight antibiotics on the purgative action of DKT, rhubarb, or Sennoside A, a constituent of rhubarb, in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purgative actions of rhubarb and Sennoside A were significantly intensified when glycyrrhiza was co-administered orally to mice. Liquiritin and liquiritin apioside but not glycyrrhizin showed significant amplification of the purgative action in a dose-dependent manner. The purgative actions of DKT and Sennoside A were significantly reduced by the pre-administration of ampicillin, cefcapene pivoxil, faropenem, fosfomycin, or kanamycin, but were not affected by the pre-administration of clarithromycin or levofloxacin. On the other hand, the purgative action of Sennoside A was significantly reduced by the pre-administration of minocycline, whereas that of DKT was not affected. The effect of minocycline on the purgative action of Sennoside A was lost when glycyrrhiza was co-administered.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that liquiritin and liquiritin apioside contribute as active substances for the purgative action of DKT, and some antibiotics reduce the purgative action of DKT and Sennoside A. Furthermore, glycyrrhiza has the ability to recover the purgative action of Sennoside A suppressed by minocycline via an unknown mechanism.
The FASEB Journal, 2015, 29(1): 716.10.
Protective mechanism on gastric lesion of Sennoside A and Sennoside B[Reference:
WebLink]
Sennoside A and sennoside B is evacuant to increase the sensitivity of the colon.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In vivo test, we performed HCl·ethanol-induced gastritis test, indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer test, gastric secretion in pylorus-ligated test, H+/K+ATPase activity test, gastric emptying and intestinal motility test. In vitro test, we examined acid-neutralizing capacity, quantity of PGE2 and inhibition of H. pylori colonization and we confirmed apoptosis using DAPI nuclear staining, FACS analysis. Sennoside A and B inhibit lesion index in gastritis and gastric ulcer in rats. These results showed that these components reduced gastric juice, an aggressive factor and total acidity and increased pH moderately. In addition, it was made sure that proton pump inhibiton influenced on gastric acid secretion control and that colonization inhibiting activity on H. pylori.
CONCLUSIONS:
As protection enhancing factors to gastric damage, Sennoside A and B increased PGE2 in a concentration-dependent manner.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Feb 27;152(1):190-200.
Rheinanthrone, a metabolite of sennoside A, triggers macrophage activation to decrease aquaporin-3 expression in the colon, causing the laxative effect of rhubarb extract.[Pubmed:
24412547]
Aquaporin-3 (AQP3) is expressed in mucosal epithelial cells in the colon and is important for regulating fecal water content. We examined the role of AQP3 in the laxative effect of rhubarb extract.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
After orally administering rhubarb extract or its major component (Sennoside A) to rats, the fecal water content, AQP3 expression and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) concentrations in the colon were examined. The mechanism by which Sennoside A decreases the expression of AQP3 was examined using the human colon cancer HT-29 cells and macrophage-derived Raw264.7 cells. During diarrhea by rhubarb extract administration, the PGE2 levels in the colon increased while the AQP3 expression significantly decreased. Similar changes were also observed when Sennoside A was administered. When Sennoside A or its metabolites, rheinanthrone and rhein were added to Raw264.7 cells, a significant increase in the PGE2 concentration was observed only in cells treated with rheinanthrone. Fifteen minutes after adding PGE2 to the HT-29 cells, the AQP3 expression decreased to approximately 40% of the control. When pretreated with indomethacin, Sennoside A neither decreased the AQP3 expression nor induced diarrhea.
CONCLUSIONS:
Sennoside A may decrease AQP3 expression in the colon to inhibit water transport from the luminal to the vascular side, leading to a laxative effect. The decreases in the levels of AQP3 are caused by rheinanthrone, which is a metabolite of Sennoside A, this metabolite activates the macrophages in the colon and increases the secretion of PGE2; PGE2 acts as a paracrine factor and decreases AQP3 expression in colon mucosal epithelial cells.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(9):1106-9.
High-performance liquid chromatographic determination and metabolic study of sennoside a in daiokanzoto by mouse intestinal bacteria.[Pubmed:
21881253]
Daiokanzoto (DKT, combination of rhubarb and glycyrrhiza), a Kampo medicine, is clinically effective for constipation. Sennoside A is well known to induce diarrhea. Sennoside A is a prodrug that is transformed into an active metabolite, rheinanthrone, by intestinal bacteria.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we investigated the effects of glycyrrhiza on the activity of Sennoside A metabolism in intestinal bacteria using mouse feces. A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for the determination of Sennoside A in incubation mixture of DKT with mouse feces was established. The retention time of Sennoside A was 9.26±0.02 min with a TSKgel ODS-80TsQA column by linear gradient elution using a mobile phase containing aqueous phosphoric acid and acetonitrile and detection at 265 nm. We found that the activity of Sennoside A metabolism in intestinal bacteria was significantly accelerated when glycyrrhiza, liquiritin or liquiritin apioside coexisted with Sennoside A, whereas that of glycyrrhizin was not altered.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method is applicable for determination of the activity of Sennoside A metabolism by anaerobic incubation of DKT with mouse feces.
3,3',4',5,6,7,8-heptamethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN95021
CAS No: 1178-24-1
Price: $268/10mg
Lonicerin
Catalog No: CFN95055
CAS No: 25694-72-8
Price: $168/10mg
Parvisoflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95077
CAS No: 49776-79-6
Price: $413/5mg
Emodin-8-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No: CFN95132
CAS No: 66466-22-6
Price: $368/5mg
1,2-Epoxy-10(14)-furanogermacren-6-one
Catalog No: CFN95214
CAS No: 383368-24-9
Price: $318/10mg
2-Methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
Catalog No: CFN95269
CAS No: 2348-82-5
Price: $70/20mg
New compound 11
Catalog No: CFN95351
CAS No: N/A
Price: $318/10mg
Hydroxytyrosol 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95367
CAS No: 76873-99-9
Price: $318/10mg
(2S)-5,7,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95406
CAS No: 74628-43-6
Price: $318/10mg
Mahuannin E
Catalog No: CFN95585
CAS No: 1173887-70-1
Price: $318/5mg