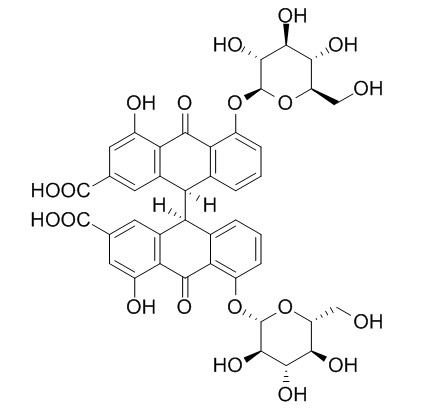
Sennoside B
Sennoside B, a major purgative component, has a potential utility in the treatment of proliferative diseases, through inhibiting PDGF-stimulated cell proliferation by binding to PDGF-BB and its receptor and by down-regulating the PDGFR-beta signaling pathway. It and sennoside A also possess significant gastroprotective activities .
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Front Nutr.2023, 10:1168095.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018, 2018:3610494
Plant Science2024, 338:111914
Phytomedicine.2024, 125:155350.
Nutrients.2017, 10(1)
Bull. Pharm. Sci., Assiut University2020, 43(2):149-155.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 174:116598.
Fitoterapia.2022, 157:105130.
Preprints2024, 2085.v1
Molecules.2023, 28(5):2376.
Related and Featured Products
Life Sci. 2009 Jun 19;84(25-26):915-22.
Sennoside B inhibits PDGF receptor signaling and cell proliferation induced by PDGF-BB in human osteosarcoma cells.[Pubmed:
19393247]
AIMS:
To address the possibility that Sennoside B inhibition of cell proliferation is mediated via interference with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling.
MAIN METHODS:
Human osteosarcoma MG63 cells were treated with PDGF in the presence or absence of Sennoside B. Activation of the PDGF signaling pathway was monitored using western immunoblotting with specific antibodies against the PDGF receptor, phosphotyrosine and components of the downstream signaling cascade. Activation of cell metabolism and proliferation was assessed by chromogenic reduction of MTT.
KEY FINDINGS:
Sennoside B was found to inhibit PDGF-BB-induced phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor (PDGFR) in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Downstream signaling was also affected; pre-incubation of PDGF-BB with Sennoside B inhibited the phosphorylation of pathway components including Ak strain To address the possibility that Sennoside B inhibition of cell proliferation is mediated via interference with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Human osteosarcoma MG63 cells were treated with PDGF in the presence or absence of Sennoside B. Activation of the PDGF signaling pathway was monitored using western immunoblotting with specific antibodies against the PDGF receptor, phosphotyrosine and components of the downstream signaling cascade. Activation of cell metabolism and proliferation was assessed by chromogenic reduction of MTT. Sennoside B was found to inhibit PDGF-BB-induced phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor (PDGFR) in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Downstream signaling was also affected; pre-incubation of PDGF-BB with Sennoside B inhibited the phosphorylation of pathway components including Ak strain transforming protein (AKT), signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT-5) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Further, we found that Sennoside B can bind directly to the extracellular domains of both PDGF-BB and the PDGF-beta receptor (PDGFR-beta). The effect was specific for Sennoside B; other similar compounds including aloe-emodin, rhein and the meso isomer (sennoside A) failed to inhibit PDGFR activation or downstream signaling. Sennoside B also inhibited PDGF-BB stimulation of MG63 cell proliferation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Sennoside B can inhibit PDGF-stimulated cell proliferation by binding to PDGF-BB and its receptor and by down-regulating the PDGFR-beta signaling pathway. Sennoside B is therefore of potential utility in the treatment of proliferative diseases in which PDGF signaling plays a central role.
J Drug Target. 2015 Feb;23(2):180-90.
Experimental evaluation of radioiodinated sennoside B as a necrosis-avid tracer agent.[Pubmed:
25330022]
Necrosis-avid agents are a class of compounds that selectively accumulate in the necrotic tissues after systemic administration, which can be used for in vivo necrosis imaging and targeted therapies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to search for a necrosis-avid tracer agent with improved drugability, we labelled iodine-131 on Sennoside B (SB) as a naturally occurring median dianthrone compound. The necrosis targetability and clearance properties of (131)I-Sennoside B were evaluated in model rats with liver and muscle necrosis. On SPECT/CT images, a "hot spot" in the infarcted liver lobe and necrotic muscle was persistently observed at 24 h and 72 h post-injection (p.i.). Gamma counting of the tissues of interest revealed a radioactivity ratio of necrotic to viable liver at 4.6 and 3.4 and of necrotic to viable muscle at 7.0 and 8.8 at 24 h and 72 h p.i., respectively. The good match of autoradiographs and fluoromicroscopic images with corresponding histochemical staining suggested preferential uptake of (131)I-Sennoside B in necrotic tissue. Pharmacokinetic study revealed that (131)I-Sennoside B has an elimination half-life of 8.6 h.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study indicates that (131)I-Sennoside B shows not only prominent necrosis avidity but also favourable pharmacokinetics, which may serve as a potential necrosis-avid diagnostic agent for assessment of tissue viability.
Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015 Sep; 23(5): 458–464.
Gastroprotective Activities of Sennoside A and Sennoside B via the Up-Regulation of Prostaglandin E2 and the Inhibition of H+/K+-ATPase.[Pubmed:
26336586 ]
Sennoside A (erythro) and Sennoside B (threo) are dianthrone glycosides and diastereomers. We investigated their abilities to prevent the gastric lesions associated with diseases, such as, gastritis and gastric ulcer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To elucidate their gastroprotective effects, the inhibitions of HCl•EtOH-induced gastritis and indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers were assessed in rats. It was observed that both sennoside A and Sennoside B increased prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels and inhibited H(+)/K(+)-ATPase (proton pump). In a rat model, both compounds reduced gastric juice, total acidity and increased pH, indicating that proton pump inhibition reduces gastric acid secretion. Furthermore, sennoside A and B increased PGE2 in a concentration-dependent manner. In a gastric emptying and intestinal transporting rate experiment, both sennoside A and Sennoside B accelerated motility.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results thus suggest that sennoside A and Sennoside B possess significant gastroprotective activities and they might be useful for the treatment of gastric disease.
Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2011 May;40(3):355-7.
[Determination of sennoside A and sennoside B simultaneously in health food by HPLC].[Pubmed:
21695913]
To develop an analytical method for determination of sennoside A and Sennoside B simultaneously in health food by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Samples were extracted by ultrasound extraction and determined by HPLC with a UV detector. Using a Synergi Hydro-RP (250 mm x 4.6 mm, 4 microm) column and a mixture of CH3CN: 1.0% CH3COOH (17:83) as mobile phase for separation. The detection wavelength was at 270 nm. The contents were calculated with an external standard. The linearity was good in the ranges of 1.40 - 28.0 microg/ml for sennoside A and 1.45 - 29.0 microg/ml for Sennoside B. The average recovery rates of sennoside A and Sennoside B were 85.2% -97.2% and 86.1% -96.2%. The RSD was 7.5% and 6.8%, the limit of detection was 0.8 mg/kg and 0. 6 mg/kg, and the limit df quantification was 2.1 mg/kg and 2.0 mg/kg for sennoside A and Sennoside B respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The method is simple, accurate and suitable for the determination of sennoside A and Sennoside B in health food.