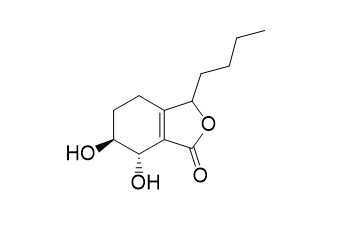
Senkyunolide N
Senkyunolide N exhibits prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-I (COX-I) and endoperoxide synthase-II (COX-II)) Inhibitory activity at pH 7 and at a concentration of 250 pg ml(-1) .
Senkyunolide N exhibits topoisomerase-I and -II enzyme inhibitory activity at concentrations of 100, 200 and 200 microg ml(-1).
Senkyolide N has insecticidal effect.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J of Archaeological Science:Reports2024, 53:104298
Nutrients.2020, 12(3):595.
Heliyon.2024, 10(23):e40758.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(5):2914.
J Ethnopharmacol.2025, 350:120002.
J Nat Prod.2022, doi: 10.1021
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(49):27139-27149
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2015, 2015:165457
J of Food Quality2020, 8851285.
Inflammation.2022, 45(6):2529-2543.
Related and Featured Products
Phytomedicine . 2002 May;9(4):312-318.
Antioxidant, cyclooxygenase and topoisomerase inhibitory compounds from Apium graveolens Linn. seeds[Pubmed:
12120812]
Cyclooxygenase inhibitory and antioxidant bioassay-directed extraction and purification of celery seeds yielded sedanolide (1), senkyunolide-N (2), senkyunolide-J (3), 3-hydroxymethyl-6-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ol (4), L-tryptophan (6), and 7-[3-(3,4-dihydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-furan-2-yloxy)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy]-5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-chromen-4-one (7). The structures of compounds 1-7 were determined using spectroscopic methods. Compound 4 is reported here for the first time. At 250 pg ml(-1), compounds 1-4, 6 and 7 displayed prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-I (COX-I) and prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-II (COX-II) inhibitory activities at pH 7. The acetylated product (5) of compound 4 also inhibited COX-I and COX-II enzymes when tested at 250 microg ml(-1). Compounds 6 and 7 exhibited good antioxidant activity at concentrations of 125 and 250 microg ml(-1). Only compounds 1-3 exhibited topoisomerase-I and -II enzyme inhibitory activity at concentrations of 100, 200 and 200 microg ml(-1), respectively.
J Agric Food Chem . 2001 Jan;49(1):142-145.
Mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal compounds from Apium graveolens L. seeds[Pubmed:
11305251]
The methanolic extract of Apium graveolens seeds was investigated for bioactive compounds and resulted in the isolation and characterization of mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal compounds sedanolide (1), senkyunolide-N (2), and senkyunolide-J (3). Their structures were determined by 1H and 13C NMR spectral methods. Compounds 1-3 gave 100% mortality at 25, 100, and 100 microg mL(-1), respectively, on the nematode, Panagrellus redivivus. Compound 1 showed 100% mortality at 50 microg mL(-1) on nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, and fourth-instar mosquito larvae, Aedes aegyptii. Also, it inhibited the growth of Candida albicans and Candida parapsilasis at 100 microg mL(-1). Compounds 2 and 3 were isolated for the first time from A. graveolens. This is the first report of the mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal activities of compounds 1-3.
J Agric Food Chem . 2001 Jan;49(1):142-145.
Mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal compounds from Apium graveolens L. seeds[Pubmed:
11305251]
The methanolic extract of Apium graveolens seeds was investigated for bioactive compounds and resulted in the isolation and characterization of mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal compounds sedanolide (1), senkyunolide-N (2), and senkyunolide-J (3). Their structures were determined by 1H and 13C NMR spectral methods. Compounds 1-3 gave 100% mortality at 25, 100, and 100 microg mL(-1), respectively, on the nematode, Panagrellus redivivus. Compound 1 showed 100% mortality at 50 microg mL(-1) on nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans, and fourth-instar mosquito larvae, Aedes aegyptii. Also, it inhibited the growth of Candida albicans and Candida parapsilasis at 100 microg mL(-1). Compounds 2 and 3 were isolated for the first time from A. graveolens. This is the first report of the mosquitocidal, nematicidal, and antifungal activities of compounds 1-3.
Phytomedicine . 2002 May;9(4):312-318.
Antioxidant, cyclooxygenase and topoisomerase inhibitory compounds from Apium graveolens Linn. seeds[Pubmed:
12120812]
Cyclooxygenase inhibitory and antioxidant bioassay-directed extraction and purification of celery seeds yielded sedanolide (1), senkyunolide-N (2), senkyunolide-J (3), 3-hydroxymethyl-6-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-ol (4), L-tryptophan (6), and 7-[3-(3,4-dihydroxy-4-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-furan-2-yloxy)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy]-5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-chromen-4-one (7). The structures of compounds 1-7 were determined using spectroscopic methods. Compound 4 is reported here for the first time. At 250 pg ml(-1), compounds 1-4, 6 and 7 displayed prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-I (COX-I) and prostaglandin H endoperoxide synthase-II (COX-II) inhibitory activities at pH 7. The acetylated product (5) of compound 4 also inhibited COX-I and COX-II enzymes when tested at 250 microg ml(-1). Compounds 6 and 7 exhibited good antioxidant activity at concentrations of 125 and 250 microg ml(-1). Only compounds 1-3 exhibited topoisomerase-I and -II enzyme inhibitory activity at concentrations of 100, 200 and 200 microg ml(-1), respectively.