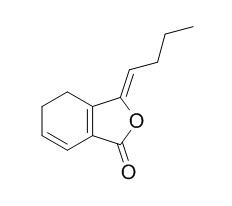
Ligustilide
Ligustilide possesses neuroprotective, vasorelaxation, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities, it blocked the activation of MAPKs/IKK and the downstream transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB. It has the potential to be developed into an effective drug for the treatment of various pain syndromes including primary dysmenorrhoea.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Translational Neuroscience2024, 15:20220339
Analytical sci. & Tech2016, 186-193
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(20):12516.
Bio-protocol2018, 9(14):e3301
Journal of Applied Biology & Biotechnology2023,11(4):148-158
Methods Protoc.2024, 7(6):95.
Asian J of Pharmaceutical&Clinical 2018, 11(2)
Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.2024, 149:105620.
J Food Drug Anal.2023, 31(2):254-277.
J of Pharmaceutical Analysis2020, doi: 10.1016
Related and Featured Products
Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 Jan;46(1):42-6.
[Protective effect of ligustilide against low potassium induced apoptosis in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons].[Pubmed:
25807794]
To investigate the effect of Ligustilide (LIG) on low potassium-induced apoptosis in primary cultured cerebellar granule neurons (CGN).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Apoptosis was induced by low potassium in cultured neonatal rat CGN in vitro. The CGN was divided into control/model/CGP54626 + Ligustilide and Ligustilide group. The neuronal viability of each group was measured by MTT assay. The protein expression levels of the key insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF)-1 signaling effectors,including the phosphorylated IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R), Akt, ERK1/2, CREB and activated caspase 3 were examined by Western blot analysis. Ligustilide ranging from 2.5 to 20 micromol/L could protect against low potassium-induced apoptosis of CGN ini a concentration-dependent manner. 20 micromol/L Ligustilide significantly induced upregulation of the phosphorylated levels of IGF-1, Akt, ERK1/2 and CREB, and downregulation of cleaved-caspase 3 expression, which could be blocked by a selective gamma-aminobutyric acid B (GABAs) receptor antagonist CGP54626.
CONCLUSIONS:
Ligustilide concentration-dependently protects against low potassium-induced apoptosis in CGN at least partly through GABAa receptor activation and its downstream IGF-1 signaling pathway.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 May 22;111(3):677-80.
Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two main constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta.[Pubmed:
17222996 ]
Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Umbelliferae) is a widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicinal herb for cardiovascular diseases in China. However, the cardiovascular actions of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two of the most abundant Ligusticum chuanxiong constituents, have yet to be examined.
CONCLUSIONS:
The objective of the present study was to investigate the vasorelaxation effects of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A and their underlying mechanisms in rat isolated aorta. Both constituents had similar relaxation potencies against contractions to 9,11-dideoxy-9alpha,11alpha-methanoepoxyprostaglandin F(2alpha), phenylephrine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and KCl. Their vasorelaxation effects were not affected by endothelium removal, the adenylate cyclase inhibitor 9-(tetrahydro-2-furanyl)-9H-purin-6-amine, the soluble guanylate cyclase inhibitor 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one, or the non-selective K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report to demonstrate the vasorelaxation activities of Ligustilide and senkyunolide A in contractions to various contractile agents in rat isolated aorta. The underlying mechanisms await further investigations.
Brain Res. 2015 Jan 21;1595:19-28.
Ligustilide prevents cognitive impairment and attenuates neurotoxicity in D-galactose induced aging mice brain.[Pubmed:
25446001]
Ligustilide (LIG) is a principal active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, Radix Angelica sinensis, which has versatile pharmacological activities including neuroprotection. Previous studies have demonstrated that Ligustilide has beneficial effects on cognition deficits associated with cerebral damage or neurodegenerative disorders. In present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effect of Ligustilide on cognitive impairment and neurotoxicity in the brain of aging mouse induced by d-galactose (d-gal).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aging model mice were induced by subcutaneous (S.C.) injection of d-gal once daily for 8 weeks and Ligustilide (80 mg/kg) was simultaneously administered orally. The Morris water maze (MWM) test was used to assess the spatial learning and memory abilities. The activity of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase and the content of lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) in brain were examined. The levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), growth-associated protein GAP-43, and cleaved caspase-3 in brain were also determined by immunohistochemistry. The MWM test showed that Ligustilide administration markedly improved behavioral performance of d-gal treated mice. This action could be partly explained by the results that Ligustilide reduced the level of MDA as well as increased the activity of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase in the brain of d-gal induced aging mice. Moreover, Ligustilide significantly raised the expression of GAP-43 and reduced cleaved caspase-3 and GFAP levels in the brain of d-gal treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated that Ligustilide improves d-gal-induced cognitive dysfunction and brain toxicity, which suggests that Ligustilide may be developed as a new medicine for the treatment of aged-related conditions.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;69:42-6.
Ligustilide inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy during C2C12 cells differentiation.[Pubmed:
25661336]
Ligustilide is widely thought to be the most potent bioactive constituent of Angelica sinensis. We have previously reported the role of Ligustilide in preventing TNF-α-induced apoptosis and identified the presence of autophagosome clusters. Then, we hypothesised that autophagy may contribute to muscle loss and that Ligustilide could protect cell fibres by regulating the autophagic process. The aim of this study was to identify the effects of Ligustilide on autophagy regulation during cell differentiation in the presence of TNF-α.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We then observed intracellular morphologic changes and autophagosome formation using transmission electron microscopy. LC3B expression was assessed by immunofluorescence and Atg-7, Atg-5, Atg-12 and LC3B expression levels were detected by western blot. The results revealed a reduction in the number of TNF-α-induced autophagosomes after Ligustilide treatment accompanied by a decrease in Atg-7, Atg-5, Atg-12 and LC3B expression, as well as a reduction of the LC3BII/I ratio in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings provide evidence supporting a protective effect of Ligustilide against TNF-α-induced autophagy during myotubes formation.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Sep;11(9):1166-72.
Ligustilide prevents LPS-induced iNOS expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by preventing ROS production and down-regulating the MAPK, NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways.[Pubmed:
21457761 ]
Angelica sinensis (AS), an herb used in traditional Chinese medicine, is thought to have anti-inflammatory activities. Ligustilide is its most abundant ingredient.
This study sought to determine Ligustilide's effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ligustilide significantly suppressed the production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). The inhibition of NO was concomitant with a decrease in the protein and mRNA levels of LPS-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Furthermore, activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in the nucleus and the cytosolic degradation of IκBα were abrogated by Ligustilide. Ligustilide also inhibited the phosphorylation of IκB kinase (IKK) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including p38 MAPK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). The intracellular reactive oxygen species (iROS) level was also significantly decreased.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Ligustilide exhibits anti-inflammatory activities by blocking the activation of MAPKs/IKK and the downstream transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κB, which may result from Ligustilide's down-regulation of iROS production.
Neurobiol.Aging, 2014, 35(1):169-78.
Klotho upregulation contributes to the neuroprotection of ligustilide in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.[Pubmed:
23973442 ]
Klotho, an aging-suppressor gene, encodes a protein that potentially acts as a neuroprotective factor by modulating insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling and oxidative stress. In the present study, we investigated the potential role of Klotho in the therapeutic effect of Ligustilide against Alzheimer's disease (AD)-like neuropathologies and memory impairment in aged senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ligustilide treatment (10 and 40 mg/kg for 8 weeks, intragastrically) in 10-month-old SAMP8 mice reduced memory deficits, amyloid-β(1)-42 accumulation, tau phosphorylation, and neuron loss, increased mitochondrial manganese-superoxide dismutase and catalase expression and activity, and decreased malondialdehyde, protein carbonyl, and 8-hydroxydesoxyguanosine levels in the brain. Ligustilide upregulated Klotho expression in the cerebral choroid plexus and serum, decreased Akt and Forkhead box class O1 phosphorylation. Moreover, Ligustilide inhibited the insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway and induced Forkhead box class O1 activation in 293T cells along with Klotho upregulation.
CONCLUSIONS:
An inverse correlation was found between Klotho expression and the AD phenotype, suggesting that Klotho might be a novel therapeutic target for age-related AD, and Klotho upregulation might contribute to the neuroprotective effect of Ligustilide against AD.
Rhamnetin 3-galactoside
Catalog No: CFN95116
CAS No: 62858-07-5
Price: $318/10mg
ent-16beta,17-dihydroxy-9(11)-kauren-19-oic acid
Catalog No: CFN95172
CAS No: 55483-24-4
Price: $318/10mg
Vanillic acid glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95257
CAS No: 32142-31-7
Price: $368/10mg
Isosilychristin
Catalog No: CFN95369
CAS No: 77182-66-2
Price: $318/5mg
3',8-Dihydroxyvestitol
Catalog No: CFN95384
CAS No: 122587-87-5
Price: $413/5mg
10-O-trans-p-Feruloylscandoside
Catalog No: CFN95392
CAS No: 1428268-72-7
Price: $318/10mg
5,6,7,3',4'-Pentamethoxyflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95394
CAS No: 104193-93-3
Price: $318/5mg
(Z)-3,11-dimethy-7-methylene-9,14-epoxy-1,6,10-dodecatrien-3-ol
Catalog No: CFN95402
CAS No: 1392202-57-1
Price: $318/10mg
Barbaloin-related compound A
Catalog No: CFN95453
CAS No: 473225-21-7
Price: $318/5mg
Ephedrannin D1
Catalog No: CFN95547
CAS No: 1592431-55-4
Price: $318/5mg