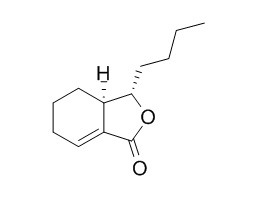
Neocnidilide
Neocnidilide has insecticidal activity, it exhibits LC50 values of 9.90 micromol/mL of diet concentration against larvae of D. melanogaster. Neocnidilide has antifungal activity. It can enhance the skin penetration of benzoic acid.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2014, 113-120
Molecules.2017, 22(2)
Food Res Int.2019, 123:125-134
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(40):22237-22249.
Vietnam Journal of Food Control2022, 5(3):pp.390-401.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2024, 17(8):988.
Functional Ecology2020, doi: 10.1111.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(19):10660.
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Buildings2023, 13(5), 1112.
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(17):1521-7.
Isolation of the volatile fraction from Apium graveolens L. (Apiaceae) by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and hydrodistillation: chemical composition and antifungal activity.[Pubmed:
22974401 ]
Apium graveolens L. (wild celery), belonging to the family of Apiaceae, is a scaposus hemicryptophyte. Instead, the cultivate plant is an annual or biennial herb widely used as a spice and seasoning in food. A broad range of biological activities have been attributed to A. graveolens. These include antimicrobial activity, larvicidal activity, hepatoprotective activity, nematicidal and mosquito repellent potential and antihyperlipidaemic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the authors compare the composition of the volatile fractions of A. graveolens collected in natural populations in Portugal and Italy and evaluate their potential as antifungal agents.The composition of the volatile oils obtained by hydrodistillation and their antifungal activity are reported. The oils were analysed by gas chromatography-flame ionisation detector and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry methods and their composition were compared with that of the volatile extracts isolated by supercritical CO2. A chemical variability in the extracts depending on the origin of the plants and on the extraction method was observed. The results showed the presence of sedanenolide, Neocnidilide and neophytadiene as main components. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal lethal concentration were used to evaluate the antifungal activity of the oils against Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida krusei, Candida guilliermondii, Candida parapsilosis, Cryptococcus neoformans, Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale, Trichophyton verrucosum, Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, Epidermophyton floccosum, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus. The oil from Italy rich in neophytadiene is the more active, with MIC values of 0.04-0.64 μL mL(-1).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results show that A. graveolens volatile extracts may be useful in the clinical treatment of fungal diseases.
Yakugaku Zasshi. 1992 Sep;112(9):638-44.
Studies on the baths with crude drug: the effects of Senkyu extract as skin penetration enhancer.[Pubmed:
1469611]
The effects of Senkyu (Cnidii Rhizoma and Ligustici chuanxiong Rhizoma) on the drug skin penetration were studied to clarify its effectivity as the baths.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ether and methanol extracts, and some essential oils of Senkyu (i.e. ligustilide, Neocnidilide and butylidenephthalide) enhanced remarkably the skin penetration of benzoic acid. Furthermore, an appreciable correlation between the enhancing ratio and the skin/donor partition coefficient of benzoic acid was observed.
CONCLUSIONS:
These facts suggest that the constituents of Senkyu influence the skin penetration by enhancing the partition coefficient.
J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jul 13;53(14):5549-53.
Larvicidal and adulticidal activity of alkylphthalide derivatives from rhizome of Cnidium officinale against Drosophila melanogaster.[Pubmed:
15998112]
The insecticidal activity of the chloroform extract of Cnidium officinale rhizomes and its constituents was investigated against larvae and adults of Drosophila melanogaster and compared with that of rotenone.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided isolation of the chloroform extract of C. officinale resulted in the isolation and characterization of four alkylphthalides, cnidilide (1), (Z)-ligustilide (2), (3S)-butylphthalide (3), and Neocnidilide (4). The structures of these compounds were established by spectroscopic analysis. The isolated compounds 2, 3, and 4 exhibited LC50 values of 2.54, 4.99, and 9.90 micromol/mL of diet concentration against larvae of D. melanogaster, respectively. Against both sexes (males/females, 1:1) of adults (5-7 days old), compound 3 showed the most potent activity of the compounds isolated with the LD50 value of 5.93 microg/adult, comparable to that of rotenone (LD50 = 3.68 microg/adult).
CONCLUSIONS:
Structure-activity relationships of phthalides isolated suggest that the presence of conjugation with the carbonyl group in the lactone ring appeared to play an important role in the larvicidal activity. Acetylcholinesterase (prepared from the adult heads of D. melanogaster) inhibitory activity was also investigated in vitro to determine the insecticide mode of action for the acute adulticidal activity.