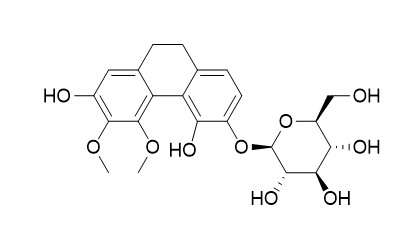
Diosniposide B
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Nutr Biochem.2022, 107:109064.
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:607403.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):221
Journal of Functional Foods2022, 99: 105331.
J Appl Microbiol.2024, 135(7):lxae180.
J Pharmaceut Biomed2020, 178:112894
Molecules.2019, 24(9):E1719
Int J Mol Sci.202, 25(17):9246.
Biomed Chromatogr.2016, 30(10):1573-81
Saudi Pharm J.2019, 27(1):145-153
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol . 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1164-1170.
Phenolic derivatives from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica and their anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective activities[Pubmed:
24973689]
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Dioscorea nipponica (Dioscoreaceae) have been used as traditional medicines for diabetes, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases in Korea. The aim of the study was to isolate the bioactive components from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica and to evaluate their anti-neuroinfalmmatory and neuroprotective activities.
Material and methods: The phytochemical investigation of 50% EtOH extract of Dioscorea nipponica using successive column chromatography over silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and preparative high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) resulted in the isolation and identification of 17 phenolic derivatives, including four new phenolic compounds (1-4). The structural elucidation of these compounds was based on spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy techniques, mass spectrometry, and optical rotation. All isolated compounds were evaluated for their effects on nerve growth factor (NGF) secretion in a C6 rat glioma cell line and nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated BV2 cells. The neurite outgrowth of compound 16 was further evaluated by using mouse neuroblastoma N2a cell lines.
Results: Three new stilbene derivatives, diosniponol C (1), D (2) and diosniposide A (3) and one new phenanthrene glycoside, Diosniposide B (4), together with 13 known compounds were isolated from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica. Of the tested compounds (1-17), phenanthrene, 3,7-dihydroxy-2,4,6-trimethoxy-phenanthrene (16) was the most potent NGF inducer, with 162.35±16.18% stimulation, and strongly reduced NO levels with an IC50 value of 19.56 μM in BV2 microglial cells. Also, it significantly increased neurite outgrowth in N2a cells.
Conclusions: This study supports the ethnopharmacological use of Dioscorea nipponica rhizomes as traditional medicine.
J Ethnopharmacol . 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1164-1170.
Phenolic derivatives from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica and their anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective activities[Pubmed:
24973689]
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Dioscorea nipponica (Dioscoreaceae) have been used as traditional medicines for diabetes, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases in Korea. The aim of the study was to isolate the bioactive components from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica and to evaluate their anti-neuroinfalmmatory and neuroprotective activities.
Material and methods: The phytochemical investigation of 50% EtOH extract of Dioscorea nipponica using successive column chromatography over silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and preparative high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) resulted in the isolation and identification of 17 phenolic derivatives, including four new phenolic compounds (1-4). The structural elucidation of these compounds was based on spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy techniques, mass spectrometry, and optical rotation. All isolated compounds were evaluated for their effects on nerve growth factor (NGF) secretion in a C6 rat glioma cell line and nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated BV2 cells. The neurite outgrowth of compound 16 was further evaluated by using mouse neuroblastoma N2a cell lines.
Results: Three new stilbene derivatives, diosniponol C (1), D (2) and diosniposide A (3) and one new phenanthrene glycoside, Diosniposide B (4), together with 13 known compounds were isolated from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica. Of the tested compounds (1-17), phenanthrene, 3,7-dihydroxy-2,4,6-trimethoxy-phenanthrene (16) was the most potent NGF inducer, with 162.35±16.18% stimulation, and strongly reduced NO levels with an IC50 value of 19.56 μM in BV2 microglial cells. Also, it significantly increased neurite outgrowth in N2a cells.
Conclusions: This study supports the ethnopharmacological use of Dioscorea nipponica rhizomes as traditional medicine.