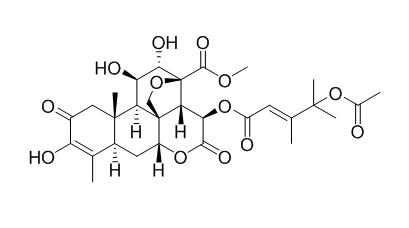
Bruceantinol
Bruceantinol has antiviral activity, it can inhibit pepper mottle virus in pepper; it shows antibabesial activity against Babesia gibsoni in vitro, with the IC50 value of 12 ng/mL. Bruceantinol shows in vitro inhibitory activity against Trypanosoma evansi.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Srinagarind Medical Journal2019, 34(1)
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(6):526.
Sci Rep.2021, 11(1):11936.
Molecules2021, 26(1),230
Korea Food Research Institute2024, 4798082
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:765521.
Foods. 2022, 11(23):3905.
Molecules2020, 25(4):892
Proc. Sci. Math.2024, V25:108-123
Toxicol In Vitro.2023, 86:105521.
Related and Featured Products
Virus Res. 2017 Jan 2;227:49-56.
Quassinoids isolated from Brucea javanica inhibit pepper mottle virus in pepper.[Pubmed:
27686478 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged pepper mottle virus (PepMoV) based leaf-disc method and systemic host method were developed to identify antiviral agents. Preliminary experiments using a PepMoV-GFP based leaf-disc method led to the isolation of five quassinoids, including brusatol (1), bruceantin (2), brucein A (3), Bruceantinol (4), and brucein B (5), from the CH3OH extract of Brucea javanica.
CONCLUSIONS:
All isolated compounds exhibited inactivation effects in systemic host plants, and compounds 3 and 4 were potent, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 10μM. Furthermore, compound 3 was found to have a protective effect at the tested concentration of 40μM.
J Nat Prod. 2007 Oct;70(10):1654-7.
Screening of Indonesian medicinal plant extracts for antibabesial activity and isolation of new quassinoids from Brucea javanica.[Pubmed:
17896817]
Boiled extracts derived from 28 Indonesian medicinal plants were screened for their antibabesial activity against Babesia gibsoni in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Of these extracts, the fruit of Brucea javanica was the most active in inhibiting parasite growth at a concentration of 10 microg/mL. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the fruit extract of Br. javanica led to the isolation of two new quassinoids, Bruceantinol B and bruceine J, and the structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of their spectroscopic data and by chemical transformation to known compounds. In addition, the known quassinoids bruceines A-D, Bruceantinol, and yadanziolide A were isolated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Antibabesial activities were also examined in vitro, and bruceine A and Bruceantinol were shown to be more potent than diminazene aceturate, a drug (IC50 = 103 ng/mL) used clinically against B. gibsoni, with IC50 values of 4 and 12 ng/mL, respectively.
J Nat Med. 2012 Jan;66(1):233-40.
Antitrypanosomal activities of acetylated bruceines A and C; a structure-activity relationship study.[Pubmed:
21822605]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The crude extract of Brucea javanica showed strong in vitro inhibitory activity against Trypanosoma evansi. Among the isolated quassinoids, bruceines A, C, and Bruceantinol were found to be the most potent compounds against T. evansi. To gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between the free hydroxyl groups and the activity, several O-acetylated derivatives of bruceines A and C were synthesized and their in vitro antitrypanosomal activities against trypomastigotes of T. evansi were examined and compared with those of the original compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
The following structure-activity relationships were observed: (1) the free hydroxyl groups at positions C-3, C-11, and C-12 are essential for antitrypanosomal activity; (2) the C-11 and C-12 hydroxyl groups are more important for the activity than the enolic hydroxyl group at C-3, and; (3) the free hydroxyl group at C-4' of bruceine C does not have any significant effect on the activity.