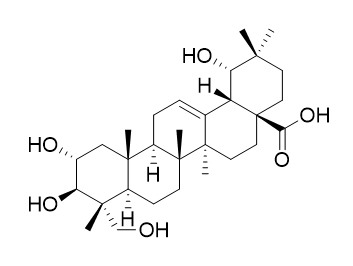
Arjungenin
Arjungenin shows β-glucuronidase inhibitory activity, it shows antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities. Arjungenin exhibits moderate antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis (MICs within a range of 64 and 256 ug/mL). Arjungenin shows significant protection against domoic acid induced toxicity in Caco-2 cell line.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Oxid Med Cell Longev.2020, 2020:8887251.
Int J Nanomedicine.2024, 19:1683-1697.
Sci Rep. 2024, 14(1):70.
J Ethnopharmacol.2023, 313:116534.
Hong Kong Baptist University2023, 048330T.
Food Chem.2022, 373(Pt B):131364.
Prev Nutr Food Sci.2025, 30(1):92-100.
Int J Med Sci.2021, 18(10):2155-2161.
J of Advanced Scientific R.2020, 11(3), p109-120.
Heliyon2020, 6(6):e04337.
Related and Featured Products
Cytotechnology. 2017 Aug;69(4):725-739.
Modulatory effects of Terminalia arjuna against domoic acid induced toxicity in Caco-2 cell line.[Pubmed:
28342004 ]
Domoic acid is a potent marine algal toxin produced by diatomic genus of Pseudo-nitzschia causing amnesic shell fish poisoning. Domoic acid toxicosis mainly involves excitotoxic effects coupled with oxidative stress.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study was aimed to evaluate the protective effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of Terminalia arjuna (TA) against domoic acid induced toxic effects in Caco-2 cell line. It was observed that the toxicity induced by domoic acid in Caco-2 cells was mediated by oxidative insult leading to morphological changes, DNA damage and apoptosis. In our study pre-treatment of the cells with TA (10, 20 and 30 μg/ml) showed significant protection against domoic acid induced morphological, oxidative and apoptotic damages in a dose dependent manner. The effect of phytocompounds present in TA viz., kaempferol and Arjungenin showed significant protection against domoic acid induced toxicity in Caco-2 cell line.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hence, it could be inferred that the protective effect of TA extract against domoic acid induced toxicity could be due to the individual or synergistic effects of kaempferol and argungenin. However, further clinical studies are warranted to consider TA as a natural remedy to prevent amnesic shell fish poisoning.
Fitoterapia. 2016 Apr;110:89-95.
Antibacterial and cytotoxic triterpenoids from the roots of Combretum racemosum.[Pubmed:
26946378]
A new pentacyclic triterpenoid glucoside, together with fourteen known compounds, was isolated from the roots of Combretum racemosum. Combretaceae).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structure of the new compound was established as 28-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-2α,3β,21β,23-tetrahydroxyolean-18-en-28-oate (1) on the basis of detailed spectroscopic data including MS, 1D, and 2D NMR. The inhibitory activity of compounds 1-15 against promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 and human erythromyeloblastoid leukemia K562 cell lines was evaluated. Compounds 11 (3-O-β-acetyl-ursolic acid), 14 (betulinic acid), and 15 (quadranoside II) exhibited significant cytotoxicity, with IC50 values of 13 to 50 μM. Among the isolated triterpenes, compounds 1, 3 (Arjungenin), 5 (terminolic acid), and 11 exhibited moderate antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis (MICs within a range of 64 and 256 μg/mL).
Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung B, 2005, 60(3):347-350.
Some chemical constituents of Terminalia glaucescens and their enzymes inhibition activity.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new triterpenoid, glaucinoic acid (2α, 3β, 19α, 24-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-30-oic acid) (1) along with several known compounds, arjunic acid (2), Arjungenin (3), sericoside (4), and friedelin (5) were isolated from the stem barks of Terminalia glaucescens.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds showed β-glucuronidase inhibitory activity. The structures were identified on the basis of spectroscopic techniques.
Version 2. F1000Res. 2017 Aug 30 [revised 2017 Dec 8];6:1601.
In silico analysis of natural compounds targeting structural and nonstructural proteins of chikungunya virus.[Pubmed:
29333236]
Chikungunya fever presents as a high-grade fever during its acute febrile phase and can be prolonged for months as chronic arthritis in affected individuals. Currently, there are no effective drugs or vaccines against this virus. The present study was undertaken to evaluate protein-ligand interactions of all chikungunya virus (CHIKV) proteins with natural compounds from a MolBase library in order to identify potential inhibitors of CHIKV.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Virtual screening of the natural compound library against four non-structural and five structural proteins of CHIKV was performed. Homology models of the viral proteins with unknown structures were created and energy minimized by molecular dynamic simulations. Molecular docking was performed to identify the potential inhibitors for CHIKV. The absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) toxicity parameters for the potential inhibitors were predicted for further prioritization of the compounds. Results: Our analysis predicted three compounds, Catechin-5-O-gallate, Rosmarinic acid and Arjungenin, to interact with CHIKV proteins; two (Catechin-5-O-gallate and Rosmarinic acid) with capsid protein, and one (Arjungenin) with the E3.
CONCLUSIONS:
The compounds identified show promise as potential antivirals, but further in vitro studies are required to test their efficacy against CHIKV.
Phytochemistry Letters, 2008, 1(4):183-187.
Polyhydroxyoleanane-type triterpenoids from Combretum molle and their anti-inflammatory activity.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new oleanane-type triterpene saponin, β-d-glucopyranosyl 2α,3β,6β-trihydroxy-23-galloylolean-12-en-28-oate (1), together with four known oleanane-type pentacyclic triterpenoids, combregenin (2), Arjungenin (3), arjunglucoside I (4), and combreglucoside (5) were isolated from the stem bark of Combretum molle. Their structures were established mainly on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR spectral data. Compounds 1–3 exhibited more significant activity against carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat compared to compounds 4 and 5.Graphical abstractThe new triterpene saponin, β-d-glucopyranosyl 2α,3β,6β-trihydroxy-23-galloylolean-12-en-28-oate (1) together with the known combregenin (2), Arjungenin (3), arjunglucoside I (4), and combreglucoside (5) were isolated from the stem bark of Combretum molle.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their structures were identified by interpretation of their spectral data, mainly ESIMS, 1D NMR (1H, 13C NMR, DEPT) and 2D NMR (COSY, HSQC and HMBC), and by comparison with the literature. Compounds 1–3 exhibited more significant anti-inflammatory activity against carrageenan-induced paw edema in rat compared to compounds 4 and 5.