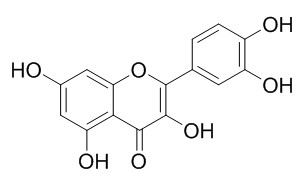
Quercetin
Quercetin is one of the most prominent dietary antioxidants, it is claimed to exert beneficial health effects, this includes protection against various diseases such as osteoporosis, certain forms of cancer, pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases but also against aging. It is a stimulator of recombinant SIRT1 and also a PI3K inhibitor with IC50 of 2.4±0.6 μM, 3.0±0.0 μM and 5.4±0.3 μM for PI3K γ, PI3K δ and PI3K β, respectively. It also attenuated the function VEGFR, androgen receptor and the expressions of NF-κB, IL Receptor, FAK, ERK,Nrf2.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Res Int.2019, 123:125-134
Toxins (Basel).2021, 13(9):593.
Molecules.2022, 27(22):7887.
Am J Chin Med.2016, 44(6):1255-1271
Pharmacognosy Journal.2022, 14,4,327-337.
Comput Biol Chem.2019, 83:107096
Industrial Crops and Products2018, 353-362
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117410.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 978:176800.
GENENCELL2023, 25:4356740
Related and Featured Products
Limocitrin
Catalog No: CFN92385
CAS No: 489-33-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Spinacetin
Catalog No: CFN95194
CAS No: 3153-83-1
Price: $318/5mg
Jaceidin
Catalog No: CFN99032
CAS No: 10173-01-0
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Jaceidin triacetate
Catalog No: CFN99482
CAS No: 14397-69-4
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Chrysosplenetin
Catalog No: CFN97026
CAS No: 603-56-5
Price: $138/20mg
4',5,7-Trihydroxy 3,3',6,8-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN70415
CAS No: 58130-91-9
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
3',4',7,8-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN70432
CAS No: 65548-55-2
Price: $100/20mg
4'-hydroxy-6,7,8,3'-tetramethoxyflavonol
Catalog No: CFN91846
CAS No: 1879030-01-9
Price: $318/5mg
5,7,3',4'-Tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN91116
CAS No: 855-97-0
Price: $30/20mg
Retusin
Catalog No: CFN89520
CAS No: 1245-15-4
Price: $158/10mg
Ophthalmic Res. 2015;53(3):109-16.
Quercetin Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Choroidal and Retinal Angiogenesis in vitro.[Pubmed:
25676100]
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of Quercetin on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced choroidal and retinal angiogenesis in vitro using a rhesus macaque choroid-retinal endothelial (RF/6A) cell line.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
RF/6A cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. Then the cells were treated with different concentrations (from 0 to 100 μM) of Quercetin and 100 ng/ml VEGF. The cell proliferation was assessed using cholecystokinin octapeptide dye. The cell migration was investigated by a Transwell assay. The tube formation was measured on Matrigel. Furthermore, the impact of Quercetin's effects on VEGF-induced activation of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) downstream signal pathways was tested by Western blot analysis. Quercetin inhibits RF/6A cell proliferation in a dose-dependent fashion: 22.7, 31.5 and 36.7% inhibition on treatment with 10, 50 and 100 μM Quercetin, respectively. VEGF-induced migration and tube formation of RF/6A cells were also significantly inhibited by Quercetin in a dose-dependent manner. Quercetin inhibits VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 downstream signal pathways of RF/6A.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results show that Quercetin inhibits VEGF-induced cell proliferation, migration and tube formation of RF/6A. We suggest that Quercetin inhibits VEGF-induced choroidal and retinal angiogenesis in vitro. Collectively, the findings in the present study suggest that Quercetin inhibits VEGF-induced choroidal and retinal angiogenesis by targeting the VEGFR-2 pathway. This suggests that Quercetin is a choroidal and retinal angiogenesis inhibitor.
Pharmacogn Mag. 2015 Apr-Jun;11(42):404-9.
Quercetin induces human colon cancer cells apoptosis by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B Pathway.[Pubmed:
25829782]
Quercetin can inhibit the growth of cancer cells with the ability to act as chemopreventers. Its cancer-preventive effect has been attributed to various mechanisms, including the induction of cell-cycle arrest and/or apoptosis as well as the antioxidant functions. Nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) is a signaling pathway that controls transcriptional activation of genes important for tight regulation of many cellular processes and is aberrantly expressed in many types of cancer. Inhibitors of NF-κB pathway have shown potential anti-tumor activities. However, it is not fully elucidated in colon cancer.
CONCLUSIONS:
In this study, we demonstrate that Quercetin induces apoptosis in human colon cancer CACO-2 and SW-620 cells through inhibiting NF-κB pathway, as well as down-regulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 and up-regulation of Bax, thus providing basis for clinical application of Quercetin in colon cancer cases.
Carcinogenesis. 2001 Mar;22(3):409-14.
Quercetin inhibits the expression and function of the androgen receptor in LNCaP prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:
11238180]
The androgen receptor (AR) is involved in the development and progression of prostate cancer. In order to find new compounds that may present novel mechanisms to attenuate the function of AR, we investigated the effect of a natural flavonoid chemical, Quercetin, on androgen action in an androgen-responsive LNCaP prostate cancer cell line.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Western blot analysis showed that AR protein expression was inhibited by Quercetin in a dose-dependent manner. To demonstrate that the repression effects on AR expression can actually reduce its function, we found that Quercetin inhibited the secretion of the prostate-specific, androgen-regulated tumor markers, PSA and hK2. The mRNA levels of androgen-regulated genes such as PSA, NKX3.1 as well as ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) were down-regulated by Quercetin. Transient transfections further showed that Quercetin inhibited AR-mediated PSA expression at the transcription level. Finally, it was demonstrated that Quercetin could repress the expression of the AR gene at the transcription level.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our result suggests that Quercetin can attenuate the function of AR by repressing its expression and has the potential to become a chemopreventive and/or chemotherapeutic agent for prostate cancer.
Ophthalmic Res. 2015;53(3):109-16.
Quercetin Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Choroidal and Retinal Angiogenesis in vitro.[Pubmed:
25676100]
Cell lines:RF/6A cells
Concentrations: 10, 50 and 100 μM /mL
Incubation Time: ---
Method:
RF/6A cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. Then the cells were treated with different concentrations (from 0 to 100 μM) of Quercetin and 100 ng/ml VEGF. The cell proliferation was assessed using cholecystokinin octapeptide dye. The cell migration was investigated by a Transwell assay. The tube formation was measured on Matrigel. Furthermore, the impact of Quercetin's effects on VEGF-induced activation of VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) downstream signal pathways was tested by Western blot analysis.
J Dig Dis. 2015 Apr 10.
Protective effects of quercetin against chronic mixed reflux esophagitis in rats (Rattus norvegicus) by inhibiting the NF-kappaB p65 and interleukin-8 signaling pathway.[Pubmed:
25858763]
To observe the effects of Quercetin on chronic mixed reflux esophagitis (RE) in rats by inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB p65 (NF-κBp65) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) signaling pathways.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Forty-eight healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into six groups, with 8 rats in each group: the normal intact group, the sham operation group, the RE control group, the RE group treated with omeprazole or 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg Quercetin. The animals were sacrificed after 6 weeks of different interventions. The pathological characteristics of esophageal mucosa were observed according to the diagnostic criteria and the expressions of NF-κBp65 and IL-8 were assessed by immunohistochemistry and real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Compared with the RE control group, esophageal mucosal injury was improved and the expressions of NF-κBp65 and IL-8 were significantly decreased in the RE group treated with omeprazole or Quercetin (P < 0.05). Compared with the omeprazole group, the gross and microscopic scores of esophageal mucosal injury and the expressions of NF-κBp65 and IL-8 in the 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg Quercetin groups were not increased (P > 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between the RE groups treated with 100 mg/kg Quercetin and 200 mg/kg Quercetin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Quercetin can prevent esophageal mucosal injury in RE rats by suppressing the NF-κBp65 and IL- 8 signaling pathways.
Neuroreport. 2015 May 6;26(7):387-93.
Quercetin inhibits the migration and proliferation of astrocytes in wound healing.[Pubmed:
25793633]
A previous study showed that Quercetin inhibits astrogliosis in a scratch-wound model, but did not identify the underlying mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we show that Quercetin exerts no effect on apoptosis or the viability of astrocytes, but significantly inhibits their proliferation, arresting them in the G1 phase and decreasing the percentage of cells in the S and G2 phase. In addition, we found that Quercetin significantly decreased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and FAK, a downstream ERK signaling protein. Inhibition of this pathway with U0126, an inhibitor of MAP kinase, retarded wound closure, whereas sustained p-ERK1/2 activation, induced by vanadate, restored astrocyte migration.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings thus indicate that Quercetin inhibits healing in the scratch-wound model of primary astrocytes in two ways: blockade of the G1 to S phase cell cycle transition and inhibition of the ERK/FAK signaling pathway, which may contribute toward decreasing astroglial scar formation in vivo.
J Biomed Res. 2015 Apr;29(2):139-44.
Quercetin attenuates the development of 7, 12-dimethyl benz (a) anthracene (DMBA) and croton oil-induced skin cancer in mice.[Pubmed:
25859269]
Animal Models: Swiss albino mouse
Formulation: ---
Dosages: 200 mg/kg, 400 mg/kg body weight daily for 16 weeks
Administration: p.o.