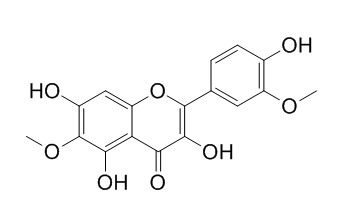
Spinacetin
Spinacetin has anti-inflammatory effects, it weakly inhibited nitric oxide production and reduced prostaglandin E2 levels to different extents. It shows the activities in preventing inflammatory processes, which might be at least partially attributed to the abolishment of Syk-dependent activation of IgE/Ag-mediated mast cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Separation Science Plus2022, sscp.202200048.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).2023, 14:1138676.
Molecules2022, 27(3),1140.
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(11): 1802.
Molecules.2021, 26(9):2791.
University of Burgos2024, ssrn.4795441.
Food Sci Biotechnol.2024, 33(15):3629-3637.
Int Immunopharmacol.2023, 123:110572.
Food Res Int.2018, 106:909-919
Journal of Ginseng Research2021, 25 November
Related and Featured Products
Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 30;9:824.
Spinacetin Suppresses the Mast Cell Activation and Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis in Mouse Model.[Pubmed:
30104977 ]
We previously reported the anti-inflammatory and anti-asthmatic activities of the extract of the Inula japonica Thunb. Aiming for discovery of a novel anti-inflammatory compound, we isolated Spinacetin from the extract and investigated its in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory effect and the related mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Effect of Spinacetin on the Syk signaling pathway was studied in bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs), and that on the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) was investigated in Rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-2H3 cells and human mast cell line (HMC-1). The in vivo anti-inflammatory activity was assessed with passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) reaction assay. Spinacetin significantly inhibited the release of histamine, and production of inflammatory mediators such as leukotriene C4 (LTC4) and interlukin-6 (IL-6) in IgE/Ag stimulated BMMCs. Analysis of the signaling pathways demonstrated that Spinacetin inhibited activation of Syk, linker of activated T cells (LAT), phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ), cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), MAPKs, Akt/NF-κB, and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization but with no effect on Fyn and Lyn. On the other hand, Spinacetin suppressed IgE/Ag-induced activation of RBL-2H3 cells with inhibition against phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated-protein kinase (ERK), c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), p38 MAPKs, PLCγ, translocation of cPLA2, and Akt/IκBα/NF-κB signal. However, Spinacetin had no effect on PMA and A23187-induced activation of HMC-1. Furthermore, oral administration of Spinacetin dose-dependently attenuated IgE/Ag-mediated PCA reaction in mouse model.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, Spinacetin showed the activities in preventing inflammatory processes, which might be at least partially attributed to the abolishment of Syk-dependent activation of IgE/Ag-mediated mast cells.
Nat Prod Res. 2013;27(11):1007-11.
Spasmolytic activity of Artemisia copa aqueous extract and isolated compounds.[Pubmed:
22577954 ]
Artemisia copa Phil. (Compositae) is used in popular medicine as a digestive and for gastric pains.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The effects of A. copa aqueous extract and its isolated compounds were evaluated on isolated rat jejunum. The extract inhibited non-competitively the cumulative concentration-response curves induced by acetylcholine and CaCl2. The tonic jejunum contractions induced by 80 mM KCl were inhibited by A. copa. Relaxant effects of A. copa on the tonic contraction induced by 25 mM KCl, [EC50: 0.94 mg mL(-1) (0.64-1.39)], was not inhibited by glibenclamide, TEA, l-NAME or methylene blue. Chrysoeriol, Spinacetin and luteolin (30 µg mL(-1)), produced an antagonism on the CaCl2 concentration-response curve, showing an inhibition of the maximum contractions (70.0% ± 5.0%, 49.1% ± 4.5% and 77.0% ± 3.5% of E max, respectively), whereas tricin did not inhibit when the same concentration was used.
CONCLUSIONS:
A. copa exerts spasmolytic activity by blocking calcium channels and three isolated compounds could be, at least partly, responsible for the effect.
Planta Med. 2006 Jan;72(1):72-4.
Flavonoids from Artemisia copa with anti-inflammatory activity.[Pubmed:
16450301 ]
Bioactivity-guided fractionation of the dichloromethane and ethanol extracts from the aerial parts of Artemisia copa led to the isolation of the flavonoids Spinacetin, jaceosidin, axillarin, penduletin, tricin and chrysoeriol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
These compounds were studied for possible inhibitory activity on the generation of inflammatory mediators in a cell line of mouse macrophages (RAW 264.7) stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Spinacetin and jaceosidin weakly inhibited nitric oxide production whereas all flavonoids reduced prostaglandin E2 levels to different extents. The most active flavonoid was jaceosidin that inhibited cyclooxygenase-2 activity in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 2.8 microM. In addition, the other flavonoids partially inhibited synovial phospholipase A2 activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These mechanisms may provide a basis for explaining the anti-inflammatory activity of this plant.