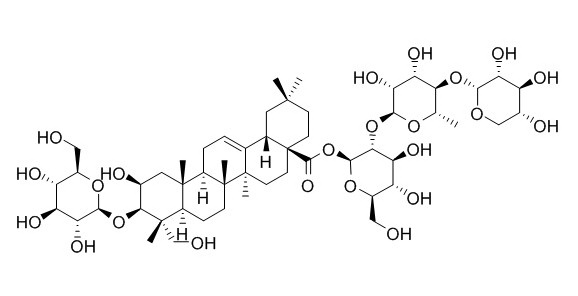
Polygalasaponin F
Polygalasaponin F possesses anxiolytic and sedative-hypnotic activities, and has cognition improving and cerebral protective effects. Polygalasaponin F can inhibit the release of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and NO induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and reduce the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthases. Polygalasaponin F can induce long-term potentiation in hippocampal dentate gyrus in anesthetized rats via NMDAR activation mediated by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase II, extracellular signal-regulated kinase and cAMP response element-binding protein signaling pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 176:116765.
Environ Toxicol.2024, tox.24246
J. Mater. Life Sci.2024, 3:2:78-87
Molecules.2022, 27(7):2360.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2018, 49(4):349-361
Cosmetics2021, 8(3),91.
Natural Product Communications2020, doi: 10.1177.
Journal of Functional Foods2023, 104:105542
Horticulturae2020, 6(4),76.
J Ginseng Res.2020, 44(4):611-618.
Related and Featured Products
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014;16(8):865-75.
Polygalasaponin F inhibits secretion of inflammatory cytokines via NF-κB pathway regulation.[Pubmed:
25082394]
To study the anti-neuroinflammatory mechanisms of Polygalasaponin F (PS-F), ELISA method was used to detect the secretion of inflammatory cytokines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Western blot was used to detect the protein expression and phosphorylation levels. Immunofluorescence assay was used to observe the NF-κB nuclear translocation. PS-F could inhibit the release of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and NO induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and reduce the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthases (iNOS). As for MAPK-signaling pathway, PS-F could only inhibit the phosphorylation levels of p38 MAPK, but did not significantly affect the phosphorylation levels of JNK and ERK1/2 protein kinases. PS-F could inhibit NF-κB nuclear translocation in a dose-dependent manner. The results of Western blot assay were consistent with immunofluorescence assays. Meanwhile, p38-specific inhibitor SB203580 (20 μM) and p65-specific inhibitor PDTC (100 μM) were, respectively, administered as a positive control. In addition, PS-F could significantly inhibit the cytotoxicity of conditioned medium prepared by LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia (LPS conditioned media) to neuronal PC12 cells and improve cell viability.
CONCLUSIONS:
PS-F inhibits the secretions of neuroinflammatory cytokines by the regulation of NF-κB-signaling pathway.
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014 Jan;16(1):59-69.
Polygalasaponin F against rotenone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via mitochondria protection pathway.Polygalasaponin F against rotenone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via mitochondria protection pathway.[Pubmed:
24382325]
To investigate the protective effect and the underlying mechanism of Polygalasaponin F (PS-F) against rotenone-induced PC12 cells, the cell viability was evaluated using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide assay.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The cell apoptosis rate was analyzed using flow cytometry. The reactive oxygen species was examined using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate, and the adenosine triphosphate depletion was examined using a luciferase-coupled quantification assay. JC-1 staining was used to detect the mitochondrial membrane potential. Western blotting analysis was used to determine cytochrome c, p53, Bax, Bcl-2, and caspase-3. Treatment of PC12 cells with rotenone (1-10 μmol/l) significantly reduced the cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner. Treatment with Polygalasaponin F (0.1, 1, and 10 μmol/l) increased the viability of rotenone-induced PC12 cells, decreased rotenone-induced apoptosis, restored rotenone-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and suppressed rotenone-induced protein expression. Polygalasaponin F showed a dose-dependent manner in all the treatments. Polygalasaponin F protects PC12 cells against rotenone-induced apoptosis via ameliorating the mitochondrial dysfunction.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, Polygalasaponin F may be a potential bioactive compound for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Apr;33(4):431-7.
Polygalasaponin F induces long-term potentiation in adult rat hippocampus via NMDA receptor activation.[Pubmed:
22286914]
To investigate the effect and underlying mechanisms of Polygalasaponin F (PGSF), a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Polygala japonica, on long-term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampus dentate gyrus (DG) of anesthetized rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Population spike (PS) of hippocampal DG was recorded in anesthetized male Wistar rats. Polygalasaponin F, the NMDAR inhibitor MK801 and the CaMKII inhibitor KN93 were intracerebroventricularly administered. Western blotting analysis was used to examine the phosphorylation expressions of NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B), Ca(2 )/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). Intracerebroventricular administration of Polygalasaponin F (1 and 10 μmol/L) produced long-lasting increase of PS amplitude in hippocampal DG in a dose-dependent manner. Pre-injection of MK801 (100 μmol/L) or KN93 (100 μmol/L) completely blocked Polygalasaponin F-induced LTP. Furthermore, the phosphorylation of NR2B, CaMKII, ERK, and CREB in hippocampus was significantly increased 5-60 min after LTP induction. The up-regulation of p-CaMKII expression could be completely abolished by pre-injection of MK801. The up-regulation of p-ERK and p-CREB expressions could be partially blocked by pre-injection of KN93.
CONCLUSIONS:
Polygalasaponin F could induce LTP in hippocampal DG in anesthetized rats via NMDAR activation mediated by CaMKII, ERK and CREB signaling pathway.
Biomed Chromatogr. 2015 Sep;29(9):1388-92.
Quantification of polygalasaponin F in rat plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its pharmacokinetics application.[Pubmed:
25645627]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A rapid and highly selective liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric (LC-MS/MS) method for determination of Polygalasaponin F (PF) in rat plasma was developed and validated. The chromatographic separation was achieved on a reverse-phase Zorbax SB-C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm), using 2 mm ammonium acetate (pH adjusted to 6.0 with acetic acid) and acetonitrile (25:75, v/v) as a mobile phase at 30 °C. MS/MS detection was performed using an electrospray ionization operating in positive ion multiple reaction monitoring mode by monitoring the ion transitions from m/z 1091.5 → 471.2 (PF) and m/z 700.4 → 235.4 (internal standard), respectively. The calibration curve showed a good linearity in the concentration range 0.0544-13.6 µg/mL, with a limit of quantification of 0.0544 µg/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:
The intra- and inter-day precisions were <9.7% in rat plasma. The method was validated as per US Food and Drug Administration guidelines and successfully applied to pharmacokinetic study of PF in rats.
7-Neohesperidosides
Catalog No: CFN95018
CAS No: 28383-41-7
Price: $288/5mg
5,7,2',4'-Tetrahydroxy-8,3'-di(gamma,gamma-dimethylallyl)-isoflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95084
CAS No: 141846-47-1
Price: $413/5mg
Torosachrysone 8-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No: CFN95131
CAS No: 94356-13-5
Price: $318/5mg
7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-phenylhept-4-en-3-one (DPHB)
Catalog No: CFN95139
CAS No: 79559-60-7
Price: $268/20mg
Ampelopsin G
Catalog No: CFN95148
CAS No: 151487-09-1
Price: $318/5mg
Apigenin 4'-O-(2'',6''-di-O-E-p-coumaroyl)glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95276
CAS No: 71781-79-8
Price: $318/10mg
2,11,12-Trihydroxy-7,20-epoxy-8,11,13-abietatriene
Catalog No: CFN95428
CAS No: 1608462-12-9
Price: $318/10mg
Maingayone
Catalog No: CFN95479
CAS No: 271585-66-1
Price: $318/10mg
Sophoraflavone A
Catalog No: CFN95510
CAS No: 105594-08-9
Price: $318/10mg
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran (ABF)
Catalog No: CFN95511
CAS No: 67121-26-0
Price: $318/5mg