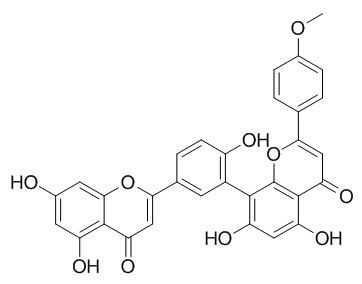
Podocarpusflavone A
Podocarpusflavone A is the strongest noncytotoxic non-nucleotide molecule exhibiting a specific inhibitory activity against the RNA polymerase domain of DV-NS5 and thus is promising for chemotherapy development against dengue fever. Podocarpusflavone A also shows antimalarial activity in vitro against the chloroquine-sensitive F32 and chloroquine-resistant FcM29 strains of Plasmodium falciparum.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 950:175772.
Biomolecules.2024, 14(4):451.
Arch Biochem Biophys.2020, 687:108384.
Korean Journal of Plant Resources2021, 34(1):52-58.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(13):7115.
Res Rep Urol.2022, 14:313-326.
Korean J. Crop Sci.2018, 63(2):131-139
Mol Med Rep.2022, 26(4):299.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.2024, 03148-x.
Food Chem.2024, 458:140201.
Related and Featured Products
Planta Med. 2012 May;78(7):672-7.
Biflavonoids of Dacrydium balansae with potent inhibitory activity on dengue 2 NS5 polymerase.[Pubmed:
22411725]
In order to find new molecules for antiviral drug design, we screened 102 ethyl acetate extracts from New-Caledonian flora for antiviral activity against the dengue 2 virus RNA-dependant RNA polymerase (DV-NS5 RdRp).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The leaf extract of Dacrydium balansae, which strongly inhibited the DV-NS5, was submitted to bioguided fractionation. Four biflavonoids ( 1- 4), three sterols ( 5- 7), and two stilbene derivatives ( 8- 9) were identified and evaluated for their antiviral potential on the DV-NS5 RdRp. Biflavonoids appeared to be potent inhibitors of DV-NS5 RdRp with IC (50)s between 0.26 and 3.12 µM. Inhibitory activity evaluations against the RNA polymerase from other Flaviviridae viruses allowed us to conclude that these compounds are specific inhibitors of the DV RNA polymerase. The strongest inhibitions were observed with hinokiflavone ( 4), but Podocarpusflavone A ( 2) is the strongest noncytotoxic inhibitor of the DV-NS5 and it also displayed polymerase inhibitory activity in a DV replicon.
CONCLUSIONS:
A preliminary structure-activity relationship study (SARs) revealed the necessity of the biflavonoid skeleton, the influence of number and position of methoxylations, and the importance of a free rotation of the linkage between the two apigenin monomers of the biflavonoids. To the best of our knowledge, Podocarpusflavone A ( 2) is the strongest noncytotoxic non-nucleotide molecule exhibiting a specific inhibitory activity against the RNA polymerase domain of DV-NS5 and thus is promising for chemotherapy development against dengue fever.
Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2007 Jan;101(1):23-30.
Antimalarial and vasorelaxant constituents of the leaves of Allanblackia monticola (Guttiferae).[Pubmed:
17244407 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Phytochemical investigation of the leaves of Allanblackia monticola led to the isolation and characterisation of five prenylated xanthones [1,6-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxy-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)xanthone 1, alpha-mangostin 2, tovophyllin A 3, allanxanthone C 4 and 1,7-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)xanthone 5], two biflavonoid derivatives (amentoflavone 6 and Podocarpusflavone A 7) and one pentacyclic triterpene (friedelan-3-one 8). The structures of these compounds were established on the basis of homo- and hetero-nuclear, one- and two-dimensional, nuclear magnetic resonance. Compounds 2-8 and a crude methanolic extract of A. monticola leaves were each tested for antimalarial activity in vitro, using the chloroquine-sensitive F32 and chloroquine-resistant FcM29 strains of Plasmodium falciparum; the median inhibitory concentrations (IC(50)) recorded varied from 0.7 to 83.5 mug/ml. The cytotoxicities of the compounds and crude extract, against cultures of human melanoma cells (A375), were then investigated, and cytotoxicity/antimalarial IC(50) ratios of 0.6-16.75 were recorded.
CONCLUSIONS:
In tests involving aortic rings from guinea pigs, a crude extract of the leaves of A. monticola was found to induce concentration-dependent vasorelaxation, causing up to 82% and 42% inhibition of noradrenaline- and KCl-induced contractions, respectively. The corresponding values for compounds 2 and 6 when tested against noradrenaline-induced contractions were approximately 18% and 35%, respectively.