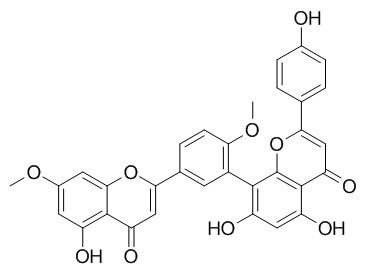
Ginkgetin
Ginkgetin is a good STAT3 inhibitor , which has anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-influenza virus and anti-fungal activities. Ginkgetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells via activation of caspase 3 and inhibition of survival genes as a potent chemotherapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology 2022, 34,53-62
Molecules.2023, 28(13):4907.
Auburn University2015, 1-58
Int. J. Mol. Sci.2022, 23(8), 4130.
Fitoterapia.2015, 100:179-86
Food Bioscience2023, 59:103903
Int J Mol Sci.2015, 16(1):1232-51
Mol Pharmacol.2021, 99(2):163-174.
BMC Complement Med Ther.2023, 23(1):264.
Analytical methods2019, 11(6)
Related and Featured Products
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 1;23(9):2692-5.
Ginkgetin induces apoptosis via activation of caspase and inhibition of survival genes in PC-3 prostate cancer cells.[Pubmed:
23523142]
Ginkgetin is a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. Though it was known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, anti-fungal activity, osteoblast differentiation stimulating activity and neuro-protective effects, the underlying antitumor mechanism of Ginkgetin still remains unclear. Thus, in the present study, anti-cancer mechanism of Ginkgetin was elucidated in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ginkgetin suppressed the viability of PC-3 cells in a concentration-dependent manner and also significantly increased the sub-G1 DNA contents of cell cycle in PC-3 cells. Ginkgetin activated caspase-3 and attenuated the expression of survival genes such as Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin and Cyclin D1 at protein and mRNA levels. Consistently, pan-caspase inhibitor Z-DEVD-fmk blocked sub G1 accumulation and cleavages of PRAP and caspase 3 induced by Ginkgetin in PC-3 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Overall, these findings suggest that Ginkgetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 cells via activation of caspase 3 and inhibition of survival genes as a potent chemotherapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment.
Free Radic Res. 2015 May 12:1-39.
Neuroprotective effects of ginkgetin against neuro-injury in Parkinson's disease model induced by MPTP via chelating iron.[Pubmed:
25968939]
Disruption of neuronal iron homeostasis and oxidative stress are closely related to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD). Ginkgetin, a natural biflavonoid isolated from leaves of Ginkgo biloba L, has many known effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-influenza virus, and anti-fungal activities, but its underlying mechanism of the neuroprotective effects in PD remains unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study utilized PD models induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)) and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) to explore the neuroprotective ability of Ginkgetin in vivo and in vitro. Our results showed that Ginkgetin could provide significant protection from MPP(+)-induced cell damage in vitro by decreasing the levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species and maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential. Meanwhile, Ginkgetin dramatically inhibited cell apoptosis induced by MPP+ through the caspase-3 and Bcl2/Bax pathway. Moreover, Ginkgetin significantly improved sensorimotor coordination in a mouse PD model induced by MPTP by dramatically inhibiting the decrease of tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the substantia nigra and superoxide dismutase activity in the striatum. Interestingly, Ginkgetin could strongly chelate ferrous ion and thereby inhibit the increase of the intracellular labile iron pool through downregulating L-ferritin and upregulating transferrin receptor 1.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the neuroprotective mechanism of Ginkgetin against neurological injury induced by MPTP occurs via regulating iron homeostasis. Therefore, Ginkgetin may provide neuroprotective therapy for PD and iron metabolism disorder related diseases.
Cancer Sci. 2015 Apr;106(4):413-20.
Ginkgetin inhibits the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer cells through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activity.[Pubmed:
25611086]
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is constitutively activated in human cancers. Therefore, STAT3 is a therapeutic target of cancer drug discovery. We previously reported that natural products inhibited constitutively activated STAT3 in human prostate tumor cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We used a dual-luciferase assay to screen 200 natural products isolated from herbal medicines and we identified Ginkgetin obtained from the leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. as a STAT3 inhibitor. Ginkgetin inhibited both inducible and constitutively activated STAT3 and blocked the nuclear translocation of p-STAT3 in DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Furthermore, Ginkgetin selectively inhibited the growth of prostate tumor cells stimulated with activated STAT3. Ginkgetin induced STAT3 dephosphorylation at Try705 and inhibited its localization to the nucleus, leading to the inhibition of expression of STAT3 target genes such as cell survival-related genes (cyclin D1 and survivin) and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL). Therefore, Ginkgetin inhibited the growth of STAT3-activated tumor cells. We also found that Ginkgetin inhibited tumor growth in xenografted nude mice and downregulated p-STAT3(Tyr705) and survivin in tumor tissues.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report that Ginkgetin exerts antitumor activity by inhibiting STAT3. Therefore, Ginkgetin is a good STAT3 inhibitor and may be a useful lead molecule for development of a therapeutic STAT3 inhibitor.
Planta Med. 2002 Apr;68(4):316-21.
Effects of Ginkgetin from Ginkgo biloba Leaves on cyclooxygenases and in vivo skin inflammation.[Pubmed:
11988854]
Ginkgetin, a biflavone from Ginkgo biloba leaves, was previously reported to be a phospholipase A2 inhibitor and this compound showed the potent antiarthritic activity in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis as well as analgesic activity.
This investigation was carried out to find effects on cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and -2 including an in vivo effect.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ginkgetin (1 - 10 microM) and the biflavonoid mixture (10 - 50 microg/ml), mainly a 1 : 1 mixture of Ginkgetin and isoGinkgetin, from G. biloba leaves, inhibited production of prostaglandin E2 from lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. This inhibition was mediated, at least in part, by down-regulation of COX-2 expression, but not by direct inhibition of COX-1 or COX-2 activity. Down-regulation of COX-2 by Ginkgetin was also proved in the dorsal skin of ICR mouse treated by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA). At total doses of 1,000 microg/site on the dorsal skin (15 mm x 15 mm), Ginkgetin inhibited prostaglandin E2 production by 65.6 % along with a marked suppression of COX-2 induction. In addition, Ginkgetin and the biflavonoid mixture (100 - 1,000 microg/ear) dose-dependently inhibited skin inflammation of croton oil induced ear edema in mice by topical application.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study suggests that Ginkgetin from G. biloba leaves down-regulates COX-2 induction in vivo and this down-regulating potential is associated with an anti-inflammatory activity against skin inflammatory responses.