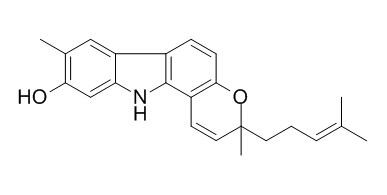
Isomahanine
Isomahanine and mahanine show antibacterial activity towards Flavobacterium columnare and Streptococcus iniae which caused columnaris disease and streptococcosis respectively; isomahanine has the strongest activity against F. columnare (isolate ALM-00-173) and S. iniae (isolate LA94-426) based on 24-h 50% inhibition concentration (IC50) and minimum inhibition concentration (MIC). Isomahanine is also a potent inhibitor of sEH , with IC50 values of 22.565±651.7.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Science and Preservation2024, 31(3):486-498.
Heliyon.2023, e12684.
Korean J. Crop Sci.2018, 63(2):131-139
Molecules.2023, 28(17):6315.
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2021, 20(6):1165-1170.
Biomed Pharmacother.2023, 163:114785.
Chemistry of Plant Raw Materials2019, 4:135-147
Microchemical Journal2024: 196:109676.
Molecules.2019, 24(21):E3834
Food Chem. 2020, 320:126530
Related and Featured Products
J Agric Food Chem. 2003 Oct 22;51(22):6461-7.
Comparison of antioxidative properties of carbazole alkaloids from Murraya koenigii leaves.[Pubmed:
14558763]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A new dimeric carbazole alkaloid, 8,10'-[3,3',11,11'-tetrahydro-9,9'-dihydroxy-3,3',5,8'-tetramethyl-3,3'-bis(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)]bipyrano[3,2-a]carbazole (12), was isolated from the CH(2)Cl(2) extract of Murraya koenigii together with six known carbazole alkaloids, koenimbine (6), O-methylmurrayamine A (7), O-methylmahanine (8), Isomahanine (9), bismahanine (10), and bispyrayafoline (11). Their structures were determined on the basis of (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic and mass spectrometric (MS) data. The antioxidative properties of 12 carbazole alkaloids isolated from leaves of M. koenigii were evaluated on the basis of the oil stability index together with their radical scavenging ability against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. On the basis of the lag time to reach a steady state, the 12 carbazoles were classified into three groups.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is suggested that an aryl hydroxyl substituent on the carbazole rings plays a role in stabilizing the thermal oxidation and rate of reaction against DPPH radical.
J. Agr. Chem. Env., 2013, 02(4):90-100.
Antibacterial compounds from Rutaceae with activities against Flavobacterium columnare and Streptococcus iniae[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the ethyl acetate extract of Murraya koenegii (Rutaceae) leaves, Isomahanine (1) and mahanine (2) were isolated that showed antibacterial activity towards Flavobacterium columnare and Streptococcus iniae which caused columnaris disease and streptococcosis respectively. Isomahanine was found to have the strongest activity against F. columnare (isolate ALM-00-173) and S. iniae (isolate LA94-426) based on 24-h 50% inhibition concentration (IC50) and minimum inhibition concentration (MIC). Although compound (7), a nicotinamide isolated from Amyris texana had the lowest MIC (2.8 ± 0 mg/L) of any of the test compounds against F. columnare, the 24-h IC50 of 14.8 ± 0.6 mg/L was higher than that of Isomahanine and subsequently the 24-h IC50 RDC values for (7) were almost a magnitude of order higher than those obtained for Isomahanine.
CONCLUSIONS:
Isomahanine also had the strongest activity against S. iniae, with a 24-h IC50 of 1.3 ± 0.1 mg/L and MIC of 3.5 ± 0 mg/L, respectively.
J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Ch., 2015:1-5.
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase activity by compounds isolated from the aerial parts of Glycosmis stenocarpa.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of this study is to search for soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors from natural plants, bioassay-guided fractionation of lipophilic n-hexane and chloroform layers of an extract of the aerial parts of Glycosmis stenocarpa led to the isolation of 12 compounds (1-12) including murrayafoline-A (1), Isomahanine (2), bisIsomahanine (3), saropeptate (4), (24 S)-ergost-4-en-3,6-dione (5), stigmasta-4-en-3,6-dion (6), stigmast-4-en-3-one (7), β-sitosterol (8), 24-methylpollinastanol (9), trans-phytol (10), neosarmentol III (11) and (+)-epiloliolide (12). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data. Among them, neosarmentol III (11) was isolated from nature for the first time. All the isolated compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory activity against sEH.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among isolated carbazole-type compounds, Isomahanine (2) and bisIsomahanine (3) were identified as a potent inhibitor of sEH, with IC50 values of 22.5 ± 1.7 and 7.7 ± 1.2 µM, respectively. Moreover, the inhibitory action of 2 and 3 represented mixed-type enzyme inhibition.