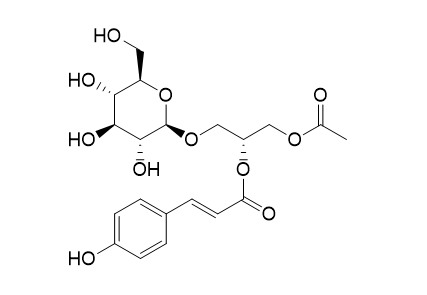
Regaloside I
Regaloside I, which has the structure of phenylpropanolglycerol glycoside, acts as an active compound that inhibits the upregulation of CAPZA1 and inhibits UVA-induced changes in HDF shape, which in turn inhibits collagen reduction.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Chem Res Toxicol.2023, 36(2):213-229.
J Health Sci Med Res.2023, 31584.
Biology (Basel).2020, 9(11):363.
J Ethnopharmacol.2025, 350:120002.
Journal of Apiculture2023.38(3):249-254.
J Pharmaceutical Research Int.2021, 33(41A):275-284.
Front Pharmacol.2020, 11:683.
Chem Biol Interact.2024, 394:110995.
JMSACL2023, 09.002
BMC Complement Altern Med.2017, 17(1):384
Related and Featured Products
Exp Dermatol . 2016 Aug;25 Suppl 3:45-51.
Morphological change of skin fibroblasts induced by UV Irradiation is involved in photoaging[Pubmed:
27539902]
Human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) are typically flattened or extensible shaped and play a critical role in the metabolism of extracellular matrix components. As the properties of fibroblasts in the dermis are considered to be influenced by their morphology, we investigated the morphological changes induced in fibroblasts by ultraviolet (UV) irradiation as well as the relationship between these changes and collagen metabolism. In this study, we showed that UVA exposure induced morphological changes and reduced collagen contents in HDFs. These morphological changes were accompanied a reduction in actin filaments and upregulation of the actin filament polymerization inhibitor, capping protein muscle Z-line ɑ1 (CAPZA1). External actin filament growth inhibitors also affected the shape of HDFs and reduced collagen levels. These results suggest that UVA exposure may inhibit the polymerization of actin filaments and induce morphological changes in skin fibroblasts. These morphological changes in fibroblasts may accelerate reductions in collagen synthesis. This mechanism may be one of the processes responsible for collagen reductions observed in photoaged skin. When natural materials that suppress these morphological changes in HDFs were evaluated, we found that an extract of Lilium 'Casa Blanca' (LCB) suppressed UVA-induced alterations in the shape of HDFs, which are typically followed by inhibition of collagen reduction. An analysis of the active compounds in LCB extract led to the identification of Regaloside I, which had a structure of phenylpropanoid glycerol glucoside, as the active compound inhibiting the upregulation of CAPZA1. Therefore, inhibition of UVA-induced morphological changes in HDFs is considered to be promising way for the suppression of collagen reduction in photoaging.
Exp Dermatol . 2016 Aug;25 Suppl 3:45-51.
Morphological change of skin fibroblasts induced by UV Irradiation is involved in photoaging[Pubmed:
27539902]
Human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) are typically flattened or extensible shaped and play a critical role in the metabolism of extracellular matrix components. As the properties of fibroblasts in the dermis are considered to be influenced by their morphology, we investigated the morphological changes induced in fibroblasts by ultraviolet (UV) irradiation as well as the relationship between these changes and collagen metabolism. In this study, we showed that UVA exposure induced morphological changes and reduced collagen contents in HDFs. These morphological changes were accompanied a reduction in actin filaments and upregulation of the actin filament polymerization inhibitor, capping protein muscle Z-line ɑ1 (CAPZA1). External actin filament growth inhibitors also affected the shape of HDFs and reduced collagen levels. These results suggest that UVA exposure may inhibit the polymerization of actin filaments and induce morphological changes in skin fibroblasts. These morphological changes in fibroblasts may accelerate reductions in collagen synthesis. This mechanism may be one of the processes responsible for collagen reductions observed in photoaged skin. When natural materials that suppress these morphological changes in HDFs were evaluated, we found that an extract of Lilium 'Casa Blanca' (LCB) suppressed UVA-induced alterations in the shape of HDFs, which are typically followed by inhibition of collagen reduction. An analysis of the active compounds in LCB extract led to the identification of Regaloside I, which had a structure of phenylpropanoid glycerol glucoside, as the active compound inhibiting the upregulation of CAPZA1. Therefore, inhibition of UVA-induced morphological changes in HDFs is considered to be promising way for the suppression of collagen reduction in photoaging.
Poricoic acid B
Catalog No: CFN95050
CAS No: 137551-39-4
Price: $318/20mg
Asiaticoside B
Catalog No: CFN95124
CAS No: 125265-68-1
Price: $158/20mg
(3R,5S,E)-1,7-Diphenylhept-1-ene-3,5-diol
Catalog No: CFN95227
CAS No: 232261-31-3
Price: $318/5mg
Cuscutamine
Catalog No: CFN95323
CAS No: 122170-93-8
Price: $318/5mg
Notoginsenoside L13
Catalog No: CFN95332
CAS No: 2485859-56-9
Price: $318/5mg
Quercetin 3,5-O-diglucoside
Catalog No: CFN95486
CAS No: 206257-35-4
Price: $368/10mg
12beta-Acetoxy-3,7,11,15,23-pentaoxo-lanost-8,20-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No: CFN95505
CAS No: 1309931-91-6
Price: $318/5mg
4-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No: CFN95508
CAS No: 53539-37-0
Price: $318/5mg
Ganolucidic acid E
Catalog No: CFN95536
CAS No: 114567-50-9
Price: $318/5mg
Methyl lucidenate A
Catalog No: CFN95583
CAS No: 105742-79-8
Price: $318/5mg