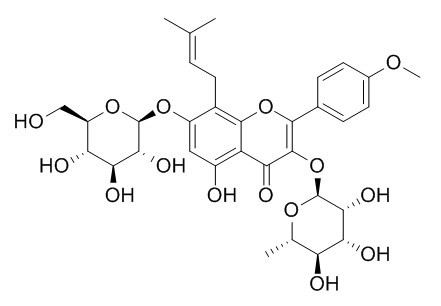
Icariin
Icariin inhibits PDE5 and PDE4 activities with IC50s of 432 nM and 73.50 μM, respectively. Icariin also is a PPARα activator. Icariin has been reported to have anti-hypoxic, phytoestrogenic, anti-osteoporotic, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-depressant-like activities. Icariin is effective in the attenuation of AHR and chronic airway inflammatory changes in OVA-induced murine asthma model, and this effect is associated with regulation of Th17/Treg responses. Icariin inhibited NF-κB signaling activation and the NLRP3-inflammasome/caspase-1/IL-1β axis.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Journal of Herbal Medicine2024, 48:100950
Food Chem.2017, 221:1135-1144
PLoS One.2021, 16(9):e0257243.
APMIS.2019, 127(10):688-695
Front Chem.2022, 10:1048467.
Front Aging Neurosci.2018, 10:269
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(6):466.
BioResources J.2020, 15(3).
Molecules.2018, 23(2)
Applied Biological Chemistry 2022, 65,5(2022).
Related and Featured Products
J Cell Biochem. 2015 Apr;116(4):580-8.
Icariin inhibits foam cell formation by down-regulating the expression of CD36 and up-regulating the expression of SR-BI.[Pubmed:
25389062 ]
Icariin is an important pharmacologically active flavonol diglycoside that can inhibit inflammation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effect of Icariin in the formation of foam cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, macrophages were cultured with LPS and oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) in the presence or absence of Icariin. RT-PCR and western blot were used to detect the levels of mRNA and protein expression of CD36, scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-BI) and the phosphorylation of p38MAPK. It was demonstrated that 4 μM or 20 μM Icariin treatment significantly inhibited the cholesterol ester (CE)/total cholesterol (TC) and oxLDL-mediated foam cell formation (P < 0.05). The binding of oxLDL to LPS-activated macrophages was also significantly hindered by Icariin (P < 0.05). Furthermore, Icariin down-regulated the expression of CD36 in LPS-activated macrophages in a dose-dependent manner and CD36 over-expression restored the inhibitory effect of Icariin on foam cell formation. The phosphorylation of p38MAPK was reduced by Icariin, indicating that Icariin reduced the expression of CD36 through the p38MAPK pathway. In addition, Icariin up-regulated SR-BI protein expression in a dose-dependent manner, and SR-BI gene silencing restored the inhibitory effect of Icariin on foam cell formation. These data demonstrate that Icariin inhibited foam cell formation by down-regulating the expression of CD36 and up-regulating the expression of SR-BI.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, our findings provide a new explanation as to why Icariin could inhibit atherosclerosis.
Immunobiology. 2015 Jun;220(6):789-97.
Regulation of Th17/Treg function contributes to the attenuation of chronic airway inflammation by icariin in ovalbumin-induced murine asthma model.[Pubmed:
25613226]
Icariin which is a flavonoid glucoside isolated from Epimedium brevicornu Maxim, has been reported to have anti-osteoporotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-depressant-like activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we observed the effect of Icariin on airway inflammation of ovalbumin (OVA)-induced murine asthma model and the associated regulatory mode on T-helper (Th)17 and regulatory T (Treg) cell function. Our data revealed that chronic OVA inhalation induced a dramatic increase in airway resistance (RL) and decrease in the lung dynamic compliance (Cdyn), and Icariin and DEX treatment caused significant attenuation of such airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR). BALF cell counts demonstrated that Icariin and DEX led to a prominent reduction in total leukocyte as well as lymphocyte, eosinophil, neutrophil, basophil and monocyte counts. Histological analysis results indicated that Icariin and DEX alleviated the inflammatory cells infiltrating into the peribronchial tissues and goblet cells hyperplasia and mucus hyper-production. Flow cytometry test demonstrated that Icariin or DEX administration resulted in a significant percentage reduction in CD4+RORγt+ T cells and elevation of CD4+Foxp3+ T cells in BALF. Furthermore, Icariin or DEX caused a significant reduction in IL-6, IL-17 and TGF-β level in BALF. Unfortunately, Icariin had no effect on IL-10 level in BALF. Western blot assay found that Icariin or DEX suppressed RORγt and promoted Foxp3 expression in the lung tissue. qPCR analysis revealed that Icariin and DEX resulted in a notable decrease in RORγt and increase in Foxp3 mRNA expression in isolated spleen CD4+ T cell.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, our results suggested that Icariin was effective in the attenuation of AHR and chronic airway inflammatory changes in OVA-induced murine asthma model, and this effect was associated with regulation of Th17/Treg responses, which indicated that Icariin may be used as a potential therapeutic method to treat asthma with Th17/Treg imbalance phenotype.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jan;30:157-162.
Icariin attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of inflammatory response mediated by NF-κB, PPARα and PPARγ in rats.[Pubmed:
26679678 ]
Icariin (ICA), an active flavonoid extracted from Chinese medicinal herb Epimedii, has been reported to exhibit many pharmacological effects including alleviating brain injury. However, little is known about the protection of ICA on ischemic stroke.
Hence, this study was designed to investigate the neuroprotective effect of ICA and explore its underlying mechanisms on ischemic stroke induced by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The animals were pretreated with ICA at doses of 10, 30mg/kg twice per day for 3 consecutive days followed by cerebral I/R injury induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 2h and reperfusion for 24h. Neurological function and infarct volume were observed at 24h after reperfusion, the protein expression levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), PPARα and PPARγ, inhibitory κB-α (IκB-α) degradation and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) p65 phosphorylation were detected by Western blot, respectively. It was found that pretreatment with ICA could decrease neurological deficit score, diminish the infarct volume, and reduce the protein levels of IL-1β and TGF-β1. Moreover, ICA suppressed IκB-α degradation and NF-κB activation induced by I/R. Furthermore, the present study also showed that ICA up-regulated PPARα and PPARγ protein levels.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that ICA has neuroprotective effect on ischemic stroke in rats through inhibition of inflammatory responses mediated by NF-κB and PPARα and PPARγ.
Cell Prolif. 2014 Dec;47(6):527-39.
Icariin attenuates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro.[Pubmed:
25355404]
OBJECTIVES:
Icariin, a prenylated flavonol glycoside isolated from traditional Chinese medicinal herb of the genus Epimedium, has been demonstrated to be a potential alternative therapy for osteoporosis, and its action mechanism so far has been mainly attributed to its phytoestrogenic property. As blood supply to bone is considerably reduced with ageing and by the menopause, we hypothesized that Icariin treatment would reduce bone loss by preventing ischaemia-induced hypoxic damages to bone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
To investigate effects of Icariin treatment on cultured rat calvarial osteoblasts exposed to hypoxic conditions (2% oxygen).
RESULTS:
Compared to normoxic control, cell viability decreased with time to 50% by 48 h in the hypoxic group, and Icariin attenuated the reduction, dose dependently, with 10(-6) and 10(-5) m Icariin, a prenylated flavonol glycoside isolated from traditional Chinese medicinal herb of the genus Epimedium, has been demonstrated to be a potential alternative therapy for osteoporosis, and its action mechanism so far has been mainly attributed to its phytoestrogenic property. As blood supply to bone is considerably reduced with ageing and by the menopause, we hypothesized that Icariin treatment would reduce bone loss by preventing ischaemia-induced hypoxic damages to bone.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate effects of Icariin treatment on cultured rat calvarial osteoblasts exposed to hypoxic conditions (2% oxygen).
Compared to normoxic control, cell viability decreased with time to 50% by 48 h in the hypoxic group, and Icariin attenuated the reduction, dose dependently, with 10(-6) and 10(-5) m concentrations showing significant protective effects. Icariin also inhibited increase of lactate dehydrogenase activity in culture media. Measurements on oxidative stress, cell cycling and cell survival indicated that Icariin protected osteoblasts by reducing production of reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde, increasing superoxide dismutase activity, arresting the cell cycle and inhibiting apoptosis. Icariin also preserved osteogenic differentiation potential of the hypoxic cells in a dose-dependent manner, compared to the hypoxia alone group, as revealed by increased levels of RUNX-2, OSX and BMP-2 gene expression, alkaline phosphatase activity, and formation of mineralized nodules.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results demonstrated that Icariin attenuated oxidative stress and apoptosis and preserved viability and osteogenic potential of osteoblasts exposed to hypoxia in vitro, and suggested that its anti-osteoporotic effect may be attributed to its anti-hypoxic activity and phytoestrogenic properties.
Neuroscience. 2015 May 21;294:193-205.
Icariin exerts an antidepressant effect in an unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression in rats and is associated with the regulation of hippocampal neuroinflammation.[Pubmed:
25791226]
Icariin (ICA), a flavonoid extracted from the traditional Chinese herb Herba Epimedii that can freely cross the blood-brain barrier, inhibits neuroinflammation and attenuates oxidative stress damage. Our previous studies demonstrated that Icariin exerts an antidepressant-like activity in a social defeat mouse model. However, it is unknown whether Icariin is beneficial for the treatment of depression via its modulation of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of Icariin on the depression-like behaviors in an unpredictable chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats exposed to CMS showed behavioral deficits in physical state, the sucrose preference test (SPT) and the forced swimming test (FST) and exhibited a significant increase in oxidative-nitrosative stress markers, inflammatory mediators, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway and increased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA expression in the hippocampus, which was reversed by chronic treatment with Icariin (20 or 40 mg/kg). Interestingly, Icariin negatively regulated the activation of the nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome/caspase-1/IL-1β axis in the hippocampus of CMS rats. These results confirm that Icariin exerts antidepressant-like effects, which may be mediated, at least in part, by enhanced antioxidant status and anti-inflammatory effects on the brain tissue via the inhibition of NF-κB signaling activation and the NLRP3-inflammasome/caspase-1/IL-1β axis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings provide new information to understand the antidepressant action of Icariin, which is targeted to the NLRP3-inflammasom in brain.