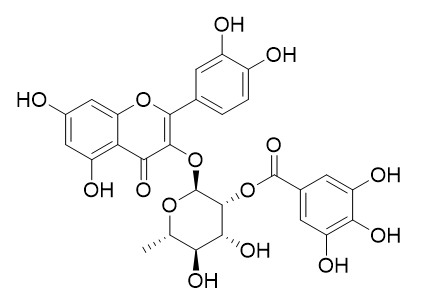
2''-O-Galloylquercitrin
2''-O-Galloylquercitrin is a natural product from Acer ginnala.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Nutrients.2023, 15(12):2644.
J Sep Sci.2020, 201901140
FEBS J.2022, 10.1111:febs.16676.
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 960:176121.
J Appl Biol Chem2021, 64(3):245-251.
Foods.2024, 13(23):3861.
Journal of Research in Pharmacy.2022, 26(6):p1752-1757.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(14):11496.
Molecules.2015, 20(11):20014-30
Molecules.2019, 24(6):E1177
Related and Featured Products
J Food Sci. 2010 Oct;75(8):H239-43.
Activity-guided isolation and identification of radical scavenging components in Gao-Cha tea.[Pubmed:
21535501 ]
Gao-Cha is a traditional Chinese health tea made from Acer ginnala.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We performed a components and radical scavenging activity analysis to identify any medicinal components in this tea. High performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC)-1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryhydrazyl (HPTLC-DPPH) assay showed that the methanolic extract contained strong radical scavengers. Quantitative analysis revealed that the IC(50) of the extract against 1 mM DPPH was 52.7 ± 0.6 μg/mL. Bioactive-guided isolations led to procurement of 3 radical scavengers with IC(50)s of 17.5 ± 2.1, 29.3 ± 2.5, and 21.6 ± 1.7 μg/mL, respectively. Analysis of the high resolution-electric spray ionization-mass spectrometer and (1)H, (13)C, distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer at 135°, heteronuclear quantum coherence, correlating spectroscopy coupling, and heteronuclear multiple bond coherence (HMBC) data revealed that the compounds were methyl 3, 4, 5-trihydroxybenzoate (1), quercetin-3-O-α-rhamnopyranoside (2), and 2,6-bis (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)-aceritol (3).
CONCLUSIONS:
Bioactive combined components analysis revealed that, apart from compounds 1, 2, and 3, the tea possibly contained radical scavengers: ginnalin A (4) and B (5), 2''-O-Galloylquercitrin (6) and 3″-O-Galloyl-quercitrin (7). Compounds 2, 6, and 7 were isolated from Acer ginnala for the first time. The positions of the 2 galloyl moieties in compound 3 were unambiguously established by the HMBC spectrum for the first time.