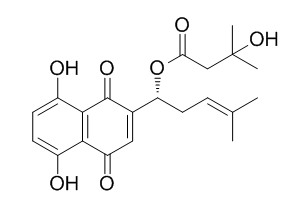
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin is an ATP non-competitive inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases such as v-Src and EGFR, and has been shown to induce apoptosis in several human tumor cell lines.
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin has anti-adipogenic, antiinflammatory and antitumor effects, it activated AMPK, which was followed by the downregulation of mature SREBP‑1c and fat-forming enzymes, leading to the inhibition of adipogenesis. Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin can significantly decrease viability of HCT116 cells (IC50 values of 30.9 ug/mL).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Phytother Res.2022, 10.1002:ptr.7602.
Food Chem.2024, 446:138870.
Food Chemistry: X2023, 101032.
Antioxidants (Basel).2019, 8(8):E307
Protoplasma.2024, 261(6):1267-1280.
Planta Med.2018, 84(15):1101-1109
Eur J Pharmacol.2018, 832:96-103
Journal of Oil Palm Research2019, 31(2):238-247
Front Plant Sci.2018, 9:1424
Oxid Med Cell Longev2019, 9056845:13
Related and Featured Products
EXCLI J. 2017 Feb 16;16:73-88.
Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of naphthoquinone pigments from Onosma visianii Clem.[Pubmed:
28435429]
In this study, the antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of isolated compounds from the roots of Onosma visianii were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
By using different chromatographic techniques and appropriate spectroscopic methods, the seven naphthoquinones were described: deoxyshikonin ( 1 ), isobutyrylshikonin ( 2 ), α-methylbutyrylshikonin ( 3 ), acetylshikonin ( 4 ), Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin( 5 ), 5,8-O-dimethyl isobutyrylshikonin ( 6 ) and 5,8-O-dimethyl deoxyshikonin ( 7 ). Among the tested compounds, 3 and 4 exhibited the highest antibacterial activities toward all tested bacterial species (MIC50 and MIC90 for gram positive bacteria: 6.40 μg/mL-12.79 μg/mL and 6.82 μg/mL-13.60 μg/mL, respectively; for gram negative bacteria: 4.27 μg/mL-8.53 μg/mL and 4.77 μg/mL-9.54 μg/mL, respectively). Also, naphthoquinones 3 and 4 exhibited strong cytotoxic activity against MDA-MB-231 cells (IC50 values 86.0 μg/mL and 80.2 μg/mL, respectively), while compounds 1 , 3 , 4 and 5 significantly decreased viability of HCT116 cells (IC50 values of 97.8 μg/mL, 15.2 μg/mL, 24.6 μg/mL and 30.9 μg/mL, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicated that all tested naphthoquinone pigments are potential candidates for clinical uses as antibacterial and cytotoxic agents.
Int J Mol Med. 2016 Mar;37(3):816-24.
AMPK and SREBP-1c mediate the anti-adipogenic effect of β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin.[Pubmed:
26865314]
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin (β-HIVS), which is a natural naphthoquinone compound, is one of the main chemicals isolated from a therapeutic plant, Lithospermum erythrorhizon.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we demonstrated that β-HIVS inhibited the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-mediated modulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)‑1c. The anti-adipogenic effect of β-HIVS was accompanied by the increased phosphorylation of AMPK and precursor SREBP‑1c. In β-HIVS-treated 3T3-L1 cells, AMPK was activated and phosphorylated precursor SREBP‑1c, preventing the cleavage of precursor SREBP‑1c to mature SREBP‑1c. Expression of the fat-forming enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)1, fatty acid synthase (FAS) and stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)1, which are transcribed by mature SREBP‑1c, were downregulated, resulting in reduced intracellular fat accumulation. The anti-adipogenic effect of β-HIVS was significantly attenuated by AMPK knockdown. Knockdown of AMPK using siRNA decreased the phosphorylation of precursor SREBP‑1c and increased the levels of mature SREBP. The levels of the fat-forming enzymes, ACC1, FAS and SCD1, as well as intracellular fat accumulation were also significantly increased by AMPK knockdown.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that β-HIVS activated AMPK, which was followed by the downregulation of mature SREBP‑1c and fat-forming enzymes, leading to the inhibition of adipogenesis.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Nov 21;144(2):335-45.
In vitro and in vivo anticancer effects of Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract on B16F10 murine melanoma.[Pubmed:
22995444 ]
Lithospermum erythrorhizon has long been used in traditional Asian medicine for the treatment of diseases including skin cancer. In this study, hexane extract from the roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon (LEH) was chemically characterized and its anticancer activity was tested against the most aggressive form of skin cancer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The in vitro anticancer studies viz. cell growth, cell cycle and apoptosis, and the expression of tumor regulating proteins were analyzed against B16F10 melanoma cells. In addition, C57BL/6 mice models were used to evaluate the in vivo anticancer potential of LEH. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with LEH at doses of 0.1 and 10mg/kg every 3 days. The tumor inhibition ratio was determined after 21 days of treatment and the histopathological analyses of the tumor tissues were compared. Further, LEH was purified and its active compounds were structurally elucidated and identified by NMR spectra and quantified by HPLC analyses. LEH effectively inhibits the growth of melanoma cells with an IC(50) of 2.73μg/ml. Cell cycle analysis revealed that LEH increased the percentage of cells in sub-G1 phase by dose dependent manner. LEH exhibited down regulation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins and up regulation of apoptotic Bax protein expression. Importantly, LEH induced cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and activated the caspase cascade (caspase 3) with this cleavage mediating the apoptosis of B16F10 cells. LEH treatment at a dose of 10mg/kg for 21 days in experimental mice implanted with tumors resulted in significant reduction of the tumor growth (43%) and weight (36%). Histopathology analysis of LEH treated tumor tissues showed evidence of increased necrotic cells in a concentration dependent manner. Meanwhile, five naphthoquinone compounds [Shikonin (1); Deoxyshikonin (2); Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin (3); Acetylshikonin (4) and Isobutyrylshikonin (5)] were purified from LEH and responsible for its anticancer activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
LEH induced apoptosis in B16F10 cells by activation of caspase 3 and inducing sub-G1 cell cycle arrest. LEH exhibited both in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity. Shikonin derivatives in the LEH are responsible for the anticancer activity.
Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Mar;65:82-9.
Anti-inflammatory effects of β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin in BV2 microglia are mediated through suppression of the PI3K/Akt/NF-kB pathway and activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.[Pubmed:
24365262]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated whether Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin (β-HIVS) affects the production of proinflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in BV2 microglial cells. Our data showed that β-HIVS inhibited secretion of NO and PGE2 and downregulated expression of their main regulatory genes, inducible NO synthesis (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). β-HIVS also reduced the LPS-induced DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) by suppressing nuclear translocation of the NF-κB subunits and inhibiting the degradation and phosphorylation of IκBα. Furthermore, an NF-κB inhibitor, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), attenuated LPS-stimulated iNOS and COX-2 expression, suggesting that NF-κB inhibition is a main effector in the expression of iNOS and COX-2. We also found that LPS-induced NF-κB activation is regulated through inhibition of PI3K/Akt phosphorylation in response to β-HIVS. Additionally, β-HIVS caused the induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) via upregulation of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), both of which are involved in the secretion of proinflammatory mediators such as NO and PGE2.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our data indicate that β-HIVS diminishes the proinflammatory mediators NO and PGE2 and the expression of their regulatory genes, iNOS and COX-2, in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by inhibiting PI3K/Akt-dependent NF-κB activation and inducing Nrf2-mediated HO-1 expression.
Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39(6):969-76.
Simultaneous Addition of Shikonin and Its Derivatives with Lipopolysaccharide Induces Rapid Macrophage Death.[Pubmed:
27251498 ]
Macrophages play pivotal roles in inflammatory responses. Previous studies showed that various natural products exert antiinflammatory effects by regulating macrophage activation.
Recent studies have shown that shikonin (SHK) and its derivatives (Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin , acetylshikonin, and isobutylshikonin), which are 1,4-naphthoquinone pigments extracted from the roots of Lithospermum erythrorhizon, have various pharmacological, including antiinflammatory and antitumor, effects.
Even though there have been many studies on the antiinflammatory activities of SHK derivatives, only a few have described their direct effects on macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effects of SHK derivatives on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated macrophages. Low doses of SHK derivatives induced significant macrophage cytotoxicity (mouse macrophage-like J774.1/JA-4 cells and mouse peritoneal macrophages) in the presence of LPS. SHK activated caspases-3 and -7, which led to DNA fragmentation, but this cytotoxicity was prevented through a pan-caspase inhibitor in LPS-treated JA-4 cells. Maximal cytotoxic effects were achieved when SHK was added immediately before LPS addition.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that SHK derivatives induce caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death of LPS-treated macrophages and suggest that SHK acts during an early stage of LPS signaling.
Mol Med Rep. 2010 May-Jun;3(3):515-8.
Anti-neoplastic effect of β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin on a human choriocarcinoma cell line.[Pubmed:
21472272 ]
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin (β-HIVS), a compound isolated from the traditional asian medicinal herb Lithospermum radix, is an ATP non-competitive inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases such as v-Src and EGFR, and has been shown to induce apoptosis in several human tumor cell lines.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of β-HIVS in the choriocarcinoma cell line, BeWo. BeWo cells were treated with various concentrations of β-HIVS, and changes in cell growth, the cell cycle, apoptosis, and related parameters were examined. An MTT assay showed that BeWo cells were sensitive to the growth inhibitory effect of β-HIVS. Cell cycle analysis indicated that exposure to β-HIVS decreased the proportion of cells in the S phase and increased the proportion in the G0/G1 phases of the cell cycle. Induction of apoptosis was confirmed by Annexin V staining of externalized phosphatidylserine and by the loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. This induction occurred in conjunction with the altered expression of genes related to cell growth, malignant phenotype, and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that β-HIVS may serve as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of choriocarcinoma.