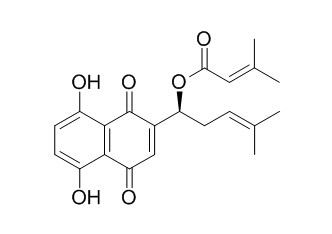
Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin
Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin has radical scavenging activity, it exhibits inhibitory activities on PTP1B with IC50 values of 0.36±0.08 umol·L-1, it may be a new type of leading compounds for the treatment of diabetes. Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin has great potential as topo I inhibitors compared to other compounds and CPT-11, with 2-3uM inhibition value. Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin can be potential therapeutics against tumor cell growth because of its unique DNA damaging abilities additional to enzyme inhibition similar to those of doxorubicin.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Applied Biological Chemistry 2021, 64(75)
Universidade Estadual Paulista2017, 11449
Natural Product Res.&Deve.2022, 1001-6880.
Sci Rep.2024, 14(1):3684.
Food Chem.2024, 446:138870.
Life Sci.2022, 298:120488.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 963:176280.
Biol Pharm Bull.2017, 40(6):797-806
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 2022:3483511
J Ginseng Res.2023, 47(4):593-603.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2010 May 28;73(5):860-4.
Cytotoxic naphthoquinones from Alkanna cappadocica ( perpendicular).[Pubmed:
20405844 ]
In a continuing program to discover new anticancer agents from plants, especially naphthoquinones from the Alkanna genus, Alkanna cappadocica was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided fractionation of a dichloromethane/methanol (1:1) extract of the roots led to the isolation of four new and four known naphthoquinones. The known compounds are 11-deoxyalkannin (1), Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin (2), 11-O-acetylalkannin (3), and alkannin (4). The new compounds 5-O-methyl-11-deoxyalkannin (5), 8-O-methyl-11-deoxyalkannin (6), 5-O-methyl-11-O-acetylalkannin (7), and 5-O-methyl-Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin (8) were characterized by spectroscopic analyses (LC-ESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR). Cytotoxicity of the isolated compounds was evaluated versus 12 human cancer cell lines, HT-29, MDA-MB-231, PC-3, AU565, Hep G2, LNCaP, MCF7, HeLa, SK-BR-3, DU 145, Saos-2, and Hep 3B together with two normal cell lines, VERO and 3T3, by using the MTT assay. Compound 7 showed remarkable cytotoxicity with IC(50) values between 0.09 and 14.07 muM.
It was more potent than the other compounds in six out of 12 cancer cell lines and the positive controls doxorubicin and etoposide.
CONCLUSIONS:
The mono-O-methylated alkannin derivatives and their cytotoxicities are reported for the first time.
Mol. Simulat., 2012, 38(12):980-6.
DFT study on the radical scavenging activity of β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin derivatives[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The radical scavenging activity of β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin(Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin) derivatives has been studied by using density functional theory.
The hydrogen bond property of the studied structures was investigated using the atoms in molecules theory. It turned out that the hydrogen bond is important for good radical scavenging activity. The hydrogen atom transfer for β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin derivatives is difficult to occur compared with the zero compound phenol. However, β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin derivatives appear to be good candidates for the one-electron transfer, particularly for β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin derivatives with electron-donating groups. Their naphthoquinone planar conformation and the extended electronic delocalisation between adjacent substituent groups determine low adiabatic ionisation potential (IP) values.
CONCLUSIONS:
The IPvalues of β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin derivatives with –NHPh, –N(CH)Ph, –N(CHCH)O and –N(CH)groups are lower than that of the parent compound β,β-dimethylacrylalkannin, suggesting that these derivatives are expected to be the promising candidates for radical scavenging activity compounds. Taking this system as an example, we present an efficient method for the investigation of radical scavenging activity from theoretical point of view.