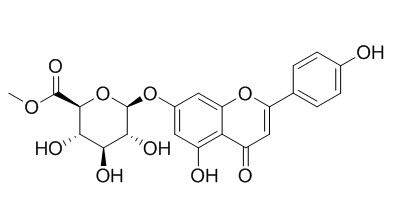
Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide
Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide did not affect GAG level or secretion, may potentially be used in osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type I pharmacotherapy in patients with normal GAG content. Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide which normalized collagen synthesis in OI cells may exert their effects through beta1-integrin-mediated signaling.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2020, 25(21):5091.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2017, 494(3-4):587-593
South African J of Plant&Soil2018, 29-32
Tissue Cell.2022, 78:101901.
Biomed Pharmacother.2021, 139:111585.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83:106403.
FEMS Microbiol Lett.2017, 364(11)
ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci.2024, 7(2):395-405.
Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess.2020, 37(9):1437-1448.
Anticancer Res.2020, 40(10):5529-5538.
Related and Featured Products
Mol Med Rep. 2010 May-Jun;3(3):537-41.
Differential effect of flavonoids on glycosaminoglycan content and distribution in skin fibroblasts of patients with type I osteogenesis imperfecta.[Pubmed:
21472276]
We recently reported that, in osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type I with diminished type I collagen biosynthesis, flavonoids such as apigenin 7-O-glucuronide, Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide and pectolinarin normalized the level of collagen type I without affecting total protein synthesis. In addition to collagen, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) play an important role in the formation of a functional supramolecular complex in the extracellular matrix, and any changes in their content and/or composition may be involved in the OI phenotype.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We previously detected a marked increase in sulphated GAG content in the OI fibroblasts of more severely affected patients (OI types II and III). These alterations were more pronounced in medium than in cells. Although, in OI type I cells, the increase observed in medium was much smaller (approximately 1.5-fold), it resulted in an increase of approximately 3-fold of the GAG to collagen type I ratio. Therefore, in the potential pharmacotherapy of OI type I with flavonoids, their effect on GAG level may be of importance. In the OI cells, some of the tested flavonoids applied at a concentration of 30 µM affected GAG content in quite the opposite way than type I collagen. Aglicones inhibiting collagen synthesis caused a marked increase in GAG concentration in medium, in contrast to the flavonoid glycosides, which exerted a stimulatory effect on type I collagen synthesis, but had a different effect on GAG content and distribution.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these, Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide did not affect GAG level or secretion, and thus may potentially be used in OI type I pharmacotherapy in patients with normal GAG content. However, in patients with increased concentrations of GAG, pectolinarin, which decreases GAG content by approximately 40%, may be more beneficial.
Int J Mol Med. 2007 Dec;20(6):889-95.
Stimulation of collagen biosynthesis by flavonoid glycosides in skin fibroblasts of osteogenesis imperfecta type I and the potential mechanism of their action.[Pubmed:
17982699]
The aim of the present study was to identify bioactive compounds stimulating collagen biosynthesis with potential for osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) type I pharmacological therapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Of the compounds tested, apigenin glycosides 7-O-glucuronide, 7-O-methylglucuronide and pectolinarin at 30 microM were found to significantly induce collagen type I synthesis in OI fibroblasts without an effect on the overall protein synthesis. None of the compounds displayed any toxicity at that concentration. Secretion of collagen into media was not affected by apigenin 7-O-glucuronide and was slightly increased in cells treated with Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide and pectolinarin. Furthermore, procollagen secreted by treated cells underwent a more rapid processing into collagen as compared with control untreated cells. In addition, we elucidated the possible mechanism involved in their action. Stimulation of collagen biosynthesis was not due to an increase in cell proliferation, because no differences in DNA content between the compound-treated and untreated cells were observed. Since flavonoids are known as strong inhibitors of metalloproteinases degrading matrix proteins, the increased level of collagen could result from the inhibition of their activity. However, the compounds with a stimulatory effect on collagen synthesis did not influence the activities of collagenase type I, gelatinases A and B, and stromelysin.
On the contrary, all compounds stimulated the activity of prolidase which catalyzes the final step of collagen degradation and plays an important role in collagen biosynthesis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Stimulation of collagen synthesis and prolidase activity by apigenin 7-O-glucuronide was accompanied by an increase in IGF-I receptor expression. In contrast, the compounds Apigenin 7-O-methylglucuronide and pectolinarin which normalized collagen synthesis in OI cells may exert their effects through beta1-integrin-mediated signaling.