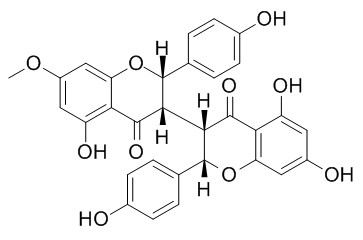
7-Methoxyneochamaejasmine A
7-Methoxyneochamaejasmine A has a strong inhibitory effect on Festuca rubra L. and Medicago sativa seedlings.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(12):1530.
PLoS One.2018, 13(3):e0193386
Pharmacogn J.2022, 14(2):350-357
Nutr Res Pract.2020, 14(3):203-217.
Planta Medica International2022, 9(01):e108-e115.
Front Nutr.2024, 11:1507886
Foods.2022, 11(12):1708.
J Liq Chromatogr R T2018, 41(12):761-769
Oncology Letters2018, 4690-4696
European Journal of Integrative Medicine2018, 20:165-172
Related and Featured Products
Plant Growth Regulation, 2015 , 77 (3) :335-342.
Potential allelochemicals in root zone soils of Stellera chamaejasme L. and variations at different geographical growing sites[Reference:
WebLink]
Populations of Stellera chamaejasme L. have been increasing constantly in recent years in some areas of the grassland in north China but why this toxic weed has become highly competitive is not clear. In order to determine if any potential allelochemicals are released into the soil environment by S. chamaejasme, we investigated the chemical composition of a water-washed solution of the living roots with rhizosphere soil.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This led to the isolation and identification of seven compounds: umbelliferone (1), daphnoretin (2), chamaechromone (3), 7-Methoxyneochamaejasmine A (4), mesoneochamaejasmin A (5), neochamaejasmin B (6), dihydrodaphnodorin B (7). All are secondary metabolites of S. chamaejasme. Bioassay showed that 1, 5 and 6 had a strong inhibitory effect on Festuca rubra L. and Medicago sativa seedlings. These compounds were quantified by high performance liquid chromatography in 25 root zone soil samples of S. chamaejasme collected at altitudes between 165 and 4741 m from the northeast to the Tibetan Plateau of China. All samples contained at least one of the phytotoxic compounds. Their content did not correlate with the altitude of the growing site. However, the level of chamaechromone negatively correlated with the soil pH.
CONCLUSIONS:
Principle components analysis indicated that the flavonoids might come from the same source. These potential allelochemicals from root release into the soil might play an important role in the highly competitive nature and broad ecological adaptability of S. chamaejasme in the wild.
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2002 Dec;4(4):259-63.
Chemical constituents of Stellera chamaejasme L.[Pubmed:
12450253]
A new biflavanone, 7-Methoxyneochamaejasmine A, and a new chromone derivative, isomohsenone, were isolated from the roots of Stellera chamaejasme L.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures of two compounds were determined by means of ESI-MS, 1H NMR and 13C NMR, especially 2D NMR spectral analyses.