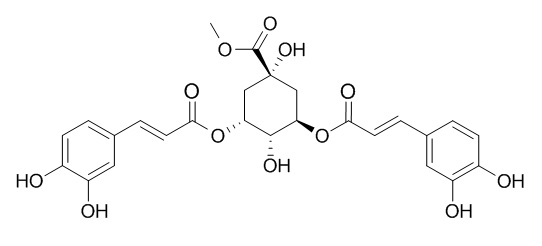
3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester
3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester exhibits potent inhibitory activities against the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs); it exhibits cytotoxicity actions against human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. 3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester shows high efficiency and low toxicity with antivirus activity against RSV.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2019, 172:268-277
Toxins (Basel).2023, 15(3):231.
Eur J Pharm Sci.2016, 94:33-45
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2019, 50(4):285-290
Journal of Food Composition and Analysis2021, 100:103905.
Molecules.2021, 26(3):695.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(23):14545.
Journal of Life Science2017, 233-240
Front Cell Infect Microbiol.2018, 8:292
J. Food Composition and Analysis2022, 114:104731
Related and Featured Products
Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2015 , 46 (11) :1597-602.
Study on chemical constituents from Re-Du-Ning Injection(Ⅱ)[Reference:
WebLink]
To investigate the chemical constituents from Re-Du-Ning Injection(RDN).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The chemical constituents were isolated by chromatography on silica gel, ODS, Sephadex LH-20, and Toyopearl HW-40 columns and reverse phase MPLC and HPLC repeatedly. Their structures were identified by spectral data and physicochemical property. Sixteen compounds were isolated and identified as 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid(1), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester(2), 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid(3), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester(4), 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid(5), 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester(6), 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid(7), 3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester(8), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid(9), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester(10), secologanic acid(11), vogeloside(12), 7-epi-vogeloside(13), E-aldosecologanin(14), Z-aldosecologanin(15), and 5H,8H-pyrano [4,3-d] thiazolo [3,2-a] pyridine-3-carboxylic acid(16). Compounds 1—10 showed high efficiency and low toxicity with antivirus activity against RSV.
CONCLUSIONS:
All the isolated compounds are reported from RDN Injection for the first time, and caffeoylquinic acids may be one of antivirus pharmacodynamic material bases of RDN.
Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Jul;31(7):900-4.
Constituents of the flowers of Erigeron annuus with inhibitory activity on the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and aldose reductase.[Pubmed:
18704333 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Seven phenolic compounds, caffeic acid (1), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (2), 4-methoxybenzoic acid (3), protocatechuic acid (4), eugenol O-beta-D: -glucopyranoside (5), 3,6-di-O-feruloylsucrose (6), and 3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (7), were isolated from an EtOAc-soluble partition of the flowers of Erigeron annuus. The structures of 1-7 were determined by spectroscopic data interpretation, particularly 1D and 2D NMR studies, and by comparison of their data with those published in the literature. All the isolates were subjected to in vitro bioassays to evaluate their inhibitory activities against the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and rat lens aldose reductase (RLAR).
CONCLUSIONS:
Of the compounds, 1, 6, and 7 exhibited potent inhibitory activities against the formation of AGEs. In the RLAR assay, compound 7 showed the most potent inhibitory activity.
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Aug 27;62(34):8608-15.
Functional analyses on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative effects of extracts and compounds from Ilex latifolia Thunb., a Chinese bitter tea.[Pubmed:
25118953 ]
Ilex latifolia Thunb., widely distributed in China, has been used as a functional food and drunk for a long time.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study was aimed to identify the bioactive constituents with antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory properties. I. latifolia was extracted with 95% ethanol and then partitioned into four fractions: petroleum ether fraction, ethyl acetate fraction, n-butanol fraction, and water fraction. Results showed that the ethyl acetate fraction was found to have significant ferric reducing antioxidant power activity, DPPH radical scavenging activity, and oxygen radical absorbance capacity, cytotoxicity against human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells, and inhibitory effect on NO production in macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Five compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction, and they were identified as ethyl caffeate (1), ursolic acid (2), chlorogenic acid (3), 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (4), and 3,5-Di-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (5), the last two of which were isolated for the first time from I. latifolia. Compounds 4 and 5 exhibited cytotoxicity actions against tumor cell line. Compound 3 showed the strongest anti-inflammatory activity of all the compounds.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results obtained in this work might contribute to the understanding of biological activities of I. latifolia and further investigation on its potential application values for food and drug.