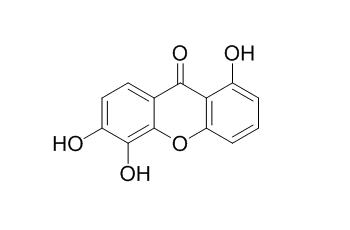
1,5,6-Trihydroxyxanthone exhibits antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria.
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules. 2014 Nov 28;19(12):19923-34.
Antibacterial and EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitory activities of polyhydroxylated xanthones from Garcinia succifolia.[Pubmed:
25460314 ]
Chemical investigation of the methanol extract of the wood of Garcinia succifolia Kurz (Clusiaceae) led to the isolation of 1,5-dihydroxyxanthone (1), 1,7-dihydroxyxanthone (2), 1,3,7-trihydroxyxanthone (3), 1,5,6-Trihydroxyxanthone (4), 1,6,7-trihydroxyxanthone (5), and 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone (6).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
All of the isolated xanthones were evaluated for their antibacterial activity against bacterial reference strains, two Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus ATTC 25923, Bacillus subtillis ATCC 6633) and two Gram-negative (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853), and environmental drug-resistant isolates (S. aureus B1, Enteroccoccus faecalis W1, and E. coli G1), as well as for their epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) of tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Only 1,5,6-trihydroxy-(4), 1,6,7-trihydroxy-(5), and 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthones (6) exhibited antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, however none was active against vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis. Additionally, 1,7-dihydroxyxanthone (2) showed synergism with oxacillin, but not with ampicillin. On the other hand, only 1,5-dihydroxyxanthone (1) and 1,7-dihydroxyxanthone (2) were found to exhibit the EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 90.34 and 223 nM, respectively.