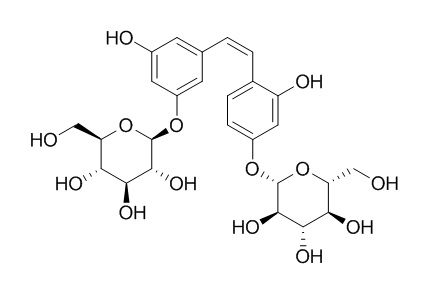
cis-Mulberroside A
cis-Mulberroside A shows high analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities, it can protect mice against ethanol-induced hepatic damage.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Chem Biodivers.2023, 20(12):e202301461.
Pharmaceutics.2023, 15(6):1771.
Toxicol In Vitro.2022, 81:105346.
Pharm Biol.2021, 59(1):134-145.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2015, 46(4):352-364
International. J. of Food Properties 2017, 20:S131-S140
Food Bioscience2023, 56:103311.
J Nat Prod.2023, 86(2):264-275.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.2024, 03148-x.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2023, 10.1002/kjm2.12764
Related and Featured Products
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2008,26(3):325-30.
Protective function of cis-mulberroside A and oxyresveratrol from Ramulus mori against ethanol-induced hepatic damage.[Pubmed:
21791383 ]
The aim of the study was to investigate the protective effects of oxyresveratrol and cis-Mulberroside A isolated from Ramulus mori on the liver of mice intoxicated with ethanol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Animals were pretreated with different doses (30 and 60mg/kg of body weight) of oxyresveratrol and cis-Mulberroside A prior to the ethanol (9g/kg of body weight) orally for 7 days. Ethanol treatment induced the decrease of reduced glutathione level and antioxidant enzymes activities, the elevation of the lipid peroxidation and cytochrome P450 2E1 activity accompanied with the increase of iron concentration and mitochondrial permeability transition. Pretreatment with oxyresveratrol and cis-Mulberroside A restored the changes in the above parameters up to the basal level. The protective effects of the two active compounds were further supported by attenuation of the degree of tissue damage and the regulation of the expression of TNF-α.
CONCLUSIONS:
It could be concluded that oxyresveratrol and cis-Mulberroside A from R. mori could protect mice against ethanol-induced hepatic damage.
Fitoterapia, 2009, 81(3):214-8.
Anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of cis-mulberroside A from Ramulus mori.[Pubmed:
19755140 ]
This study examined the analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions of cis-Mulberroside A isolated from Ramulus mori in several models of inflammatory pain in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
cis-Mulberroside A (25 and 50mg/kg) given by p.o. route 30 min before challenge produced a dose-dependent inhibition of the acetic acid-induced pain and Evans blue leakage in mice. In addition, this compound exhibited significant systemic anti-inflammatory activity in carrageenan-induced mouse paw edema in a concentration-related manner (33.1-68.5% inhibition), and similar results were achieved in formalin test. Suppressive effects of cis-Mulberroside A on the production of NO and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages were also assessed. Collectively, cis-Mulberroside A showed high analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities.
CONCLUSIONS:
The above results will be the supporting evidence for the potential anti-rheumatoid activity of R.mori in Chinese traditional medicine.