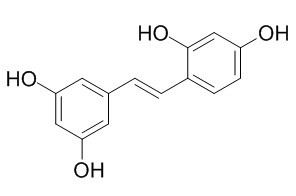
Oxyresveratrol
Oxyresveratrol , a dietary phenolic compound, has neuroprotective effect, as a potential nutritional candidate for protection against neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease; Oxyresveratrol has antioxidant activity, can reduce neuronal oxidative damage and protect hepatocytes against oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, which may be associated with activation of Nrf2, it also as an antibrowning agent for cloudy apple juices and fresh-cut apples. Oxyresveratrol exhibits a potent inhibitory effect on dopa oxidase activity of tyrosinase which catalyzes rate-limiting steps of melanin biosynthesis.Oxyresveratrol exhibits the inhibitory activity at the early and late phase of viral replication and inhibited the viral replication with pretreatment in one-step growth assay of HSV-1 and HSV-2.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Ethnopharmacol.2024, 318:116863.
Molecules.2020, 25(15):3353.
Int. J. of Food Properties2017, S108-S118
Microorganisms.2021, 9(12):2514.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2020, 13(9):262.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem.2023, 23(10):1204-1210.
Processes2021, 9(1), 153.
Molecules.2019, 24(16):E2985
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2017, 2017:1583185
J Appl Biol Chem2022, 65:343−348.
Related and Featured Products
Free Radic Biol Med. 2008 Oct 1;45(7):1019-26.
Dietary oxyresveratrol prevents parkinsonian mimetic 6-hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity.[Pubmed:
18675900 ]
Oxyresveratrol (OXY) is a polyhydroxylated stilbene existing in mulberry. Increasing lines of evidence have shown its neuroprotective effects against Alzheimer disease and stroke. However, little is known about its neuroprotective effect in Parkinson disease (PD).
Owing to its antioxidant activity, blood-brain barrier permeativity, and water solubility, we hypothesized that OXY may exert neuroprotective effects against parkinsonian mimetic 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) neurotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells have long been used as dopaminergic neurons in PD research. We found that both pretreatment and posttreatment with OXY on SH-SY5Y cells significantly reduced the release of lactate dehydrogenase, the activity of caspase-3, and the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species triggered by 6-OHDA. Compared to resveratrol, OXY exhibited a wider effective dosage range. We proved that OXY could penetrate the cell membrane by HPLC analysis of cell extracts. These results suggest that OXY may act as an intracellular antioxidant to reduce oxidative stress induced by 6-OHDA. Western blot analysis demonstrated that OXY markedly attenuated 6-OHDA-induced phosphorylation of JNK and c-Jun. Furthermore, we proved that OXY increased the basal levels of SIRT1, which may disclose new pathways accounting for the neuroprotective effects of OXY.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results suggest OXY, a dietary phenolic compound, as a potential nutritional candidate for protection against neurodegeneration in PD.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr 5;680(1-3):55-62.
Potential neuroprotective effects of oxyresveratrol against traumatic injury.[Pubmed:
22489319]
Oxyresveratrol is a potent antioxidant and free-radical scavenger found in mulberry wood (Morus alba L.) with demonstrated protective effects against cerebral ischemia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We analyzed the neuroprotective ability of Oxyresveratrol using an in vitro model of stretch-induced trauma in co-cultures of neurons and glia, or by exposing cultures to high levels of glutamate. Cultures were treated with 25 μM, 50 μM or 100 μM Oxyresveratrol at the time of injury. Trauma produced marked neuronal death when measured 24 h post-injury, and Oxyresveratrol significantly inhibited this death. Microscopic examination of glia suggested signs of toxicity in cultures treated with 100 μM Oxyresveratrol, as demonstrated by elevated S-100B protein release and a high proportion of cells with condensed nuclei. Cultures exposed to glutamate (100 μM) for 24 h exhibited ~ 37% neuronal loss, which was not inhibited by Oxyresveratrol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
These results show that the two pathologies of high glutamate exposure and trauma are differentially affected by Oxyresveratrol treatment in vitro. Further studies using Oxyresveratrol in trauma models are warranted, as toxicity to glia could be beneficial by inhibiting reactive gliosis, which often occurs after trauma.
J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Apr 4;55(7):2604-10.
Oxyresveratrol as an antibrowning agent for cloudy apple juices and fresh-cut apples.[Pubmed:
17335224]
Antibrowning activities of Morus alba L. twig extracts, Oxyresveratrol, and mulberroside A isolated from mulberry twig on cloudy apple juices and fresh-cut apple slices were evaluated by monitoring the change of a* value, total color difference (DeltaE), and visual observation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It was found, similar to 4-hexylresorcinol, that Oxyresveratrol could effectively inhibit browning in cloudy apple juices at a concentration as low as 0.01% and that mulberry twig extract also showed remarkable antibrowning effects on cloudy apple juices. However, for fresh-cut apple slices, mulberry twig extract and Oxyresveratrol needed to be used in combination at least with ascorbic acid to exhibit their antibrowning effects. Apple slice samples treated by dipping in a solution containing 0.001 M Oxyresveratrol, 0.5 M isoascorbic acid, 0.05 M calcium chloride, and 0.025 M acetylcysteine did not undergo any substantial browning reaction for 28 days at 4 degrees C.
However mulberroside A did not show antibrowning effects on cloudy apple juices although it is also a good mushroom tyrosinase inhibitor.
Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Feb 5;245:110-21.
Oxyresveratrol abrogates oxidative stress by activating ERK-Nrf2 pathway in the liver.[Pubmed:
26102008]
Oxyresveratrol is a polyphenolic phytoalexin produced by plants as an antioxidant. This study investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Oxyresveratrol as well as its underlying mechanism of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we evaluated the protective effects of Oxyresveratrol against tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBHP)-induced severe oxidative stress in HepG2 cells as well as acute liver injury caused by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in mice.
tBHP-induced reactive oxygen species production and cell death in hepatocytes were blocked by Oxyresveratrol, as indicated by MTT, TUNEL, and FACS analyses. Moreover, pretreatment with Oxyresveratrol increased nuclear translocation and transactivation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), as assessed by antioxidant response element reporter gene expression and immunofluorescence staining, and transactivated expression of both hemeoxygenase-1 and glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit. More importantly, Oxyresveratrol induced phosphorylation of Nrf2 mediated through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Further, ERK inhibitors such as PD98059 and U0126 blocked phosphorylation of Nrf2 as well as the protective effect of Oxyresveratrol in mitochondria. In mice, oral administration of Oxyresveratrol significantly prevented hepatocyte degeneration, inflammatory cell infiltration, as well as elevation of plasma markers such as ALT and AST induced by CCl4 injection.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, this study confirmed that Oxyresveratrol protected hepatocytes against oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, which might be associated with activation of Nrf2.
Free Radic Res. 2013 Mar;47(3):212-8.
The protective effects of oxyresveratrol imine derivative against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells.[Pubmed:
23298159]
Oxyresveratrol (2',3,4',5-tetrahydroxystilbene) is a naturally occurring ingredient found in mulberries that shows potential as an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective agent.
This study was performed to identify materials similar to Oxyresveratrol that may have more effective antioxidant properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We synthesized a stilbene analog referred to as Compound 1 (2',3,4',5-tetramethoxystilbene); a benzamide analog referred to as Compound 2 ((2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3,5-dimethoxybenzamide); and three imine analogs referred to as Compound 3 (3,5-dimethoxybenzylidene)-(2,4-dimethoxyphenylamine), Compound 4 ((4-methoxybenzylidene)-(3-methoxyphenyl)amine), and Compound 5 ((4-methoxybenzylidene)phenylamine). The cytoprotective effects of these compounds were subsequently evaluated using hydrogen peroxide-treated PC12 cells. The cytoprotective effects of the imine analogs were greater than the effects of Oxyresveratrol and the other analogs at concentrations of 200 μM. The Compound 3, which is the most effective imine analog of Oxyresveratrol, exhibited these cytoprotective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through the regulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression and the translocation of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that imine analogs of Oxyresveratrol may be useful agents in reducing neuronal oxidative damage.
Antiviral Res. 2008 Oct;80(1):62-70.
Anti-herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) activity of oxyresveratrol derived from Thai medicinal plant: mechanism of action and therapeutic efficacy on cutaneous HSV-1 infection in mice.[Pubmed:
18565600 ]
Oxyresveratrol, a major compound purified from Artocarpus lakoocha, a Thai traditional medicinal plant, was evaluated for its mechanism of action and therapeutic efficacy on cutaneous herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory concentrations for 50% HSV-1 plaque formation of Oxyresveratrol, three clinical isolates, thymidine kinase (TK)-deficient and phosphonoacetic acid (PAA)-resistant HSV-1 were 19.8, 23.3, 23.5, 24.8, 25.5 and 21.7microg/ml, respectively. Oxyresveratrol exhibited the inhibitory activity at the early and late phase of viral replication and inhibited the viral replication with pretreatment in one-step growth assay of HSV-1 and HSV-2. Oxyresveratrol inhibited late protein synthesis at 30microg/ml. The combination of Oxyresveratrol and acyclovir (ACV) produced synergistic anti-HSV-1 effect, as characterized by the isobologram of plaque inhibition. Mice orally treated with Oxyresveratrol (500mg/kg/dose) dose at 8 h before and three times daily had significant delay in herpetic skin lesion development (P<0.05). Topical application of 30% Oxyresveratrol ointment five times daily significantly delayed the development of skin lesions and protected mice from death (P<0.0001).
Arch Dermatol Res. 2014 Jul;306(5):475-87.
Effects of resveratrol, oxyresveratrol, and their acetylated derivatives on cellular melanogenesis.[Pubmed:
24414332]
Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol are naturally occurring phenolic compounds with various bioactivities, but their uses in cosmetics have been partly limited by their chemical instabilities.
This study was performed to examine the anti-melanogenic effects of the acetylated derivatives from resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol were chemically modified to triacetyl resveratrol and tetraacetyl Oxyresveratrol, respectively. The acetylated compounds were less susceptible than the parent compounds to oxidative discoloration. The acetylated compounds inhibited the activities of tyrosinases less than parent compounds in vitro, but they were as effective at cellular melanogenesis inhibition, indicating bioconversion to parent compounds inside cells. Supporting this notion, the parent compounds were regenerated when the acetylated compounds were digested with cell lysates. Although resveratrol and triacetyl resveratrol inhibited tyrosinase activity less effectively than Oxyresveratrol and tetraacetyl Oxyresveratrol in vitro, they inhibited cellular melanogenesis more effectively. This discrepancy was explained by strong inhibition of tyrosinase expression by resveratrol and triacetyl resveratrol. Experiments using a reconstituted skin model indicated that resveratrol derivatives can affect melanin synthesis and cell viability to different extents.
CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively, this study suggests that acetylated derivatives of resveratrol have great potential as anti-melanogenic agents for cosmetic use in terms of efficacy, safety, and stability.