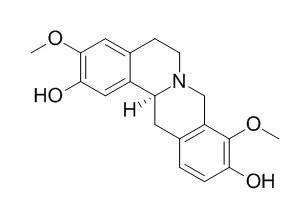
L-Stepholidine
L-Stepholidine, which has dual actions on dopamine D1 and D2 receptors, attenuates heroin self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement. It also elicits anti-dyskinesia effects.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Appl Toxicol.2024, jat.4615.
J Cell Mol Med.2023, jcmm.17968.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(14):11496.
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):21690.
Drug Des Devel Ther.2020, 14:61-71
Cell Physiol Biochem.2017, 43(4):1425-1435
Processes2020, 8(12),1540.
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 19(1)
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2021, 427:115668.
Fitoterapia.2024, 175:105958.
Related and Featured Products
Neuroreport. 2014 Jan 8;25(1):7-11.
L-Stepholidine, a naturally occurring dopamine D1 receptor agonist and D2 receptor antagonist, attenuates heroin self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement in rats.[Pubmed:
24145772]
Opiate addiction is a chronic, relapsing brain disease characterized by persistent and uncontrolled drug-seeking behavior despite negative effects. L-Stepholidine (L-SPD) is an alkaloid extract of the Chinese herb Stephania intermedia with dopamine D1 receptor partial agonistic and D2 receptor antagonistic dual actions. The unique pharmacological profile of L-SPD suggests that L-SPD may be effective for the treatment of opiate addiction.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of this study was to characterize the effects of L-SPD on heroin self-administration on a fixed-ratio 1 schedule and cue-induced reinstatement under an extinction/reinstatement protocol. The effect of L-SPD on the locomotor activity of heroin-free rats was also tested. We found that 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg of L-SPD attenuated heroin self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement without affecting locomotor activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results showed that L-SPD, which has dual actions on dopamine D1 and D2 receptors, attenuates heroin self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement.
Neurobiol Aging. 2010 Jun;31(6):926-36.
L-stepholidine reduced L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in 6-OHDA-lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease.[Pubmed:
18707801]
L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA)-induced dyskinesia (LID) remains a challenge in Parkinson's disease (PD) drug therapy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we examined the effect of L-Stepholidine (L-SPD), a known dual dopamine receptor agent, on LID in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-lesioned PD rat model. Daily administration of L-DOPA to PD rats for 22 days induced steady expression of LID, co-administration of L-Stepholidine with L-DOPA significantly ameliorated LID without compromising the therapeutic potency of L-DOPA, indicating that L-Stepholidine attenuated LID development. L-Stepholidine alone elicited stable contralateral rotational behavior without inducing significant dyskinesia. Acute administration of L-Stepholidine to rats with established LID produced significant relief of dyskinesia; this effect was mimicked by D(2) receptor antagonist haloperidol, but blunted by 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY100635. Furthermore, the mRNA level of 5-HT(1A) decreased significantly on 6-OHDA-lesioned striata, whereas chronic L-Stepholidine treatment restored 5-HT(1A) receptor mRNA level on the lesioned striata.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present data demonstrated that L-Stepholidine elicited antidyskinesia effects via both dopamine (D(2) receptor antagonistic activity) and nondopamine (5-HT(1A) agonistic activity) mechanisms.
Synapse. 2011 May;65(5):379-87.
l-Stepholidine-induced excitation of dopamine neurons in rat ventral tegmental area is associated with its 5-HT(1A) receptor partial agonistic activity.[Pubmed:
20803620]
We studied the effects of L-Stepholidine on the activity of dopamine (DA) neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) using in vivo single-unit recording technique in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that L-Stepholidine increased VTA DA neurons firing rate and induced slow oscillation in firing pattern. Moreover, L-Stepholidine, not clozapine, reversed d-amphetamine-induced inhibition which induced an excitation of VTA DA neurons. Furthermore, our data indicated that the excitatory effect of L-Stepholidine is associated with its partial agonistic action for the 5-HT(1A) receptor since the 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY100635 could block the L-Stepholidine-induced excitatory effect. However, activation of 5-HT(1A) receptor alone by specific agonist (±)-8-Hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) was insufficient to elicit excitation of VTA DA neurons, but the excitation of 8-OH-DPAT on VTA DA neurons was elicited in the presence of D₂-like receptors antagonist raclopride. Collectively, these results indicate that l-SPD excited VTA DA neurons requiring its D₂-like receptors antagonistic activity and 5-HT(1A) receptor agonistic activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present data demonstrate that D₂ receptor antagonist/5-HT(1A) receptor agonistic dual properties modulate dopaminergic transmission in a unique pattern that may underlie the different therapeutic responses between L-Stepholidine and other atypical antipsychotic drugs.
Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jan 24;559:67-71.
L-stepholidine, a natural dopamine receptor D1 agonist and D2 antagonist, inhibits heroin-induced reinstatement.[Pubmed:
24269875]
L-Stepholidine (l-SPD), an alkaloid extract of the Chinese herb Stephania intermedia, is the first compound known to exhibit mixed dopamine D1 receptor agonist/D2 antagonist properties and is a potential medication for the treatment of opiate addiction. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of pretreatment with L-SPD on heroin-seeking behavior induced by heroin priming.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were trained to self-administer heroin (0.05mg/kg per infusion) under a fixed ratio 1 schedule for 12 consecutive days and nose-poke responding was extinguished for 12 days, after which reinstatement of drug seeking was induced by heroin priming. Pretreatment with L-SPD (2.5, 5.0 and 10.0mg/kg, i.p.) inhibited the heroin-induced reinstatement of heroin-seeking behavior. Importantly, L-SPD did not affect locomotion, indicating that the observed effects of L-SPD on reinstatement are not the result of motor impairments.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present data suggested that l-SPD inhibits heroin-induced reinstatement and its potential for the treatment of heroin relapse.