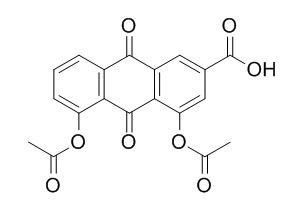
Diacerein
Diacerein, a interleukin-1 beta inhibitor, is a slow-acting medicine of the class anthraquinone used to treat joint diseases.The feasibility of targeted delivery of Diacerein to articular tissue using soluble polysaccharide chondroitin sulfate as the targeting vector, this approach has the potential to significantly increase anti-arthritic drug concentration in joints without leading to systemic toxicity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2017, 18(12)
Virus Res.2023, 335:199199.
China Pharmacy2015, 26(27)
Plants (Basel).2021, 10(5):951.
Heliyon.2024, 10(11):e32352.
Molecules.2022, 27(19):6651.
Cosmetics2025, 12(3), 108
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(8):4211.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2021, 427:115668.
Phytomedicine.2024, 126:155442.
Related and Featured Products
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014 Jul;22(7):1044-52.
The disease modifying osteoarthritis drug diacerein is able to antagonize pro inflammatory state of chondrocytes under mild mechanical stimuli.[Pubmed:
24857974]
To investigate the combination of mild mechanical stimuli and a disease modifying osteoarthritis drug (DMOAD) in inflammatory activated chondrocytes and to study the combination of drug and mechanical tension on the cellular level as a model for an integrated biophysical approach for osteoarthritis (OA) treatments.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) stimulated C28/I2 cells underwent mild mechanically treatment while cultured in the presence of the DMOAD Diacerein. The pharmacological input of Diacerein was evaluated by cell viability and cell proliferation measurements. Inflammation and treatment induced changes in key regulatory proteins and components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) were characterized by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). The effects on metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) activity and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) concentration in cell supernatants of treated cells were investigated. C28/I2 cells demonstrated significant changes in expression of inflammatory and cartilage destructive proteins in response to IL-1β stimulation. The chondroprotective action of Diacerein in mechanically stimulated cells was mediated by a decrease in interleukin-8 (IL-8), fibronectin-1 (FN-1), collagen type I (Col 1) and MMP-1 expression levels, respectively. Augmented expression of interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) and the fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) by Diacerein was not abolished by mechanical treatment. The observed effects were accompanied by a reduced cell proliferation rate, attenuated cell viability and extenuated MMP-1 activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Diacerein diversely regulates the expression of main regulatory proteins as well as components important to regenerate and set up ECM. Mechanical stimulation does not negatively influence the chondroprotective effect induced by Diacerein treatment in immortalized human C28/I2 chondrocytes.
Nanomedicine. 2014 Jul;10(5):1031-40.
Targeting of diacerein loaded lipid nanoparticles to intra-articular cartilage using chondroitin sulfate as homing carrier for treatment of osteoarthritis in rats.[Pubmed:
24512762]
Targeted delivery of antiosteoarthritic drug Diacerein to articular tissue could be a major achievement and soluble polysaccharide chondroitin sulfate (ChS) may be a suitable agent for this.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Therefore, Diacerein loaded solid lipid nanoparticles modified with ChS (ChS-DC-SLN) were prepared for synergistic effect of these agents to combat multidimensional pathology of osteoarthritis (OA). Prepared formulation were of size range 396±2.7nm, showed extended release up to 16h and increased bioavailability of Diacerein by 2.8 times. ChS-DC-SLN were evaluated for their effect on histopathology of femoro-tibial joint of rat knee and amount of ChS and rhein (an active metabolite of Diacerein) at targeted site. Concentration of rhein was significantly higher in case of ChS-DC-SLN (7.8±1.23μg/ml) than that of drug dispersion (2.9±0.45μg/ml). It can be stated that ChS served as homing to articular cartilage for targeting of drug.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, ChS-DC-SLN have great potential to enhance the overall efficacy of treatment for OA.
Clin Ther. 2013 Apr;35(4):431-9.
The efficacy of diacerein in hand osteoarthritis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study.[Pubmed:
23474153]
Diacerein is a drug used in osteoarthritis (OA) that elicits an inhibitory effect on interleukin-1 and metalloproteases. Although Diacerein has shown modest efficacy and safety in the treatment of knee and hip OA, there have been no placebo-controlled clinical trials for hand OA. The aim of the current study was to investigate the efficacy and tolerability of Diacerein in patients with hand OA.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Patients fulfilling the American College of Rheumatology criteria for hand OA participated in this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eligible patients were >40 years of age, had at least 1 tender joint, and had a joint pain visual analog scale of >30 mm. Patients received Diacerein (50 mg) or placebo BID for 12 weeks. The primary end point was the Australian/Canadian Osteoarthritis Hand Index (AUSCAN) pain score at 4 weeks. Secondary end points were AUSCAN pain score at 12 weeks and AUSCAN physical function and stiffness score, patient and physician global assessment, functional index of hand OA scores, and multidimensional health assessment questionnaire results at 4 weeks and 12 weeks. Eighty-six Korean patients were enrolled (42 Diacerein, 44 placebo). The intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses revealed no significant differences between the 2 groups in terms of change in AUSCAN pain score at 4 weeks, except for improvement in physician global assessment at 4 weeks (per-protocol analysis, P = 0.004). The safety profile of Diacerein was comparable to placebo, except for frequent discoloration of the urine (88% vs 20%).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Diacerein 50 mg BID may be ineffective in controlling the symptoms of hand OA.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999 May;7(3):255-64.
Stimulating effect of diacerein on TGF-beta1 and beta2 expression in articular chondrocytes cultured with and without interleukin-1.[Pubmed:
10329300 ]
Diacetylrhein or Diacerein has shown efficacy in the treatment of both major forms of osteoarthritis (OA), coxarthrosis as well as gonarthrosis, improving clinical symptoms of the disease (pain reduction and algo-functional index). Both in-vitro and animal models studies suggest that Diacerein may have also disease-modifying effects. The drug exerts inhibitory effects on interleukin-1-induced expression of cartilage degrading enzymes. However, its mechanism of action is not completely understood. In view of the role that could play the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta system in the repair potentialities of OA cartilage, we studied the effect of Diacerein on the expression of TGF-beta isoforms 1, 2 and 3 and that of their receptor types I and II in cultured bovine chondrocytes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cultured bovine articular chondrocytes were treated with 10(-5) m Diacerein, 10 ng/ml IL-1beta or the combination Diacerein+interleukin (IL)-1, and the expression of both TGF-beta isoforms 1, 2 and 3 and that of their receptors TbetaR-I and TbetaR-II was determined by Northern-blot and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Cell transfections of cDNA constructs containing sequences of the 5'-upstream region of TGF-beta1 promoter were also performed to determine their transcriptional activity in Diacerein-treated cultures.
The data indicated that Diacerein enhances the expression of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2. This effect was also found in the presence of IL-1, albeit with smaller intensity. In contrast, the levels of TGF-beta3 and receptors I and II remained unaffected or slighty modified by the compound. Treatment of cells transiently transfected with TGF-beta1 promoter constructs suggested that the stimulating effect on TGF-beta1 expression is mediated by the region -1038 to -1132 base pars.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggest that Diacerein effects on matrix synthesis and turn-over previously reported in cultured articular chondrocytes might be explained in part by the ability of the drug to enhance TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 expression in these cells. This mechanism of action may account for the potential disease-modifying properties of Diacerein and might give clues as to how future anti-osteoarthritic drugs should be designed.
J Chromatogr Sci. 2014 Jan;52(1):5-11.
Validated stability indicating TLC-densitometric method for the determination of diacerein.[Pubmed:
23258391]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This work presents an accurate, sensitive and selective thin-layer chromatography-densitometry method for the simultaneous determination of Diacerein in the presence of rhein, the active metabolite and hydrolytic degradation product of Diacerein, and emodin, the Diacerein impurity, in bulk powder and different pharmaceutical formulations. Chromatographic separation was performed on aluminum plates precoated with 60 F254 silica gel using hexane-ethyl acetate-acetic acid (60:40:0.8, by volume) as a developing system and with detection at 230 nm. The retention factor values of Diacerein, rhein and emodin were 0.12, 0.44 and 0.6, respectively. The method was successfully applied for the determination of these compounds with high sensitivity; the linearity ranges were found to be 0.5-10 µg/band (for Diacerein and rhein) and 0.5-7 µg/band (for emodin). The developed method was validated according to International Conference on Harmonization guidelines and was applied for the determination of Diacerein in different pharmaceutical formulations. Moreover, a statistical comparison between the results of the developed method and those of the reported reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method showed no significant differences.
CONCLUSIONS:
This method can be used for the routine analysis of Diacerein, rhein and emodin in quality control laboratories.