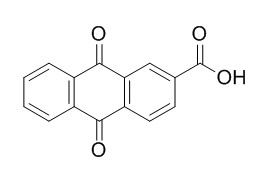
2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid
Anthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid is a novel electron shuttling mediator, shows potent anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities in vivo, thus contributing to the immune regulatory role of fruits and herbs.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal2019, 52(12):986-991
Trop J Nat Prod Res.2019, 3(1):6-9
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(40):22237-22249.
Jeju National University Graduate School2023, 24478
J.Korean Soci. Food Sci. Nutri.2024, 53(11):1166-1177
Antioxidants (Basel).2023, 13(1):12.
Front Chem.2024, 12:1385844.
Front Immunol.2017, 8:1542
iScience.2020, 23(2):100849.
Phytomedicine.2018, 47:48-57
Related and Featured Products
Mediators Inflamm. 2016; 2016: 1903849.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Anthraquinone-2-Carboxylic Acid[Pubmed:
27057092]
Anthraquinone compounds are one of the abundant polyphenols found in fruits, vegetables, and herbs. However, the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity and molecular mechanisms of anthraquinones have not been fully elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the activity of anthraquinones using acute inflammatory and nociceptive experimental conditions. Anthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid (2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid,9,10-dihydro-9,10-dioxo-2-anthracenecarboxylic acid, AQCA), one of the major anthraquinones identified from Brazilian taheebo, ameliorated various inflammatory and algesic symptoms in EtOH/HCl- and acetylsalicylic acid- (ASA-) induced gastritis, arachidonic acid-induced edema, and acetic acid-induced abdominal writhing without displaying toxic profiles in body and organ weight, gastric irritation, or serum parameters. In addition, AQCA suppressed the expression of inflammatory genes such as cyclooxygenase- (COX-) 2 in stomach tissues and lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) treated RAW264.7 cells. According to reporter gene assay and immunoblotting analyses, AQCA inhibited activation of the nuclear factor- (NF-) κB and activator protein- (AP-) 1 pathways by suppression of upstream signaling involving interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK1), p38, Src, and spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk).
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data strongly suggest that anthraquinones such as AQCA act as potent anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive components in vivo, thus contributing to the immune regulatory role of fruits and herbs.
Journal of Materials Chemistry.2011 Aug;21(39):15383-15390.
Photo-induced self-cleaning functions on 2-anthraquinone carboxylic acid treated cotton fabrics.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Self-cleaning cotton fabrics were obtained via chemically incorporating photosensitive 2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid (2-AQC) onto the fibers through a mild and efficient esterification reaction. The 2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid structures on the treated cotton were confirmed by FTIR characterization. SEM images revealed that the cotton fiber surface became rougher than that of the original cotton fiber after the treatment. TGA analysis confirmed that thermal stability of the treated fibers was almost unchanged. The 2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid treated cotton fabrics demonstrated excellent photo-induced self-cleaning properties, including decomposition of 90% aldicarb in 3 hours of UVA exposure and inactivation of over 99% of both E. coli and S. aureus in 1 hour of the light exposure.
CONCLUSIONS:
The self-cleaning functions are a result of formation of reactive oxygen species on the light irradiated and 2-Anthraquinonecarboxylic acid treated cotton. The amount of H2O2 formed on the fabrics was determined by a titration method.