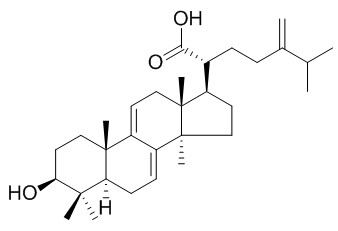
Dehydroeburicoic acid
Dehydroeburicoic acid induces necrotic cell death that involves Ca(2+) overload, mitochondrial dysfunction, and calpain activation in human glioblastomas. Dehydroeburicoic acid and Eburicoic acid have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities by the decrease of inflammatory cytokines and an increase of antioxidant enzyme activity, can protect the liver from CCl4-induced hepatic damage.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2023, 10.1002/kjm2.12764
Exp Parasitol.2017, 183:160-166
ACS Omega.2021, 6(36):23460-23474.
Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences2022, DOI: 10.4274
JAOCS2021, 98(7):779-794.
J Appl Biol Chem2022, 65:343−348.
The Korea Journal of Herbology2016, 29-35
J Pharmacol Sci.2021, 147(2):184-191.
Biochem Pharmacol.2023, 211:115502.
Korea Food Research Institute2024, 4798082
Related and Featured Products
Chem Res Toxicol. 2009 Nov;22(11):1817-26.
Dehydroeburicoic acid induces calcium- and calpain-dependent necrosis in human U87MG glioblastomas.[Pubmed:
19848398]
Dehydroeburicoic acid (DeEA) is a triterpene purified from medicinal fungi such as Antrodia camphorate, the crude extract of which is known to exert cytotoxic effects against several types of cancer cells. We aim to test the hypothesis that Dehydroeburicoic acid possesses significant cytotoxic effects against glioblastomas, one of the most frequent and malignant brain tumors in adults.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
3-(4,5-Dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide and lactate dehydrogenase release assays indicated that Dehydroeburicoic acid inhibited the proliferation of the human glioblastoma cell U87MG. In addition, Annexin V and propidium iodide staining showed that Dehydroeburicoic acid treatment led to a rapid increase of glioblastomas in the necrotic/late apoptotic fraction, whereas cell cycle analysis revealed that Dehydroeburicoic acid failed to significantly enhance the population of U87MG cells in the hypodiploid (sub-G1) fraction. Using electron microscopy, we found that Dehydroeburicoic acid induced significant cell enlargements, massive cytoplasmic vacuolization, and loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity. Dehydroeburicoic acid treatment triggered an intracellular Ca(2+) increase, and Dehydroeburicoic acid-induced cell death was significantly attenuated by BAPTA-AM but not ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid. Dehydroeburicoic acid instigated a reduction of both mitochondrial transmembrane potential and intracellular ATP level. Moreover, Dehydroeburicoic acid induced proteolysis of alpha-spectrin by calpain, and Dehydroeburicoic acid cytotoxicity in U87MG cells was caspase-independent but was effectively blocked by calpain inhibitor. Interestingly, Dehydroeburicoic acid also caused autophagic response that was prevented by calpain inhibitor.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest that in human glioblastomas, Dehydroeburicoic acid induces necrotic cell death that involves Ca(2+) overload, mitochondrial dysfunction, and calpain activation.
Food Chem. 2013 Dec 1;141(3):3020-7.
Hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury.[Pubmed:
23871054]
The hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid (TR1) and Dehydroeburicoic acid (TR2) from Antrodia camphorata (AC) against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage were investigated in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
TR1 and TR2 was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) for 7 days prior to the administration of CCl4. Pretreatment with TR1 and TR2 prevented the elevation of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and liver lipid peroxides in CCl4-treated mice. The activities of antioxidant enzymes [catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)], nitric oxide (NO) production, and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) were decreased after the treatment with TR1 and TR2 in CCl4-treated mice. Western blotting revealed that TR1 and TR2 significantly decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expressions and increased the expression of cytochrome P4502E1 (CYP2E1) in CCl4-treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, we speculate that TR1 and TR2 protect the liver from CCl4-induced hepatic damage via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Phytomedicine. 2012 Jun 15;19(8-9):788-96.
Antileukemia component, dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata induces DNA damage and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo models.[Pubmed:
22516893]
Antrodia camphorata (AC) is a native Taiwanese mushroom which is used in Asian folk medicine as a chemopreventive agent.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The triterpenoid-rich fraction (FEA) was obtained from the ethanolic extract of AC and characterized by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). FEA caused DNA damage in leukemia HL 60 cells which was characterized by phosphorylation of H2A.X and Chk2. It also exhibited apoptotic effect which was correlated to the enhancement of PARP cleavage and to the activation of caspase 3. Five major triterpenoids, antcin K (1), antcin C (2), zhankuic acid C (3), zhankuic acid A (4), and Dehydroeburicoic acid (5) were isolated from FEA. The cytotoxicity of FEA major components (1-5) was investigated showing that Dehydroeburicoic acid (DeEA) was the most potent cytotoxic component. DeEA activated DNA damage and apoptosis biomarkers similar to FEA and also inhibited topoisomerase II. In HL 60 cells xenograft animal model, DeEA treatment resulted in a marked decrease of tumor weight and size without any significant decrease in mice body weights.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our results provided the first evidence that pure AC component inhibited tumor growth in vivo model backing the traditional anticancer use of AC in Asian countries.
J Agric Food Chem. 2013 May 29;61(21):5064-71.
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory bioactivities of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid isolated from Antrodia camphorata on the inflammatory mediator expression in mice.[Pubmed:
23495748]
Eburicoic acid (TR1) and Dehydroeburicoic acid (TR2), an active ingredient from Antrodia camphorata (AC) solid-state culture, were evaluated for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Treatment with TR1 and Dehydroeburicoic acid significantly inhibited a number of acetic acid-induced writhing responses and formalin-induced pain in the late phase. In the anti-inflammatory test, TR1 and Dehydroeburicoic acid decreased paw edema at the fourth and fifth hour after λ-carrageenan (Carr) administration and increased the activities of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the paw edema tissue. We also demonstrated that TR1 and Dehydroeburicoic acid significantly attenuated the malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels in either edema paw or serum at the fifth hour after Carr injection. Western blotting revealed that TR1 and TR2 decreased Carr-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cycloxyclase (COX-2) expressions at the fifth hour in paw edema. Treatment with TR1 and Dehydroeburicoic acid also diminished neutrophil infiltration into the paw edema at the fifth hour.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study suggests that the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of TR1 and Dehydroeburicoic acid might be related to the decrease of inflammatory cytokines and an increase of antioxidant enzyme activity.