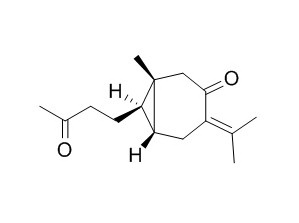
Curcumenone
Curcumenone may have protective effect on drunkenness, through increasing liver alcohol dehydrogenase activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Planta Med.2018, 84(6-07):465-474
Food Bioscience2023, 53:102687
Drug Dev Res.2020, doi: 10.1002
ACS Omega.2021, 6(36):23460-23474.
Lab Chip.2018, 18(6):971-978
Antioxidants2022, 11(2),234.
Cancers (Basel).2021, 13(6):1432.
BMB Rep.2020, 53(4):218-222.
Journal of Natural Remedies2024, 24(3):555®C575.
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(85).
Related and Featured Products
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 6;16(3):5180-93.
Spectrofluorometric and molecular docking studies on the binding of curcumenol and curcumenone to human serum albumin.[Pubmed:
25756376]
Curcumenol and Curcumenone are two major constituents of the plants of medicinally important genus of Curcuma, and often govern the pharmacological effect of these plant extracts.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
These two compounds, isolated from C. zedoaria rhizomes were studied for their binding to human serum albumin (HSA) using the fluorescence quench titration method. Molecular docking was also performed to get a more detailed insight into their interaction with HSA at the binding site. Additions of these sesquiterpenes to HSA produced significant fluorescence quenching and blue shifts in the emission spectra of HSA. Analysis of the fluorescence data pointed toward moderate binding affinity between the ligands and HSA, with Curcumenone showing a relatively higher binding constant (2.46 √ó 105 M-1) in comparison to curcumenol (1.97 √ó 104 M-1).
CONCLUSIONS:
Cluster analyses revealed that site I is the preferred binding site for both molecules with a minimum binding energy of -6.77 kcal·mol-1.
However, binding of these two molecules to site II cannot be ruled out as the binding energies were found to be -5.72 and -5.74 kcal·mol-1 for curcumenol and Curcumenone, respectively. The interactions of both ligands with HSA involved hydrophobic interactions as well as hydrogen bonding.
Fitoterapia. 2013 Jan;84:163-9.
Effects of the extracts and an active compound curcumenone isolated from Curcuma zedoaria rhizomes on alcohol-induced drunkenness in mice.[Pubmed:
23160092]
The Curcuma zedoaria rhizome has been used traditionally to treat gastrointestinal diseases as an aromatic stomachic drug, and this is currently used to treat alcohol-induced loss of appetite and nausea in Japan.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We examined the effects of various fractions and isolated compounds on alcohol-induced drunkenness and blood alcohol concentrations in mice. The 30% ethanol-extract (1000mg/kg) of C. zedoaria rhizome prevented drunkenness 60 and 120min after 40% alcohol administration. The n-hexane-soluble fraction (300mg/kg) and an isolated compound (3, 10 or 30mg/kg) prevented drunkenness at 30, 60 or 120min. The extract, n-hexane-soluble fraction and isolated compound reduced the elevation in blood alcohol concentrations 30 and 60min after 40% alcohol administration. The isolated compound (10 and 30mg/kg) enhanced liver ADH activity 30 and 60min after 40% alcohol administration. The compound was identified as Curcumenone by a direct comparison of (1)H- and (13)C-NMR spectral data.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the protective effect of the C. zedoaria extract on drunkenness might be due to an active substance, Curcumenone, and decreases in the elevation of blood alcohol concentrations through increased liver alcohol dehydrogenase activity.