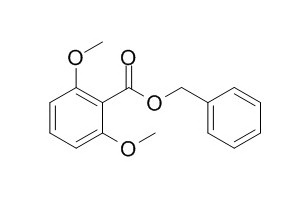
Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate
Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate shows significant analgesic effects, it induces a concentration-dependent inhibition of the spontaneous contractions of the guinea-pig ileum with IC50 values ranging from 1.49 to 4.96 microM. Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate shows antimicrobial activity against several bacteria (S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and B. subtilis) and fungi (C. albicans and T. mentagrophytes).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Sci Rep.2017, 7:467-479
JMicrobiol Biotech Food Sci2021, e4289.
Talanta.2022, 249:123645.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(10):5181.
Phytother Res.2022, 35844057.
Food Funct.2023, 14(9):4354-4367.
J Nat Med.2021, doi: 10.1007.
Anesth Pain Med (Seoul).2020, 15(4):478-485.
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal2023, 31(12):101829
J Nat Prod.2015, 78(6):1339-4
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2002 Aug;65(8):1107-10.
New furanoid diterpenes from Caesalpinia pulcherrima.[Pubmed:
12193012]
Four new cassane-type furanoditerpenoids (1-4) were isolated from the air-dried leaves of Caesalpinia pulcherrima.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Their structures were elucidated by spectral data interpretation. The exocyclic methylene compound 1 readily isomerized and oxidized to the benzofuran 4. Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (5) was also identified in this study.
CONCLUSIONS:
Antimicrobial tests on 1-5 indicated that they were active against several bacteria (S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and B. subtilis) and fungi (C. albicans and T. mentagrophytes).
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Aug 13;118(3):448-54.
Antinociceptive, hypoglycemic and spasmolytic effects of Brickellia veronicifolia.[Pubmed:
18583074]
Brickellia veronicifolia (Kunth) Gray (Asteraceae) (BV) is broadly commercialized for treating gastrointestinal diseases (stomach aches, biliary colics and dyspepsia), arthritis, diabetes and painful inflammatory complaints. In order to complete the preclinical pharmacological profile of BV, first the antinociceptive effect of an organic extract (BVE) and isolated metabolites on the hot plate and writhing tests was assessed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Then, their potential hypoglycemic effects were analyzed in normoglycemic and diabetic rats; in addition, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed. Finally, the spasmolytic activity of BVE was assessed in vivo using the gastrointestinal motility test (GMT) in mice.
The results revealed that BVE (100-600 mg/kg), 6-methoxysalicylic acid (1), 2-methoxybenzoic acid (2), Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (3), and taraxasteryl acetate (4) showed significant analgesic effects. Compounds 2 and 3 were the most active (1-100mg/kg) in the hot plate and writhing tests, respectively. In the antidiabetic assays, BVE (100mg/kg) showed an important hypoglycemic action. Furthermore, at the same dose, it provoked a significant postprandial decrease of blood glucose level after 30 min of a glucose challenge. Finally, the GMT in mice revealed the spasmolytic activity in vivo of BVE (31.6 mg/kg).
CONCLUSIONS:
The overall information tends to support the vernacular uses of the plant.
Planta Med. 2005 Apr;71(4):320-5.
Smooth muscle relaxant action of benzyl benzoates and salicylic acid derivatives from Brickellia veronicaefolia on isolated guinea-pig ileum.[Pubmed:
15856407]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A dichloromethane-MeOH extract prepared from the aerial parts of Brickellia veronicaefolia inhibited the spontaneous contractions (IC50 = 39.22 microg/mL) of the guinea-pig ileum. Bioassay-guided fractionation of the extract led to the isolation of three new benzoic acid derivatives, 1,2-bis-O-(2-methoxybenzoyl)-beta-d-glucopyranoside (1), 3-(beta-glucopyranosyloxy)Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (2) and 3-hydroxyBenzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (3), together with the known compounds taraxasteryl acetate (4), 4-allyl-2-methyloxyphenyl-beta-glucopyranoside (5), 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoic acid (6), 2-methoxybenzoic acid (7), chamazulene (8), 2-methoxybenzyl 2-hydroxybenzoate (9), Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (10), 3-methoxybenzyl 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoate (11), benzyl 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoate (12), benzyl 2,3,6-trimethoxybenzoate (13), benzyl 2-hydroxy-3,6-dimethoxybenzoate (14) and 3-methoxyBenzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (15). The isolates were characterized by spectral means.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 2 - 6, 8 - 11, 14 and 15 induced a concentration-dependent inhibition of the spontaneous contractions of the guinea-pig ileum with IC50 values ranging from 1.49 to 4.96 microM. Their activity was comparable to that of papaverine (IC50 = 4.23 microM).
J Nat Prod. 2006 Aug;69(8):1172-6.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the active components of the essential oil from Brickellia veronicaefolia by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.[Pubmed:
16933870]
The composition of the spasmolytic essential oil of the medicinal species Brickellia veronicaefolia was established by NMR spectroscopy in addition to GC-MS analysis and HPLC studies.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Seven major compounds, representing ca. 86% of the oil, were identified as Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (1), 2-hydroxybenzyl 2'-methoxybenzoate (2), chamazulene (3), beta-caryophyllene (4), germacrene D (5), bicyclogermacrene (6), and beta-eudesmol (7). A sensitive and accurate analytical 1H NMR method has been developed for the quantification of the major compounds in the essential oil of B. veronicaefolia.
CONCLUSIONS:
The method was validated using Benzyl 2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (1) and beta-caryophyllene (4), two of the active principles in the oil, and successfully applied to the determination of these pharmacologically active compounds in three different batches of the oil collected in different geographical regions and/or seasons.