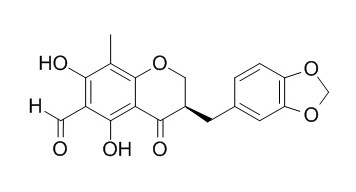
6-Aldehydoisoophiopogonanone A
6-Aldehydoisoophiopogonanone A is a natural product from Ophiopogon japonicus.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2021, 22(14):7324.
Nutraceutical Research . 2021, 19(1),p90-105.
Planta Med.2019, 85(4):347-355
Int J Mol Med.2015, 35(5):1237-45
Materials Today Communications2023, 37:107216
Inflammation.2020, 43(5):1716-1728.
Vietnam J. Chemistry2022, 60(2):211-222
Antioxidants (Basel).2022, 11(12):2496.
J Cell Mol Med . 2023, jcmm.17954.
Plant Commun.2024, 5(10):101005.
Related and Featured Products
Chromatographia February 2005, Volume 61, Issue 3-4, pp 121-125
Determination of Homoisoflavonoids in Ophiopogon japonicus by RP-HPLC[Reference:
WebLink]
The homoisoflavonoid content of 14 samples of Ophiopogon japonicus collected from different parts of China have been investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three principal homoisoflavonoids, methylophiopogonanone A, methylophiopogonanone B, and 6-Aldehydoisoophiopogonanone A, were analyzed simultaneously by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with a binary mixture of acetonitrile and 0.3% aqueous acetic acid as mobile phase. The recovery of the method was 98.5–102.6% and good linearity (r > 0.9990) was obtained for all the homoisoflavonoids over a relatively wide concentration range.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that the homoisoflavonoid content of Ophiopogon japonicus varied significantly from species to species, and from locality to locality. The quality and identity of Ophiopogon japonicus from the herb market can be determined from the homoisoflavonoid content.