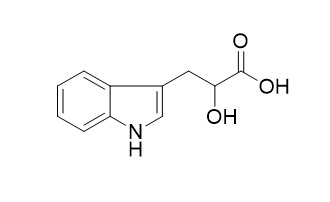
Indolelactic acid
Indolelactic acid is a phytochormone.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Plants (Basel).2024, 13(19):2793.
Asian Pac J Tropical Bio.2020, 10(6):239-247
Eur J Pharmacol.2020, 889:173589.
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(23), 8729
Int J Biol Macromol.2025, 292:139225.
Life (Basel).2021, 11(12):1399.
Acta Biochim Pol.2015, 62(2):253-8
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025, 417(17):3879-3892.
Reprod Toxicol.2020, 96:1-10.
Front Nutr.2021, 8: 687851.
Related and Featured Products
Biologia Plantarum, 1970, 12(3):246-255.
Pathways of IAA production from tryptophan by plants and by their epiphytic bacteria: Metabolism of indolepyruvic acid and indolelactic acid.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Metabolites of indolepyruvic acid and Indolelactic acid were investigated using 2 systems: a bacterial (pea stem homogenates containing the epiphytic bacteria) and a plant system (pea stem sections under sterile conditions). The products of spontaneous indolepyruvic acid decomposition in aqueous solution and during chromatography were investigated, too.Biological indolepyruvic acid conversion yields, besides those substance amounts which occur spontaneously, indoleacetic acid, indoleethanol (tryptophol) and (only in the sterile plant system) indoleacetaldehyde. An inhibitor extract from pea stems decreases the indoleacetic acid and increases the indoleethanol and indoleacetaldehyde gain.
CONCLUSIONS:
Indolelactic acid is not metabolized in the sterile plant sections. Indolelactic acid oxidation by the bacteria-containing homogenate yields indolepyruvic acid and is inhibited by the inhibitor extract.
Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 205( 1):125-137.
Identification of 3-indoleacetic acid in pinus sylvestris L. by gas chromatography-mas spectrometry, and quantitative analysis by ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography wit spectrofluorimetric detection.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The phytochormone 3-indoleacetic acid (IAA) was conclusively identified by gas chromatography-mas spetrometry of its methyl ester in purified extracts of Scots pine, Pinus sylvestris L. Preceding purification included reversed-phase ion-pair chromatography on a Nucleosil C18 column with tetrabutylammonium ion as counter ion. A number of indole acids were separated in this high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) system. In particular, IAA was separated from the reported plant constituents 4-chloro-IAA, 5-hydroxy-IAA, 3-indoleacrylic acid, 3-Indolelactic acid, 3-indolepropionic acid, 3-indolebutyric acid and tytophan. In connection with a spectrofluorine detector, the HPLC system was also used for the quantitative analysis of IAA in pine samples. Systematic errors caused a constant under-estimation of the IAA content by 12% and could easily be corrected for. The random error was 14%. Eight-week-old pine seedings contained 46 ng g−1 of IAA.
CONCLUSIONS:
The sensitivity of the method, applied to the analysis of pine extracts, was 50 pg of IAA. Evidence is presented that the method, when applied to the analysis of pine extracts, is specific of IAA.