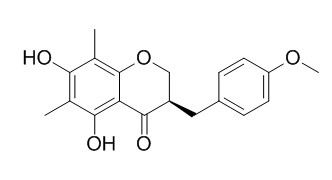
Methylophiopogonanone B
Methylophiopogonanone B has inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha activity.Methylophiopogonanone B can inhibit melanosome transfer to keratinocytes as well as melanocyte dendrite outgrowth, it also suppress pigmentation in a three-dimensional skin culture model through the inhibition of melanocyte dendrite outgrowth, it could result in the creation of very unique cosmetic products that would precisely control the darkening or lightening of skin tone.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
LWT2021, 147:111620.
JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography2023, 36:179-190
Appl. Sci.2021, 11(19),9343.
J.Soc.Cosmet.Sci.Korea2024, 50(3): 261-270
Chulalongkorn University2024, 4761190
Sains Malaysiana2024, 53(2):397-408.
Pharmacol Rep.2018, 70(6):1195-1201
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(9):3239.
Chem Biol Interact.2019, 315:108910
Applied Biological Chemistry 2021, 64(75)
Related and Featured Products
Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Mar;297(1-2):121-9.
A novel agent, methylophiopogonanone B, promotes Rho activation and tubulin depolymerization.[Pubmed:
17029007]
Cytoskeletal reorganization, including reconstruction of actin fibers and microtubules, is essential for various biological processes, such as cell migration, proliferation and dendrite formation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We show here that Methylophiopogonanone B (MOPB) induces cell morphological change via melanocyte dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation. Since members of the Rho family of small GTP-binding proteins act as master regulators of dendrite formation and actin cytoskeletal reorganization, and activated Rho promotes dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation, we studied the effects of MOPB on the small GTPases using normal human epidermal melanocytes and HeLa cells. In in vitro binding assay, MOPB significantly increased GTP-Rho, but not GTP-Rac or GTP-CDC42. Furthermore, a Rho inhibitor, a Rho kinase inhibitor and a small GTPase inhibitor each blocked MOPB-induced stress fiber formation. The effect of MOPB on actin reorganization was blocked in a Rho dominant negative mutant. These results suggest MOPB acts via the Rho signaling pathway, and it may directly or indirectly activate Rho. Quantitative Western blot analysis indicated that MOPB also induced microtubule destabilization and tubulin depolymerization.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, MOPB appears to induce Rho activation, resulting in actin cytoskeletal reorganization, including dendrite retraction and stress fiber formation.
Int.J. Cosmetic Sci., 2006, 28(2):148-148.
Control of melanosome transfer by promoting shrinkage or expansion of melanocyte dendrites.[Reference:
WebLink]
Melanosomes synthesized within melanocytes are transferred to keratinocytes through melanocyte dendrites, resulting in a constant supply of melanin to the epidermis which determines skin pigmentation. Theoretically, if we can find an effective way to control this supply of melanin to the epidermis, skin colour could be darkened or lightened.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The objective of this study was to find safe and effective methods to inhibit or promote melanosome transfer by the shrinkage or expansion of melanocyte dendrites. Methylophiopogonanone B and centaureidin inhibited melanosome transfer to keratinocytes as well as melanocyte dendrite outgrowth. Methylswertianin and comfrey extract promoted not only melanosome transfer to keratinocytes but also expansion of melanocyte dendrites. Methylophiopogonanone B and centaureidin suppressed pigmentation in a three-dimensional skin culture model through the inhibition of melanocyte dendrite outgrowth. Methylswertianin and comfrey extract activated pigmentation in a three-dimensional skin culture model by expansion of melanocyte dendrites.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our experimental findings suggest the possibility of manipulating human skin colour by controlling melanosome transfer to cause shrinkage or expansion of dendrites. A combination of effective agents, in addition to the ones identified in this work, could result in the creation of very unique cosmetic products that would precisely control the darkening or lightening of skin tone.
Heterocycles, 2009, 78(8):2061-5.
Dihydrochalcone Designed from Methylophiopogonanone B Strongly Inhibits Hypoxia-inducible Factor (HIF)-1α Activity.[Reference:
WebLink]
Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha activity of Methylophiopogonanone B (1) and its derivatives were investigated. As the modification of the structure of 1, dihydrochalcone (11) was leaded and showed one order higher activity (IC(50): 0.2 mu g/mL) than Methylophiopogonanone B (1) (IC(50): 2.2 mu g/mL).
Carbohydr Res. 2011 Feb 1;346(2):253-8.
Novel steroidal saponins from Liriope graminifolia (Linn.) Baker with anti-tumor activities.[Pubmed:
21163470]
Phytochemical investigation of the underground parts of Liriope graminifolia (Linn.) Baker resulted in the isolation of two new steroidal saponins lirigramosides A (1) and B (2) along with four known compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structures were determined by extensive spectral analysis, including two-dimensional (2D) NMR spectroscopy and chemical methods, to be 3-O-[β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→2)-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)]-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(25S)-spirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol (1), 1-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-xylopyranosyl]-(25R)-ruscogenin (2), 1-O-β-d-xylopyranosyl-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(25S)-ruscogenin (3), 3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-1-O-sulfo-(25S)-ruscogenin (4), Methylophiopogonanone B (5), and 5,7-dihydroxy-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-6-methyl-chroman-4-one, (ophiopogonanone B, 6), respectively. Compound 1 has a new (25S)-spirost-5-ene-3β,17α-diol ((25S)-pennogenin) aglycone moiety.
CONCLUSIONS:
The isolated compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against Hela and SMMC-7721 cells.