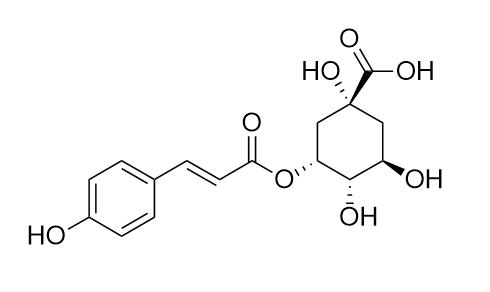
5-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
5-O-Coumaroylquinic acid (3-O-Coumaroylquinic acid), exhibits significant inhibition of PTP1B and a concentration-dependent inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase, thereby demonstrating anti-hyperglycemic properties. Additionally, this compound enhances glucose uptake and inhibits PTP1B in vitro, emphasizing its potential therapeutic applications in glucose regulation.
5-O-Coumaroylquinic acid is a potent, reversible, non-competitive α-amylase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 69.39 μM.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants.2022, 11(3):592.
Neurochem Int.2020, 133:104629
Regen Biomater.2023, 10:rbad077.
J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea2016, 163-171
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(23):17118.
Phytochem Anal.2023, pca.3305.
Nutrients.2023, 15(4):954.
Planta Med.2022, a-1876-3009.
LWT2020, 110397
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2020, 2020:1970349.
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol . 2014 Mar 28;152(3):599-602.
Walnut leaf extract inhibits PTP1B and enhances glucose-uptake in vitro[Pubmed:
24548753]
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Walnut, Juglans regia L. (Juglandaceae), is one of the medicinal plants used to treat diabetic symptoms in Austrian folk medicine. The air-dried green leaves are either used as aqueous decoctions or liquor preparations and are consumed on a daily basis. We investigated the hypoglycemic effect of a methanolic Juglans regia leaf extract on glucose uptake, protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibition and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) activation.
Material and methods: Hypoglycemic activity was assessed by glucose-uptake in C2C12 myocytes, inhibition of PTP1B and activation of PPARγ. Phytochemical characterization of the extract was carried out by LC-MS and GC-MS.
Results: Methanolic Juglans regia leaf extract enhanced the glucose uptake rate in C2C12 myocytes at concentrations of 25μg/mL compared to untreated cells. This activity may partly be explained by the inhibition of PTP1B but not PPARγ agonism. LC-MS analyses revealed chlorogenic acid (1), 3-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), a trihydroxynaphthalene-hexoside (3), as well as eight flavonoids (4-11) as main phenolic constituents in the active extract.
Conclusions: The finding that Juglans regia leaf extract enhances glucose uptake and inhibits PTP1B provides an in vitro-based rationale for the traditional use of walnut leaf preparations against elevated blood-glucose levels.
Fitoterapia . 2014 Dec;99:1-6.
Caffeoylquinic acid derivatives isolated from the aerial parts of Gynura divaricata and their yeast α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory activity[Pubmed:
25172103]
The phytochemical investigation of natural products of Gynura divaricata led to the isolation of eleven caffeoylquinic acid derivatives. They were characterized by spectrometric methods as 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (1), 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 5-O-feruloylquinic acid (3), methyl 5-O-caffeoylquinate (4), 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8), methyl 3,5-dicaffeoylquinate (9), methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) and ethyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (11). The individual compounds were screened for the inhibition of yeast α-glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) using in vitro assays. Among the isolated compounds, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8) and methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) exhibited significant inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase. In addition, 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6) and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7) had considerable inhibitory effect against PTP1B. Based on these findings, the caffeoylquinic acid derivatives were deduced to be potentially responsible for the anti-diabetic activity of G. divaricata. The preliminary structure-activity relationship study suggests that the number and positioning of caffeoyl groups in the quinic acid derivatives are important for both α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory potency. Moreover, the corresponding methyl esters of some dicaffeoylquinic acids have enhanced inhibitory activity against yeast α-glucosidase.
Food Funct . 2019 May 22;10(5):2881-2887.
Dihydrochalcone-derived polyphenols from tea crab apple (Malus hupehensis) and their inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase in vitro[Pubmed:
31070208]
Three dihydrochalcone-derived polyphenols, huperolides A-C (1-3), along with thirteen known compounds (4-16) were isolated from the leaves of Malus hupehensis, the well-known tea crab apple in China. Their chemical structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis including NMR (HSQC, HMBC, 1H-1H COSY and ROESY), HRMS and CD spectra. Huperolide A is a polyphenol with a new type of carbon skeleton, while huperolides B and C are a couple of atropisomers, which were isolated from natural sources for the first time. The antihyperglycemic effects of the isolated compounds were evaluated based on assaying their inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase. As a result, phlorizin (4), 3-hydroxyphloridzin (5), 3-O-coumaroylquinic acid (12) and β-hydroxypropiovanillone (15) showed significant concentration-dependent inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase. Therefore, those compounds might be responsible for the antihyperglycemic effect of this herb, and are the most promising compounds to lead discovery of drugs against diabetes.
Fitoterapia . 2014 Dec;99:1-6.
Caffeoylquinic acid derivatives isolated from the aerial parts of Gynura divaricata and their yeast α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory activity[Pubmed:
25172103]
The phytochemical investigation of natural products of Gynura divaricata led to the isolation of eleven caffeoylquinic acid derivatives. They were characterized by spectrometric methods as 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (1), 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 5-O-feruloylquinic acid (3), methyl 5-O-caffeoylquinate (4), 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8), methyl 3,5-dicaffeoylquinate (9), methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) and ethyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (11). The individual compounds were screened for the inhibition of yeast α-glucosidase and Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) using in vitro assays. Among the isolated compounds, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (5), 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7), methyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate (8) and methyl 4,5-dicaffeoylquinate (10) exhibited significant inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase. In addition, 5-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid (2), 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (6) and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (7) had considerable inhibitory effect against PTP1B. Based on these findings, the caffeoylquinic acid derivatives were deduced to be potentially responsible for the anti-diabetic activity of G. divaricata. The preliminary structure-activity relationship study suggests that the number and positioning of caffeoyl groups in the quinic acid derivatives are important for both α-glucosidase and PTP1B inhibitory potency. Moreover, the corresponding methyl esters of some dicaffeoylquinic acids have enhanced inhibitory activity against yeast α-glucosidase.
Food Funct . 2019 May 22;10(5):2881-2887.
Dihydrochalcone-derived polyphenols from tea crab apple (Malus hupehensis) and their inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase in vitro[Pubmed:
31070208]
Three dihydrochalcone-derived polyphenols, huperolides A-C (1-3), along with thirteen known compounds (4-16) were isolated from the leaves of Malus hupehensis, the well-known tea crab apple in China. Their chemical structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis including NMR (HSQC, HMBC, 1H-1H COSY and ROESY), HRMS and CD spectra. Huperolide A is a polyphenol with a new type of carbon skeleton, while huperolides B and C are a couple of atropisomers, which were isolated from natural sources for the first time. The antihyperglycemic effects of the isolated compounds were evaluated based on assaying their inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase. As a result, phlorizin (4), 3-hydroxyphloridzin (5), 3-O-coumaroylquinic acid (12) and β-hydroxypropiovanillone (15) showed significant concentration-dependent inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase. Therefore, those compounds might be responsible for the antihyperglycemic effect of this herb, and are the most promising compounds to lead discovery of drugs against diabetes.