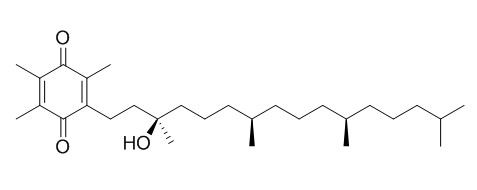
alpha-Tocopherolquinone
Alpha-Tocopherolquinone has antioxidant effect, can inhibit lipid peroxidation and reduce cell division in both the glioma cell clone and fetal brain cells; it inhibits β-amyloid aggregation and cytotoxicity, disaggregates preformed fibrils and decreases the production of reactive oxygen species, NO and inflammatory cytokines.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2022, 207:114398.
Genes Environ.2024, 46(1):13.
Nutrients.2023, 15(6):1335.
Processes2023, 11(2), 385��
J Agric Food Chem.2021, 69(11):3496-3510.
Food Science and Biotechnology2022, 10.1007.
ARPN Journal of Eng.& Applied Sci.2016, 2199-2204
Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation2024, 024-00662-1.
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy2017, 48(4):320-328
ACS Chem Biol.2019, 14(5):873-881
Related and Featured Products
J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jan;52(1):65-77.
Use of an adaptive study design in single ascending-dose pharmacokinetics of A0001 (α-tocopherylquinone) in healthy male subjects.[Pubmed:
21343342]
A0001 (alpha-Tocopherolquinone) is a potent antioxidant currently in development for the treatment of symptoms associated with inherited mitochondrial disorders.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
alpha-Tocopherolquinone pharmacokinetics were studied in a single-blind, adaptive design study following a single daily oral dose of placebo (n = 2) or ascending doses of alpha-Tocopherolquinone (n = 8) at 0.25 and 0.5 g under a fasted state or a 0.5- to 6-g dose with a high-fat meal. alpha-Tocopherolquinone plasma concentration-time profiles were similar across doses, reaching peak concentration within 4 to 6 hours, with concentrations returning to baseline within 24 hours. however, the nonproportionality was offset by administering alpha-Tocopherolquinone in divided doses (0.735 g, 3 times per day). The potential for an alpha-Tocopherolquinone:vitamin E interaction was also explored, as vitamin E use is prevalent in this patient population, and suggested that a clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction is not likely. alpha-Tocopherolquinone was well tolerated with no serious adverse events or dose-limiting toxicities.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that alpha-Tocopherolquinone has a favorable pharmacokinetic profile when administered orally with food.
Biochem Int. 1985 May;10(5):753-61.
Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by alpha-tocopherolquinone and alpha-tocopherolhydroquinone.[Pubmed:
4015671]
The antioxidant effect of alpha-Tocopherolquinone and alpha-tocopherolhydroquinone was studied in liposomes and rat liver submitochondrial particles.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Both alpha-Tocopherolquinone and alpha-tocopherolhydroquinone inhibit lipid peroxidation induced by ascorbate/Fe2+ in liposomes and by cumene hydroperoxide in submitochondrial particles. Alpha-tocopherolhydroquinone is much more effective than alpha-Tocopherolquinone in inhibiting lipid peroxidation. Submitochondrial particles, depleted of ubiquinones and reincorporated with alpha-Tocopherolquinone, are protected from lipid peroxidation only in the presence of succinate. alpha-
CONCLUSIONS:
Tocopherolquinone cannot replace endogenous ubiquinones in the respiratory chain function, nevertheless it can be reduced by the mitochondrial respiratory chain substrates, presumably through the reduced ubiquinones.
Cancer Lett. 1982 Feb;15(2):173-8.
Regulation of cell division in a human glioma cell clone by arachidonic acid and alpha-tocopherolquinone.[Pubmed:
6284351]
A human glioma cell clone (12-18 CV), derived from a previously characterized glioblastoma multiforme cell line, was established in culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Lipid peroxidation (thiobarbituric acid test) occurred when either 8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid or 5,8,11-eicosatetraenoic acid (arachidonic acid) was added to the cells in culture. The extent of lipid peroxidation was similar in fetal brain cells (CH II) treated with these polyunsaturated fatty acids. The antioxidant, alpha-Tocopherolquinone, inhibited lipid peroxidation in both the glioma cell clone and fetal brain cells. Arachidonic acid significantly reduced cell division in both the glioma cell clone and fetal brain cells. alpha-Tocopherolquinone restored cell division to control levels in both cultures.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data show that cells from a tumor clone retain the capacity for lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, cell division in a tumor clone is correlated with lipid peroxidation in the same way that cell division in other cell lines is correlated with lipid peroxidation.
Neurochem Int. 2010 Dec;57(8):914-22.
α-Tocopherolquinone inhibits β-amyloid aggregation and cytotoxicity, disaggregates preformed fibrils and decreases the production of reactive oxygen species, NO and inflammatory cytokines.[Pubmed:
20933033 ]
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex, multifactorial neurodegenerative disease. The aggregation of beta-amyloid (Aβ) into extracellular fibrillar deposition is a pathological hallmark of AD. The Aβ aggregate-induced neurotoxicity, inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress are linked strongly to the etiology of AD.
The currently available hitting-one-target drugs are insufficient for the treatment of AD. Therefore, finding multipotent agents able to modulate multiple targets simultaneously is attracting more attention.
Previous studies indicated that vitamin E or its constituent such as α-tocopherol (α-T) was able to attenuate the effects of several pathogenetic factors in AD. However, ineffective or detrimental results were obtained from a number of clinical trials of vitamin E.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we showed that naturally synthesized RRR-alpha-Tocopherolquinone(α-TQ), a main derivative of α-T, could inhibit Aβ42 fibril formation dose-dependently. Further investigations indicated that α-TQ could attenuate Aβ42-induced neurotoxicity toward SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, disaggregate preformed fibrils and interfere with natural intracellular Aβ oligomer formation. Moreover, α-TQ could decrease the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NO, and modulate the production of cytokines by decreasing TNF-α and IL-1β and increasing IL-4 formation in microglia.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, α-TQ targeting multiple pathogenetic factors deserves further investigation for prevention and treatment of AD.
Arjunglucoside I
Catalog No: CFN95049
CAS No: 62319-70-4
Price: $268/10mg
Gancaonin N
Catalog No: CFN95066
CAS No: 129145-52-4
Price: $463/5mg
Parvisoflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95077
CAS No: 49776-79-6
Price: $413/5mg
1-Methyl-2,8-dihydroxy-3-carboxy-9,10-anthraquinone
Catalog No: CFN95101
CAS No: 1401414-53-6
Price: $338/5mg
Tuberosin
Catalog No: CFN95107
CAS No: 41347-45-9
Price: $218/5mg
Marginatoxin
Catalog No: CFN95174
CAS No: 1422536-56-8
Price: $318/10mg
(3R,5S,E)-1,7-Diphenylhept-1-ene-3,5-diol
Catalog No: CFN95227
CAS No: 232261-31-3
Price: $318/5mg
Notoginsenoside L13
Catalog No: CFN95332
CAS No: 2485859-56-9
Price: $318/5mg
4'-Hydroxy-3',5,5',6,7,8-hexamethoxyflavone
Catalog No: CFN95407
CAS No: 85644-03-7
Price: $318/5mg
Benzylpropyl acetate
Catalog No: CFN95495
CAS No: 7492-40-2
Price: $318/5mg