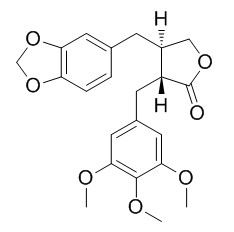
Yatein
Yatein is a lignan precursor of podophyllotoxin, a key agent in anticancer drugs. Yatein can significantly suppress HSV-1 multiplication in HeLa cells without apparent cytotoxicity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Research International2023, 113792.
Pak J Pharm Sci.2023, 36(1):51-57.
Nat Commun.2023, 14(1):8142.
Babol University of Medical Sciences2024, rs-4289336
Front Immunol.2017, 8:1542
Fitoterapia.2022, 157:105130.
Applied Biological Chem. 2020, 26(63).
Aquaculture2017, 481:94-102
Int J Mol Sci.2019, 20(3):E651
Inflammation.2021, doi: 10.1007
Related and Featured Products
Antiviral Res. 2006 Jul;70(3):112-20.
Yatein from Chamaecyparis obtusa suppresses herpes simplex virus type 1 replication in HeLa cells by interruption the immediate-early gene expression.[Pubmed:
16540181]
Yatein (C(22)H(23)O(7); M.W.399) was isolated from Chamaecyparis obtusa; Yatein significantly suppressed HSV-1 multiplication in HeLa cells without apparent cytotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To further localize the point in the HSV-1 replication cycle where arrest occurred, a set of key regulatory events leading to the viral multiplication was examined, including viral immediate-early (alpha) and late (gamma) gene expression and DNA replication. Results indicated that levels of glycoprotein B (gB) and gC mRNA expression in HeLa cells were impeded by Yatein. Data from polymerase chain reaction showed that replication of HSV-1 DNA in HeLa cells was arrested by Yatein. Furthermore, Yatein decreased ICP0 and ICP4 gene expression in HeLa cells. Results of an electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrated that Yatein interrupted the formation of alpha-trans-induction factor/C1/Oct-1/GARAT multiprotein complex. The mechanisms of antiviral action of Yatein seem to be mediated, by inhibiting HSV-1 alpha gene expression, including expression of the ICP0 and ICP4 genes, and by arresting HSV-1 DNA synthesis and structural protein expression in HeLa cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Yatein is an antiviral agent against HSV-1 replication.
Pharm Biol . 2015 Mar;53(3):378-85.
Antiproliferative activity of yatein isolated from Austrocedrus chilensis against murine myeloma cells: cytological studies and chemical investigations[Pubmed:
25420758]
Abstract
Context: Fitzroya cupressoides (Molina) I. M. Johnst. and Austrocedrus chilensis (D. Don) Pic.Serm. & Bizzarri are two Chilean Cupressaceae that are naturally resistant to biodegradation. Secondary metabolites from these species display a variety of biological activities.
Objective: To evaluate the antiproliferative activity of two lignans, a diterpene and a flavonol isolated from A. chilensis and F. cupressoides, to elucidate their cytological effects on P3X murine myeloma cells.
Materials and methods: The antiproliferative activity of Yatein, isotaxiresinol, ferruginol, and isorhamnetin was evaluated in vitro using the MTT assay. The effect of Yatein at the cellular level, due to its high antiproliferative activity was evaluated. P3X cells treated for 24 h with 12.5 and 25 μg/mL of Yatein were also examined at the cytological level using immunofluorescence and scanning and transmission electron microscopy.
Results: Yatein, a lignan isolated from A. chilensis, potentially inhibited P3X murine myeloma cell proliferation, resulting in approximately 75% cell death in response to a 25 μg/mL treatment with the lignan. P3X cells lost membrane integrity at the nuclear and cytoplasmic levels, including organelles, in response to Yatein treatment (12.5 μg/mL), and we observed changes in the cytoplasmic organization and distribution of microtubules. The other compounds tested had low activity.
Discussion and conclusions: Yatein is a lignan precursor of podophyllotoxin, a key agent in anticancer drugs. Due to its structural similarities to podophyllotoxin, Yatein could have similar cytoplasmic target(s), such as the microtubular apparatus. These findings suggest that Yatein may be of potential pharmacological interest and warrants further investigation in human cell lines.
Keywords: Anticancer; MTT; P3X; cytotoxicity; diterpene; lignans; microtubules; secondary
Cancers (Basel) . 2019 Sep 17;11(9):1384.
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Yatein-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest and Microtubule Destabilization in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells[Pubmed:
31533296]
Abstract
Yatein is an antitumor agent isolated from Calocedrus formosana Florin leaves extract. In our previous study, we found that Yatein inhibited the growth of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 and CL1-5 cells by inducing intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. To further uncover the effects and mechanisms of Yatein-induced inhibition on A549 and CL1-5 cell growth, we evaluated Yatein-mediated antitumor activity in vivo and the regulatory effects of Yatein on cell-cycle progression and microtubule dynamics. Flow cytometry and western blotting revealed that Yatein induces G2/M arrest in A549 and CL1-5 cells. Yatein also destabilized microtubules and interfered with microtubule dynamics in the two cell lines. Furthermore, we evaluated the antitumor activity of Yatein in vivo using a xenograft mouse model and found that Yatein treatment altered cyclin B/Cdc2 complex expression and significantly inhibited tumor growth. Taken together, our results suggested that Yatein effectively inhibited the growth of A549 and CL1-5 cells possibly by disrupting cell-cycle progression and microtubule dynamics.
Keywords: Calocedrus formosana; cell-cycle arrest; lung cancer; xenograft; Yatein.
Pharm Biol. 2015 Mar;53(3):378-85.
Antiproliferative activity of yatein isolated from Austrocedrus chilensis against murine myeloma cells: cytological studies and chemical investigations.[Pubmed:
25420758]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antiproliferative activity of Yatein, isotaxiresinol, ferruginol, and isorhamnetin was evaluated in vitro using the MTT assay. The effect of Yatein at the cellular level, due to its high antiproliferative activity was evaluated. P3X cells treated for 24 h with 12.5 and 25 µg/mL of Yatein were also examined at the cytological level using immunofluorescence and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Yatein, a lignan isolated from A. chilensis, potentially inhibited P3X murine myeloma cell proliferation, resulting in approximately 75% cell death in response to a 25 µg/mL treatment with the lignan. P3X cells lost membrane integrity at the nuclear and cytoplasmic levels, including organelles, in response to Yatein treatment (12.5 µg/mL), and we observed changes in the cytoplasmic organization and distribution of microtubules. The other compounds tested had low activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Yatein is a lignan precursor of podophyllotoxin, a key agent in anticancer drugs. Due to its structural similarities to podophyllotoxin, Yatein could have similar cytoplasmic target(s), such as the microtubular apparatus. These findings suggest that Yatein may be of potential pharmacological interest and warrants further investigation in human cell lines.