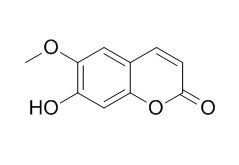
Scopoletin
Scopoletin exhibits antifungal, anti-allergic, anti-aging,
and hypouricemic activities, it exerts anti-RA action probably through suppressing IL-6 production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes via MAPK/PKC/CREB pathways. Scopoletin can ameliorate alcohol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation by modulating AMPK-SREBP pathway-mediated lipogenesis in mice fed a high-fat diet.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Aquaculture2017, 481:94-102
Anal Chim Acta.2021, 1180:338874.
J Food Sci.2024, 3841.17112.
Am J Chin Med.2023, 51(4):1019-1039.
Sains Malaysiana2024, 53(4):795-805
Mol Neurobiol.2023, 60(12):7196-7207.
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 145:112410.
Mol Biol Rep.2024, 51(1):117.
J Integr Plant Biol.2023, 13564.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy2022, 153:113404.
Related and Featured Products
J Exp Bot. 2014 Aug;65(15):4305-15.
Scopoletin is a phytoalexin against Alternaria alternata in wild tobacco dependent on jasmonate signalling.[Pubmed:
24821958]
Alternaria alternata (tobacco pathotype) is a necrotrophic fungus causing severe losses in Nicotiana species by infection of mature leaves. Similar to what has been observed in cultivated tobacco, N. tabacum, young leaves of wild tobacco, N. attenuata, were more resistant to A. alternata than mature leaves, and this was correlated with stronger blue fluorescence induced after infection. However, the nature of the fluorescence-emitting compound, its role in defence, and its regulation were not clear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Silencing feruloyl-CoA 6'-hydroxylase 1 (F6'H1), the gene encoding the key enzyme for Scopoletin biosynthesis, by virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) revealed that the blue fluorescence was mainly emitted by Scopoletin and its β-glycoside form, scopolin. Further analysis showed that Scopoletin exhibited strong antifungal activity against A. alternata in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, jasmonic acid (JA) levels were highly elicited in young leaves but much less in mature leaves after infection; and fungus-elicited Scopoletin was absent in JA-deficient plants, but was largely restored with methyl jasmonate treatments. Consistent with this, plants strongly impaired in JA biosynthesis and perception were highly susceptible to A. alternata in the same way Scopoletin/scopolin-depleted VIGS F6'H1 plants. Furthermore, silencing MYC2, a master regulator of most JA responses, reduced A. alternata-induced NaF6'H1 transcripts and Scopoletin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Thus, it is concluded that JA signalling is activated in N. attenuata leaves after infection, which subsequently regulates Scopoletin biosynthesis for the defence against A. alternata partly through MYC2, and higher levels of Scopoletin accumulated in young leaves account for their strong resistance.
Phytomedicine. 2015 Mar 15;22(3):362-8.
Scopoletin has a potential activity for anti-aging via autophagy in human lung fibroblasts.[Pubmed:
25837273]
Autophagy was known to be associated with aging in addition to cancer and neurodegeneration. The effects of Scopoletin on autophagy and anti-aging were investigated in human lung fibroblast cell line, IMR 90.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we show that Scopoletin induces autophagy. It is also identified that the modulation of p53 by Scopoletin are related to the induction of autophagy. Moreover, the level of SA-β-Gal staining, an aging marker, is reduced by Scopoletin. In addition, while the expression levels of histone deacetylases such as HDAC1, SIRT1 and SIRT6 are increased in IMR 90 cells in the presence of Scopoletin, the expression levels of histone acetyltransferases are decreased. Furthermore, Scopoletin enhances the level of transcription factors such as Nrf-2and p-FoxO1 related to anti-aging. In addition, Scopoletin modulates the reprogramming proteins.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, these findings suggest that Scopoletin could exert a positive effect on anti-aging related to autophagy through modulation of p53 in human lung fibroblasts.
Metabolism. 2014 Apr;63(4):593-601.
Scopoletin prevents alcohol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation by modulating the AMPK-SREBP pathway in diet-induced obese mice.[Pubmed:
24559844]
This study investigated the effects of Scopoletin on alcohol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in diet-induced obese mice and its mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Alcohol (25% v/v, 5g/kg body weight) was orally administered once a day for 6 weeks to mice fed with a high-fat diet (35%kcal) with or without Scopoletin (0.05%, wt/wt).
Scopoletin reduced plasma acetaldehyde, fatty acid, total cholesterol, triglyceride and insulin levels, hepatic lipid and droplets and fasting blood glucose levels that were increased by alcohol. Scopoletin significantly activated hepatic AMPK and inhibited ACC and SREBP-1c and the activities of lipogenic enzymes, such as FAS, PAP and G6PD compared to the alcohol control group. Moreover, Scopoletin significantly inhibited hepatic CYP2E1 activity and protein levels but elevated the activities of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and GST and the levels of GSH compared to the alcohol control group. The hepatic lipid peroxide level was significantly lowered by Scopoletin supplementation in alcohol-administered obese mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggested that Scopoletin can ameliorate alcohol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation by modulating AMPK-SREBP pathway-mediated lipogenesis in mice fed a high-fat diet.
J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6248-54.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products.[Pubmed:
15566295 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Scopoletin exhibited an immediate and dose-dependent hypouricemic effect after intraperitoneal administration (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) in hyperuricemic mice induced by potassium oxonate; however, it did not affect the serum uric acid level in normal mice at the tested doses. For exploring the involved mechanisms of action of Scopoletin, potential inhibitory effects on xanthine oxidase and possible uricosuric effects were investigated. Scopoletin (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) significantly inhibited the activity of xanthine oxidase in liver homogenates of hyperuricemic mice although it only showed a relatively weak, albeit competitive-type, inhibition of xanthine oxidase in a commercial assay. Furthermore, a potent uricosuric effect of Scopoletin (100, 200 mg/kg) was ascertained.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated for the first time that Scopoletin exhibits, hypouricemic activities through decreasing uric acid production and as well as a uricosuric mechanism.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1037-43.
Scopoletin suppresses IL-6 production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes of adjuvant arthritis rats induced by IL-1β stimulation.[Pubmed:
24455774]
Scopoletin, a coumarin compound naturally occurring in many medicinal plants, has previously been demonstrated to ameliorate synovial inflammation and destruction of cartilage and bone in adjuvant arthritis (AA) rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
As interleukin (IL)-6 is critically involved in the initiation and development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the present study was performed to investigate the effect of Scopoletin on IL-6 production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) to get insight into its anti-RA mechanisms. FLS were isolated from synovial membrane tissues of AA rats, and stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL). Scopoletin, at concentrations of 15, 30, and 60 μM, was shown to only moderately inhibit FLS proliferation, but dramatically reduce IL-6 production at both mRNA and protein levels. It also inhibited the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), protein kinase C (PKC) and cAMP response element binding protein (CREB).
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Scopoletin exerts anti-RA action probably through suppressing IL-6 production from FLS via MAPK/PKC/CREB pathways.
Food Funct. 2012 Aug;3(8):886-90.
Scopoletin attenuates allergy by inhibiting Th2 cytokines production in EL-4 T cells.[Pubmed:
22733205]
Scopoletin is an antioxidant found in certain weedy plants. It exerts anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, and anti-diabetic activities. It remains unknown whether Scopoletin regulates T helper (Th) cells, including Th 1 and Th 2 cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Scopoletin significantly inhibited phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin-induced interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, and IL-10 production in EL-4 T cells. In addition, Scopoletin significantly enhanced the inhibitory action of PMA/ionomycin on interferon-γ (IFN-γ) expression. In EL-4 T cells, PMA/ionomycin treatment markedly increased the expression of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and GATA-3; in contrast, Scopoletin significantly down-regulated expressions of these transcription factors. Furthermore, this downregulation depended on protein kinase C (PKC) attenuation.
CONCLUSIONS:
This leads us to suggest that the anti-allergic properties of Scopoletin might be mediated by the downregulation of cytokine expression in Th 2 cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jan 26;555(2-3):218-25.
Use of scopoletin to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of the IkappaB/NF-kappaB signal cascade in the human mast cell line HMC-1.[Pubmed:
17113069]
Scopoletin (6-methoxy-7-hydroxycoumarin) is a coumarin compound and a pharmacologically active agent that has been isolated from several plant species. However, as yet there is no clear explanation of how Scopoletin affects the production of inflammatory cytokine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We therefore used cells from the human mast cell line (HMC-1) to investigate this effect. Scopoletin significantly and dose-dependently inhibits the way in which phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) plus A23187 induces the production of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8 (P<0.05). The maximal rates at which Scopoletin (0.2 mM) inhibited the production of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8 were 41.6%+/-4.2%, 71.9%+/-2.5%, and 43.0%+/-5.7%, respectively. In activated HMC-1 cells, the expression level of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB/Rel A protein was increased in the nucleus whereas the level of NF-kappaB/Rel A in nucleus was decreased by treatment with Scopoletin. Scopoletin decreased PMA plus A23187-induced luciferase activity. Scopoletin also inhibits IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation in cytoplasm.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Scopoletin has a potential regulatory effect on inflammatory reactions that are mediated by mast cells.
Planta Med. 2005 Feb;71(2):183-5.
Hypouricemic action of scopoletin arising from xanthine oxidase inhibition and uricosuric activity.[Pubmed:
15729630 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Scopoletin exhibited an immediate and dose-dependent hypouricemic effect after intraperitoneal administration (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) in hyperuricemic mice induced by potassium oxonate; however, it did not affect the serum uric acid level in normal mice at the tested doses. For exploring the involved mechanisms of action of Scopoletin, potential inhibitory effects on xanthine oxidase and possible uricosuric effects were investigated. Scopoletin (50, 100, 200 mg/kg) significantly inhibited the activity of xanthine oxidase in liver homogenates of hyperuricemic mice although it only showed a relatively weak, albeit competitive-type, inhibition of xanthine oxidase in a commercial assay. Furthermore, a potent uricosuric effect of Scopoletin (100, 200 mg/kg) was ascertained.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results demonstrated for the first time that Scopoletin exhibits, hypouricemic activities through decreasing uric acid production and as well as a uricosuric mechanism.