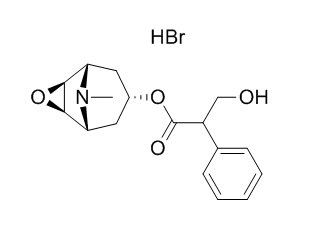
Scopolamine hydrobromide
Scopolamine hydrobromide is a competitive muscarinic acetylcholine receptor with an IC50 of 55.3 nM, it also reversibly inhibited the 5-HT3 receptor-responses with an IC50 of 2.09 μM. Sscopolamine hydrobromide nasal gel is a safe and promising therapeutic alternative to existing medications for motion sickness, it and NaHCO3 can be used to treat tetrodotoxin (TTX) poisoning.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2019, 24(6):E1177
Applied Biological Chemistry2023, 66:8
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 145:112474.
Plant Physiol.2023, 193(3):1758-1771.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(21):13406.
J.Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica2017, 571-575
Plant J.2021, 107(6):1711-1723.
Sci Rep.2018, 8:15059
Phytomedicine.2019, 57:95-104
Food Chem.2020, 332:127412
Related and Featured Products
Acta Pharm. Sin., 2007, 28(4):584-90.
Preparation of ion-activated in situ gel systems of scopolamine hydrobromide and evaluation of its antimotion sickness efficacy.[Pubmed:
17376300]
To develop a novel, in situ gel system for nasal delivery of Scopolamine hydrobromide (SCOP) and study its efficacy on motion sickness.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
SCOP in situ gels at 0.2%, 0.5%, and 1.0% gellan gum concentration (w/v) were prepared, respectively, and characterized in terms of viscosity, in vitro release, and nasal ciliotoxicity. Single photon emission computing tomography technique was used to evaluate the nasal residence time of gel containing (99m)Tc tracer. The antimotion sickness efficacy produced by the in situ gel formulation was investigated in rats and compared with those achieved after subcutaneous and oral administration.
The viscosity of the gellan gum formulations either in solution or in gel increased with increasing concentrations of gellan gum. Its release in vitro was moderate in artificial nasal fluid. The micrographic results showed that in situ gels were safe, without nasal ciliotoxicity. In comparison with phosphate buffer saline, a prolonged radioactivity of (99m)Tc in the rabbit nasal cavity was observed after administration of the gellan gum formulation. Intranasal SCOP in situ gel at a dose of 100 microg/kg decreased symptoms of motion sickness significantly in comparison with subcutaneous and oral administration (P<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS:
SCOP nasal in situ gel is a safe and promising therapeutic alternative to existing medications for motion sickness.
Acta Academiae Medicinae Shandong, 2002(3).
The antagonistic effects of NaHC03 and scopolamine hydrobromide to TTX poisoning in mice[Reference:
WebLink]
To explore the antagonistic effects of some compounds to TTX poisoning in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The death time of mice was determined, after ip injection with TTX and some other compounds. Results: NaHCO 3 and Scopolamine hydrobromide showed markedly antagonistic effect to TTX poisoning in mice, and saved the lives of mice by 80% to 100%(P0.01). The antagonistic effect of NaHCO3 to TTX poisoning was better than that of Scopolamine hydrobromide. However atropine and L-cysteine did not show sighificant effect in the treatment of TTX poisoning.
CONCLUSIONS:
NaHCO3 and Scopolamine hydrobromide can be used to treat TTX poisoning.
Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2005, 10(8):898-902.
Effects and mechanisms of ginsenoside Rg1 on learning and memory impairment induced by scopolamine hydrobromide[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the protective effects of ginsenosides Rg1 liposome (Rg1-L)on learning and memory impaiment induced by Scopolamine hydrobromide in rats, and discuss the relevant mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
AD model was made by Scopolamine hydrobromide. Y-maze was used to detect the learning and memory abilities. The active of acetylcholinesterase(AchE) in the brain of rats was measured. Rg1-L obviously improved the learning and memory abilities of AD rats and restrained the activity of AchE.
CONCLUSIONS:
Rg1-L improves the learning and memory abilities of AD. The relevant mechanisms may be related to restraining the activity of AchE, improving the lipophilic activity of Rg1 by liposome and bio avalbility.
Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:897-904.
A novel spray-dried nanoparticles-in-microparticles system for formulating scopolamine hydrobromide into orally disintegrating tablets.[Pubmed:
21720502]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Scopolamine hydrobromide (SH)-loaded microparticles were prepared from a colloidal fluid containing ionotropic-gelated chitosan nanoparticles using a spray-drying method. The spray-dried microparticles were then formulated into orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) using a wet granulation tablet formation process. A drug entrapment efficiency of about 90% (w/w) and loading capacity of 20% (w/w) were achieved for the microparticles, which ranged from 2 μm to 8 μm in diameter. Results of disintegration tests showed that the formulated ODTs could be completely dissolved within 45 seconds. Drug dissolution profiles suggested that SH is released more slowly from tablets made using the microencapsulation process compared with tablets containing SH that is free or in the form of nanoparticles. The time it took for 90% of the drug to be released increased significantly from 3 minutes for conventional ODTs to 90 minutes for ODTs with crosslinked microparticles. Compared with ODTs made with noncrosslinked microparticles, it was thus possible to achieve an even lower drug release rate using tablets with appropriate chitosan crosslinking.
CONCLUSIONS:
Results obtained indicate that the development of new ODTs designed with crosslinked microparticles might be a rational way to overcome the unwanted taste of conventional ODTs and the side effects related to SH's intrinsic characteristics.