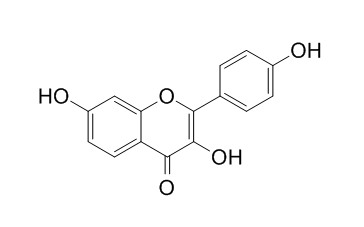
Resokaempferol
Resokaempferol inhibits the inflammatory response in activated macrophages by blocking the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway by both LPS and IL-6 signaling.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018, 2018:3610494
Front Chem.2022, 10:1048467.
J Biomol Struct Dyn.2022, 1-21.
J Food Sci Technol.2022, 59(1):212-219.
Scientific World Journal.2014, 2014:654193
Bioorg Med Chem.2018, 26(14):4201-4208
Anticancer Res.2020, 40(10):5529-5538.
J Phys Chem Lett.2021, 12(7):1793-1802.
Nutrients.2024, 16(22):3805.
Purinergic Signal.2024, doi: 10.1007.
Related and Featured Products
Photochemistry and Photobiology, 1968, 8(3):223-229.
PHOTODYNAMIC ACTION OF CHEMICALLY RELATED FLAVONES.[Reference:
WebLink]
Flavone, polyhydroxyflavones (apigenin, fisetin, kaempferol, luteolin, myricetin, quercetin, Resokaempferol and robinetin), polymethoxyflavones and acetylated and benzylated flavones were tested for photodynamic activity using Tetrahymena pyriformis T as the test organism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among these compounds, polymethoxyflavones showed the highest order of activity, followed by flavone and then flavone derivatives with OH and OCH3 groups. Resokaempferol was the only active polyhydroxyflavone, the remainder being inactive such as the benzyl‐derivative. The methoxyl group in the 5–position and an increase in number of methoxyl groups from one to three in the phenolic portion of the flavonoid tended to decrease photodynamic activity. Tetrahymena killed photodynamically by polymethoxyflavones were morphologically altered by blister‐like blebs.
CONCLUSIONS:
Polymethoxyflavones showed the lowest cytotoxicity and the greatest photodynamic activity among those flavonoids tested. The majority of the favonoids in this series have absorption spectra in the 320–370 nm region.
International Immunopharmacology, 2016, 38:104-114.
Resokaempferol-mediated anti-inflammatory effects on activated macrophages via the inhibition of JAK2/STAT3, NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways.[Reference:
WebLink]
The excessive or prolonged production of inflammatory mediators can result in numerous chronic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and cancer.
Therefore, for many inflammatory-related diseases, pharmaceutical intervention is required to restrain the excessive release of such inflammatory mediators. Novel therapeutics and mechanistic insight are sought for the management of chronic inflammatory diseases. Resokaempferol (RES) is a type of flavonoid recently reported to demonstrate anti-cancer properties. However, the anti-inflammatory capacity of RES has not been studied to date.
Therefore, this study investigated whether RES is capable of suppressing the inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and the mechanism by which this is achieved.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that RES attenuated the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1) and IL-6. RES also inhibited the nuclear translocation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 and reduced the LPS-mediated phosphorylation of Janus kinase (JAK) 2 and STAT3 at the sites of Ser727 and Tyr705. RES also inhibited the activation of NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Additionally, RES inhibited the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in exogenous IL-6-activated RAW264.7 macrophages. 、
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that RES inhibits the inflammatory response in activated macrophages by blocking the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway by both LPS and IL-6 signaling.