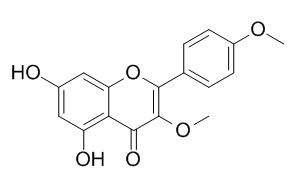
Ermanin
Ermanin shows anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing the iNOS and COX-2 expression. Ermanin may have anti-HIV-1activity. Ermanin also has a high deterrent activity at 40 ppm against Dione juno larvae.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Viruses.2021, 13(11):2118.
J AOAC Int.2021, 104(6):1634-1651.
Sains Malaysiana2024, 53(4):795-805
Journal of Functional Foods2019, 52:430-441
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2023, 31(6):388-395.
Chin J Appl. Physiol.2019, 35(3):283-288
J Agric Food Chem.2018, 66(1):351-358
Toxicol In Vitro.2024, 99:105876.
Korea Food Research Institute2024, 4798082
Foods.2022, 11(12):1708.
Related and Featured Products
Planta Med. 2010 May;76(7):721-5.
Anti-HIV-1 diterpenoids from leaves and twigs of Polyalthia sclerophylla.[Pubmed:
20013639]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided fractionation and purification of the anti-HIV-1-active MeOH extract from the leaves and twigs of Polyalthia sclerophylla led to the isolation of two new compounds, ENT-kaur-sclerodimer ( 1) and cyclotucanol 3-palmitate ( 2), along with the known ENT-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid ( 3), 15 beta-hydroxy- ENT-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid ( 4), 15 beta-acetoxy- ENT-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid ( 5), 15-oxo- ENT-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid ( 6), 16 alpha,17-dihydroxy- ENT-kauran-19-oic acid ( 7), 16 alpha-hydroxy- ENT-kauran-19-oic acid (xylopic acid) ( 8), a pseudodimer (15 alpha-hydroxy- ENT-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid/17-hydroxy- ENT-kaur-15-en-19-oic acid) ( 9), Ermanin, nicotiflorin, and allantoin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these isolates, compound 3 was the most active in both anti-syncytium (EC (50) 13.7 microg/mL and selectivity index 3.1) and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (IC (50) 34.1 microg/mL) assays.
Phytochemistry, 1991, 30(1):153-5.
Ermanin: An insect deterrent flavonoid from Passiflora foetida resin.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ten flavonoids were isolated from Passiflora foetida L. resin. One of them, Ermanin, has a high deterrent activity at 40 ppm against Dione juno larvae.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Nov;6(11):1723-8.
Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by flavonoids isolated from Tanacetum microphyllum.[Pubmed:
16979127]
Plant flavonoids show anti-inflammatory activity both in vitro and in vivo. Some flavonoids have been reported previously to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production by suppressing inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study focuses on the effect of various naturally occurring flavonoids (santin, Ermanin, centaureidin and 5,3'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxy-7-methoxycarbonylflavonol) on modulation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Western blotting showed that all flavonoids suppressed the induction of both iNOS and COX-2. Ermanin and 5,3'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxy-7-methoxycarbonylflavonol were the most potent inhibitors.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study suggests that inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression by flavonoids may be one of the mechanisms responsible for their anti-inflammatory effects, and that they may be potential agents for use in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.