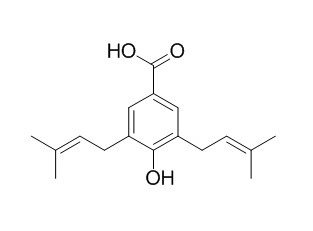
Nervogenic acid
Nervogenic acid has antioxidative, pro-coagulant, and antibacterial activities, it exhibits higher activity than that of t-butyl-4- hydroxyanisole (BHA) using the ferric thiocyanate method.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J of the Society of Cosmetic Scientists of Korea2018, 44(4):407-417
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(3):379.
J Ethnopharmacol.2017, 198:87-90
Food Chem.2023, 404(Pt A):134517.
Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine2024, 4802935.
Molecules.2019, 24(21):E3834
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(77).
JEJU National University2022, 24032.
J of Ana. Chem.2019, 74(11):1113-1121
Food Hydrocolloids2024, 152:109898
Related and Featured Products
Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Aug;8(8):1115-6.
A new nervogenic acid glycoside with pro-coagulant activity from Liparis nervosa.[Pubmed:
24079181]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In an effort to identify hemostatic components from Liparis nervosa (Thunb.) Lindl. using a bioactivity-guided fractionation approach, the n-BuOH extract was found to promote ADP-induced platelet aggregation and two compounds were isolated from the active extract.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Compound 1 was a new Nervogenic acid glycoside and the structure was elucidated as 3,5-bis(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-4-O-[beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1 -->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-benzoic acid by extensive spectroscopic measurements.
Adenosine (2) was isolated from this plant for the first time. Compound 1 also showed good pro-coagulant activity in vitro.
Planta Med. 2013 Mar;79(3-4):281-7.
New nervogenic acid derivatives from Liparis nervosa.[Pubmed:
23322560]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ten new Nervogenic acid derivatives (1-4, 6-11) and one known compound (5) have been isolated from Liparis nervosa. Their structures were determined using extensive spectroscopic analysis, including 1D and 2D NMR experiments.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 3, 4, 9, 10, and 11 were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against A549, H460, Hela, MCF-7, Caco2, and HepG2 human cancer cell lines.
Food Sci.Technol. Int.(Tokyo),1997, 3(3):285-9.
Antioxidative Constituents from the Aerial Part of Piper elongatum VAHL.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Six aromatic compounds, asebogenin (1), 2',6'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone (2), 3-geranyl-4-methoxy-benzoic acid (3), 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4), Nervogenic acid (5) and 2,2-dimethyl-6-carboxyl-8-prenyl-chromene (6) were isolated from the methanol extract of the aerial part of Piper elongatum VAHL., whose leaves are used as a folk medicine in South America. The structures of 1-6 were elucidated by MS, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopies, and chemical evidence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these compounds, 1 showed stronger antioxidative activity than that of α-tocopherol, and 4 and 5 exhibited higher activity than that of t-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (BHA) using the ferric thiocyanate method.
Carbohydr Res. 2009 Sep 8;344(13):1770-4.
Glycosylated nervogenic acid derivatives from Liparis condylobulbon (Reichb.f.) leaves.[Pubmed:
19664759]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new Nervogenic acid glycosides, 1-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl 3,5-bis(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-4-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-benzoate, 3,5-bis(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-4-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-benzoic acid, and bis{3,5-bis(3-methyl-but-2-enyl)-4-O-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-benzoyl} 1,2-O-beta-d-glucopyranose, which we named condobulbosides A-C, were isolated from a methanol extract of the leaves of Liparis condylobulbon together with an apigenin C-glycoside, schaftoside.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their structures were established on the basis of spectral techniques, namely, UV, IR, HR-MS spectroscopy, both 1D and 2D NMR experiments, and chemical reactions.
Planta Med. 1993 Dec;59(6):546-51.
Five new prenylated p-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives with antimicrobial and molluscicidal activity from Piper aduncum leaves.[Pubmed:
8302955 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five new prenylated benzoic acid derivatives, methyl 3-(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienyl)-4-methoxybenzoate (1), 1-(1-methylethyl)-4-methyl-3-cyclohexenyl 3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-4-hydroxybenzoate (2), 1-(1-methylethyl)-4-methyl-3-cyclohexenyl 3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-4-methoxybenzoate (3), methyl 3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-4-methoxybenzoate (4), and 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzoic acid (5) were isolated from the dried leaves of Piper aduncum L. (Piperaceae). Together with the new metabolites, four known prenylated benzoic acid derivatives, 3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-4-methoxybenzoic acid (6), 4-hydroxy-3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzoic acid (Nervogenic acid, 7), methyl 4-hydroxy-3,5-bis(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzoate (8), and methyl 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzoate (9) as well as, dillapiol (10), myristicin, and the three sesquiterpenes humulene, caryophyllene epoxide, and humulene epoxide were isolated. Compounds 7, 8, and 9 are reported as natural products for the first time. The structures of the isolates were elucidated by spectroscopic methods, mainly 1D-and 2D-NMR spectroscopy.
CONCLUSIONS:
Isolates 4-7, 9, and 10 were molluscicidal while 2, 5-7, and 9 displayed significant antibacterial activities.