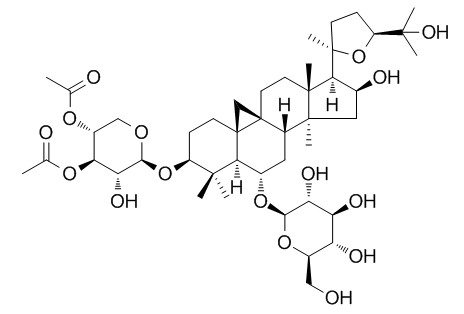
Neoastragaloside I
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2022, 15(8):982.
Front Microbiol.2022, 12:833233.
Foods. 2022, 11(23):3905.
Phytochemistry Letters2021, 43:80-87.
Int J Oncol.2016, 49(4):1497-504
Mol Plant Pathol.2022, 10.1111:mpp.13280.
Anal Biochem.2019, 569:10-15
Sci Rep. 2024, 14(1):70.
Food Chem.2021, 377:131976.
J Appl Biol Chem2021, 64(3):245-251.
Related and Featured Products
Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2012, 43(8):1462-1470.
Studies on chemical constituents from Aidi Injection.[Reference:
WebLink]
To investigate the chemical constituents from Aidi Injection.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The chemical constituents were isolated by chromatography on Sephadex LH-20 gel columns and reverse phase semi-preparation HPLC repeatedly, and their structures were identified by spectral data. Twenty-two compounds were isolated and identified as 3-O-(3', 4'-diacetyl)-β-D-xylopyranosyl-6-O-β - D-glucopyranosyl-cycloastragenol (1), astragaloside IV (2), astragaloside II (3), astragaloside I (4), isoastragaloside I (5), acetylastragaloside I (6), ginsenosid-Re (7), ginsenoside-Rf (8), ginsenoside-Rg 1 (9), ginsenoside-Rb 3 (10), notoginsenoside-R 4 (11), ginsenoside-Rb 1 (12), ginsenoside-Rc (13), ginsenoside-Rb 2 (14), ginsenoside-Rd (15), lucyoside H (16), 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→3)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→2) - α-L-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid 28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β - D-glucopyranoside (17), 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1→3)-α-L-rhamno-pyranosyl [β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-(1→2)-α - L-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid 28-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl (1→4)-β-D-gluco-pyranosyl (1→6)-β - D-glucopyranoside (18), syringin (19), elentheroside E (20), 4-(1, 2, 3-trihydroxypropyl)-2, 6-dimethoxyphenyl-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (21), and coniferin (22).
CONCLUSIONS:
LC-MS analysis shows that compounds 1-6 are originated from Astragalus membranceus, compounds 7-18 from Panax ginseng, and compounds 19-22 from Acanthopanacis senticosi. Compound 1 is a new compound named Neoastragaloside I.