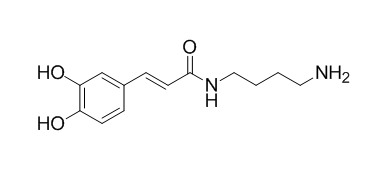
(E)-N-Caffeoylputrescine
N-Caffeoylputrescine has antioxidant activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 24(17):13230.
Phys Chem Chem Phys.2018, 20(23):15986-15994
Foods.2021, 10(11):2754.
Journal of Molecular Liquids2022, 364:120062.
J Agric Food Chem.2015, 63(44):9869-78
Phytochemistry.2021, 181:112539.
J Cell Mol Med.2022, 26(23):5807-5819.
BMC Complement Med Ther.2023, 23(1):264.
J Microbiol Biotechnol.2020, 30(2):178-186.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017, 1064:115-123
Related and Featured Products
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Jan 29;62(4):850-9.
Antioxidant activity of phenolics in leaves of three red pepper (Capsicum annuum) cultivars.[Pubmed:
24087837 ]
The antioxidant properties and phenolic profiles were first investigated in this paper on the leaves of three red pepper cultivars, Blackcuban (BCPL), Hongjinju (HPL), and Yeokgang-hongjanggun (YHPL).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Of the ethanol extract of the three cultivars, BCPL showed potent antioxidant activities against the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH) and the 2,2-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical. Nine antioxidative compounds from the red pepper leaves were isolated and identified as one polyamine phenolic conjugate, N-caffeoylputrescine ((E)-N-Caffeoylputrescine,1); three chlorogenic acid derivatives, 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (2), 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester (4), and 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid butyl ester (9); one anthocyanin, delphinidin-3-[4-trans-coumaroyl-l-rhamnosyl(1→6)glucopyranoside]-5-O-glucopyranoside (3); and four flavone glycosides, luteolin-7-O-apiofuranosyl(1→2)glucopyranoside (5), luteolin-7-O-glucopyranoside (6), apigenin 7-O-apiofuranosyl(1→2)glucopyranoside (7), apigenin-7-O-glucopyranoside (8).
CONCLUSIONS:
1 and 3 had the greatest potential for radical-scavenging activity and HepG2 cells protecting effect against oxidative stress. BCPL exhibited the highest content of 1 and 3. Of the three cultivars BCPL may be considered a good source of antioxidants.
Phytochemistry (Oxford), 1996, 42(2):389-396.
Changes in the accumulation of soluble and cell wall-bound phenolics in elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures and fungus-infected leaves of Solanum tuberosum.[Reference:
WebLink]
Cell suspension cultures of potato (Solanum tuberosum cv. Datura) treated with an elicitor preparation from Phytophthora infestans and potato leaves infected with the same fungus were used to study changes in the accumulation patterns of soluble and cell wall-bound phenolics.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were identified by chromatographic comparison with authentic substances and by spectroscopic methods (FAB mass spectrometry, 1H and 13C NMR). The soluble phenolics were 4-O-β-glucopyranosylhydroquinone (arbutin), 4-O-β-glucopyranosylbenzoate, 3-methoxy-4-O-β-glucopyranosylbenzoate (vanillate glucoside), N-(E)-caffeoylputrescine((E)-N-Caffeoylputrescine), 2-O-β-glucopyranosylbenzoate (salicylate glucoside), N-(E)-feruloylputrescine, and N-(E)-feruloylaspartate. The cell wall-bound phenolics were 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (vanillin), 4-(E)-coumarate, (E)-ferulate, N-4-(E)-coumaroyltyramine, and N-(E)-feruloyltyramine.
CONCLUSIONS:
The most prominent phenolics showing elicitor- or fungus-induced increases in accumulation rates were the soluble putrescine amides and cell wall-bound 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and tyramine amides. In addition, there was a secretion of large amounts of coumaroyltyramine into the cell culture medium.