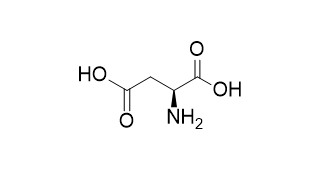
L-Aspartic acid
L-Aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons. It could as the amino donor.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int Immunopharmacol.2021, 101(Pt A):108181.
Neurochem Int.2023, 167:105537.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy2022, 153:113404.
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:607403.
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia2024, 34:1091-1100.
The Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences2023, 47(3):3.
Nutrients.2018, 10(12):E1998
Current Analytical Chemistry2024, 20(8):599-610.
Preprints2017, 2017120176
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018, 2018:8565132
Related and Featured Products
Brain Research, 1982, 237(1):248-253.
L-aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons.[Reference:
WebLink]
Individual murine spinal cord neurons were grown in dissociated tissue cultures.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Using either one or two conventional intracellular microelectrodes neurons were voltage-clamped and current-voltage (I–V) curves were constructed using command pulses.L-Aspartic acid was then applied and I–V curves repeated in the presence of this excitatory amino acid.L-Aspartic acid induced a region of negative slope conductance (RNSC) in the steady-state I–V relationships of these neurons.
CONCLUSIONS:
Such a RNSC accounts for the apparent reduction of conductance observed in response to excitatory amino acids5,7,8 and its instability likely contributes to the electrogenesis of bursting in central neurons.
Enzyme & Microbial Technology, 2000, 27( 1–2):19-25.
Selective production of L-aspartic acid and L-phenylalanine by coupling reactions of aspartase and aminotransferase in Escherichia coli.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
With l-aspartate (L-Asp) as the amino donor, l-phenylalanine (L-Phe) can be prepared from phenylpyruvate (PPA) via an amination reaction mediated by aminotransferase (encoded by aspC). On the other hand, L-Asp can be produced by an aspartase (encoded by aspA) -catalyzed reaction using fumaric acid as substrate. To overproduce aspartase in Escherichia coli, the aspA gene was cloned and overexpressed 180 times over the wild-type level. The use of AspA-overproducing E. coli strain for L-Asp production exhibited an 83% conversion, approaching to the theoretical yield, whereas the wild-type strain obtained scarcely L-Asp. Furthermore, the recombinant strain overproducing both AspA and AspC was able to produce L-Asp and L-Phe simultaneously by using fumaric acid and PPA as substrates. As a result, the conversion yields obtained for L-Asp and L-Phe were 78% and 85%, respectively. In sharp contrast, the wild-type strain attained a conversion of L-Phe less than 15% and an undetectable level of L-Asp.
CONCLUSIONS:
This result illustrates a potential and attractive process to yield both L-Asp and L-Phe by coupling AspA and AspC. A further study on the repeated use of the recombinant strain immobilized with calcium alginate showed that after eight batch runs L-Asp conversion maintained roughly constant (around 75%), whereas L-Phe conversion dropped to 65% from 81%. This result indicates the stability of AspA being superior to AspC.