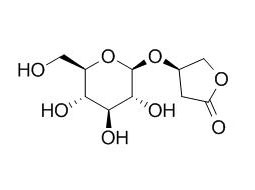
Kinsenoside
Kinsenoside shows significant antihepatotoxic, and anti-inflammatory activities. Kinsenoside could be useful for repairing beta cells in pancreatic islet injury as well as improving its function, it could promote the glucose tolerance of acute glucose increase in both diabetic and normal healthy rats. Kinsenoside inhibits osteoclastogenesis from macrophages by attenuating RANKL-induced NF-κB and NFATc1 activities, which in turn, prevents bone loss from OVX mice.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Universitat Stuttgart2022, opus-12200.
Methods Protoc.2024, 7(6):95.
Acta Edulis Fungi2020, 27(02):63-76.
Foods.2022, 11(12):1773.
Vietnam Journal of Science2022, 64(2), 69-75.
Indian Journal of Science and Technology2023, 16(SP1):48-56.
J of Advanced Scientific R.2020, 11(3), p109-120.
Food Res Int.2020, 128:108778
Phytomedicine.2024, 155760.
University of Limpopo2016, 1777
Related and Featured Products
J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Nov 1;114(2):141-5.
Antihyperglycemic activity of kinsenoside, a high yielding constituent from Anoectochilus roxburghii in streptozotocin diabetic rats.[Pubmed:
17869039 ]
Different doses of Kinsenoside, a high yielding constituent from Anoectochilus roxburghii, was orally administered to further investigate its biological activity and pharmacological mechanisms that involve in the hypoglycemic effect on streptozotocin (STZ) diabetic rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our study showed that this compound exhibited significantly antihyperglycemic activity at the dose of 15mg/kg body weight, which is speculated to be partially attributed to modulating the activity of enzymatic antioxidants, scavenging free radicals, and reducing the content of factor NO. Much more intact beta cells in the islets of Langerhans with denser insulin in Kinsenoside-treated groups than the negative control were observed, which greatly supported the morphological and functional elucidation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results displayed that Kinsenoside could be useful for repairing beta cells in pancreatic islet injury as well as improving its function. The OGTT evidenced that this compound could promote the glucose tolerance of acute glucose increase in both diabetic and normal healthy rats.
Phytother Res. 2007 Jan;21(1):58-61.
The hepatoprotective activity of kinsenoside from Anoectochilus formosanus.[Pubmed:
17078107 ]
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4)) causes chronic hepatitis, featuring an increase in hepatic hydroxyproline, spleen weight and serum GPT levels and a decrease in plasma albumin levels.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Crude extracts of fresh whole plants of Anoectochilus formosanus showed inhibition of chronic hepatitis induced by CCl(4) in mice.
Bioactivity-guided fractionation and spectroscopic analysis revealed that Kinsenoside was the most active compound. In an in vitro study, the LD(50) values for H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in BALB/c normal liver cells were significantly higher after Kinsenoside pretreatment than after vehicle alone, further confirming that Kinsenoside shows significant antihepatotoxic activity.
Osteoporos Int. 2013 May;24(5):1663-76.
Kinsenoside prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by regulating classical NF-κB pathways.[Pubmed:
23143538 ]
Kinsenoside is able to improve bone turnover rate in ovariectomized (OVX) mice. In vitro analysis shows that Kinsenoside antagonizes osteoclast development and bone resorption.
Kinsenoside, the main active compound of the traditional Taiwanese herb Anoectochilus formosanus, has an antiinflammatory effect. This study investigates whether Kinsenoside inhibits osteoporosis and osteoclastogenesis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
OVX mice were used to examine the antiosteoporotic activity of Kinsenoside. The trabecular bone microarchitecture was assessed by microcomputed tomography. In vitro experiments were performed to determine the mechanisms of the antiosteoporotic effects of Kinsenoside.
Microcomputed tomography scanning showed that Kinsenoside suppresses bone loss in OVX mice. Kinsenoside decreases plasma CTx concentration. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis also showed that Kinsenoside reduces the femoral mRNA expression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Kinsenoside inhibits osteoclast formation in bone marrow cells (BMs) and RAW 264.7 cells. Western blot was used to analyze osteoclast-associated signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Results show that Kinsenoside does not inhibit IKK phosphorylation but suppresses the phosphorylation of IκBα and p65. Kinsenoside significantly inhibits the RANKL induction of IKK activity. Kinsenoside inhibits the RANKL-triggered nuclear translocations of NF-κB and nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1). RT-PCR was used to analyze osteoclast precursor fusion and resorption-associated gene expression in BMs. Kinsenoside inhibits the expression of cathepsin K (CAK), dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein, MMP-9, and TRAP.
CONCLUSIONS:
Kinsenoside inhibits osteoclastogenesis from macrophages by attenuating RANKL-induced NF-κB and NFATc1 activities, which in turn, prevents bone loss from OVX mice.
Shock. 2011 Feb;35(2):184-90.
Kinsenoside isolated from Anoectochilus formosanus suppresses LPS-stimulated inflammatory reactions in macrophages and endotoxin shock in mice.[Pubmed:
20661184 ]
In the present study, we reported that Kinsenoside, a major component of Anoectochilus formosanus, inhibited inflammatory reactions in mouse peritoneal lavage macrophages and protects mice from endotoxin shock.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In LPS-stimulated mouse peritoneal lavage macrophages, Kinsenoside inhibited the inflammatory mediators, such as nitric oxide, TNF-[alpha], IL-1[beta], monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and macrophage migration inhibitory factor production. Furthermore, Kinsenoside decreased the formation of a nuclear factor [kappa]B-DNA complex and nuclear p65 and p50 protein levels. Kinsenoside inhibited nuclear factor [kappa]B translocation through both I[kappa]B[alpha]-dependent and -independent pathway. In contrast, it stimulated anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 generation and enhanced the mRNA expression of IL-10 and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in the same cells induced by LPS. In an animal model, both pretreatment and posttreatment of Kinsenoside increased the survival rate of ICR mice challenged by LPS (80 mg/kg, i.p.). Pretreatment with Kinsenoside decreased serum levels of TNF-[alpha], IL-1[beta], IL-10, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and migration inhibitory factor at 1 h after sublethal dose of LPS (40 mg/kg, i.p.) in mice. In contrast, Kinsenoside enhanced serum IL-10 level at 24 h after LPS injection in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Kinsenoside inhibited the production of inflammatory mediators and enhanced anti-inflammatory cytokine generation. Therefore, Kinsenoside can alleviate acute inflammatory hazards.