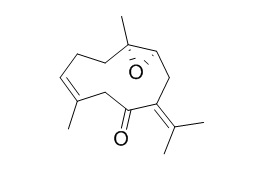
Germacrone 4,5-epoxide
(4S,5S)-(+)-Germacrone-4,5-epoxide inhibits certain subtypes of cytochrome P450 (CYP).
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Appl Toxicol.2024, jat.4615.
Phytother Res.2022, ptr.7573.
Molecules.2021, 26(2):E255.
Pharmacognosy Magazine2017, 13(52):868-874
Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy.2019, 50(1):65-71
Natural Product Res.&Deve.2022, 1001-6880.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2019, 164:119-127
Antioxidants (Basel).2021, 10(1):112.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.2024, 245:116193.
Molecules2022, 27(9):2827.
Related and Featured Products
Chem Biodivers. 2014 Jul;11(7):1034-41.
Suppression of Inflammatory cytokine production by ar-Turmerone isolated from Curcuma phaeocaulis.[Pubmed:
25044589 ]
Rhizomes of Curcuma phaeocaulis Valeton (Zingiberaceae) have traditionally been used for controlling inflammatory conditions. Numerous studies have aimed to isolate and characterize the bioactive constituents of C. phaeocaulis. It has been reported that its anti-inflammatory properties are a result of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition; however, its effect on the T-cell function remains to be elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, four known sesquiterpenoids, viz., ar-turmerone (TM), germacrone (GM), (+)-(4S,5S)-Germacrone 4,5-epoxide (GE), and curzerenone (CZ), were isolated from C. phaeocaulis rhizomes and evaluated for their effects on the CD4(+) T-cell function. While GM, GE, and CZ had no effect on the activation of splenic T cells or CD4(+) T cells, TM suppressed the interferon (IFN)-γ production, without affecting the interleukin (IL)-4 expression. TM also decreased the expression of IL-2 in CD4(+) T cells, but did not change their cell-division rates upon stimulation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that TM, a major constituent of C. phaeocaulis rhizomes selectively exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects via suppression of the inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and IL-2.
J Nat Med. 2011 Jul;65(3-4):583-7.
Compounds isolated from Curcuma aromatica Salisb. inhibit human P450 enzymes.[Pubmed:
21287405 ]
Curcuma species (Zingiberaceae) are used as both food and medicine in Asia. Ten sesquiterpenes (1-10) and two curcuminoids (11 and 12) were isolated from the rhizomes of Curcuma aromatica Salisb. and identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit cytochrome P450 (CYP). Among them, the sesquiterpene (4S,5S)-(+)-Germacrone 4,5-epoxide (7) inhibited certain subtypes of CYP more potently than or at levels comparable to the curcuminoids curcumin (11) and demethoxycurcumin (12); 7 (IC(50) = 1.0 ± 0.2 μM) > 12 (IC(50) = 7.0 ± 1.7 μM) > 11 (IC(50) = 14.9 ± 1.4 μM) for CYP3A4 inhibition; 12 (IC(50) = 1.4 ± 0.2 μM) > 11 (IC(50) = 6.0 ± 1.4 μM) > 7 (IC(50) = 7.6 ± 2.5 μM) for CYP2C9 inhibition; and 7 (IC(50) = 33.2 ± 3.6 μM) = 12 (IC(50) = 34.0 ± 14.2 μM) > 11 (IC(50) > 100 μM) for CYP1A2 inhibition.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest the possibility that Curcuma aromatica Salisb. may cause food-drug interactions via cytochrome P450 inhibition by sesquiterpene 7 and curcuminoids 11 and 12.